Sparing in Symmetrix systems
217
Data Integrity, Availability, and Protection
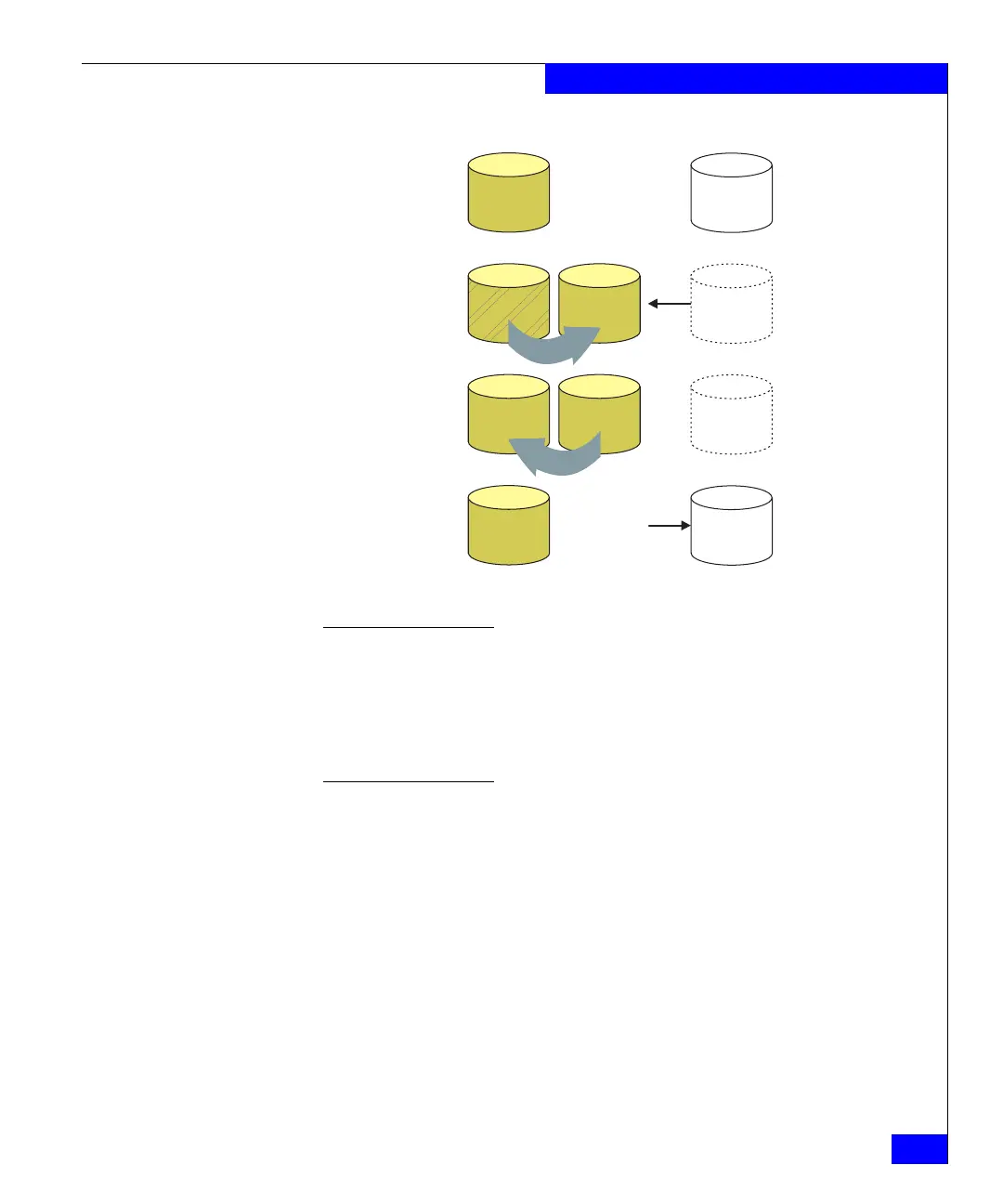
Figure 49 Dynamic sparing process
Note: Enginuity 5772 is no longer limited to invoking a single (same size or
larger) dynamic spare to a failing drive. At 5772 dynamic spares can now be
invoked at the logical device or hyper level and multiple smaller spare drives
can dynamically protect a single larger failing drive. In all previous codes
dynamic spares are invoked at the physical drive level and the requirement
for a dynamic spare is that it has to be the same size or larger than the largest
data drive.
The dynamic sparing process selects a spare drive with the same
block size (512 or 520 bytes) as the failing drive. The process also
chooses an available spare drive of equal or larger capacity. There is
no restriction preventing a 7.2K/10K/15K spare from being invoked
against any other speed failing drive. For example, it is possible that a
7.2K spare will be invoked against a 15K failing drive, which may
affect performance.
Dynamic sparing
process
With dynamic sparing, the Symmetrix system makes its copying
decision based on error statistics maintained by its directors, the
intelligent disk microprocessor self-testing information, and its active
error checking system. If the Symmetrix dynamic sparing algorithms
determine that the number of errors occurring on a volume is
Data volume D1
protected by
dynamic spare DS
D1
D1(M1) D1(M2)
DS
COPY
D1(M1) D1(M2)
DS
DS
DS
COPY
D1 failing, dynamic
spare invoked
DS mirrors D1
DS returns to
spares pool
D1
Failed disk
replaced and new
disk restored as D1

 Loading...
Loading...