[9.3.1 — Planck’s law]
© FLIR Systems AB – Publ. No. 557 369 – Ed. A
53
where:
W
λ
b
= the blackbody spectral radiant emittance at wavelength λ.
c = the velocity of light = 3 x 10
8
m/sec.
h = Planck’s constant = 6.6 x 10
-34
Joule sec.
k = Boltzmann’s constant = 1.4 x 10
-23
Joule/K.
T = the absolute temperature (K) of a blackbody.
λ = wavelength (m).
N.B. – The factor 10
-6
is used since spectral emittance in the curves is expressed
in Watt/m
2
µm. If the factor is excluded, the dimension will be Watt/m
2
m.
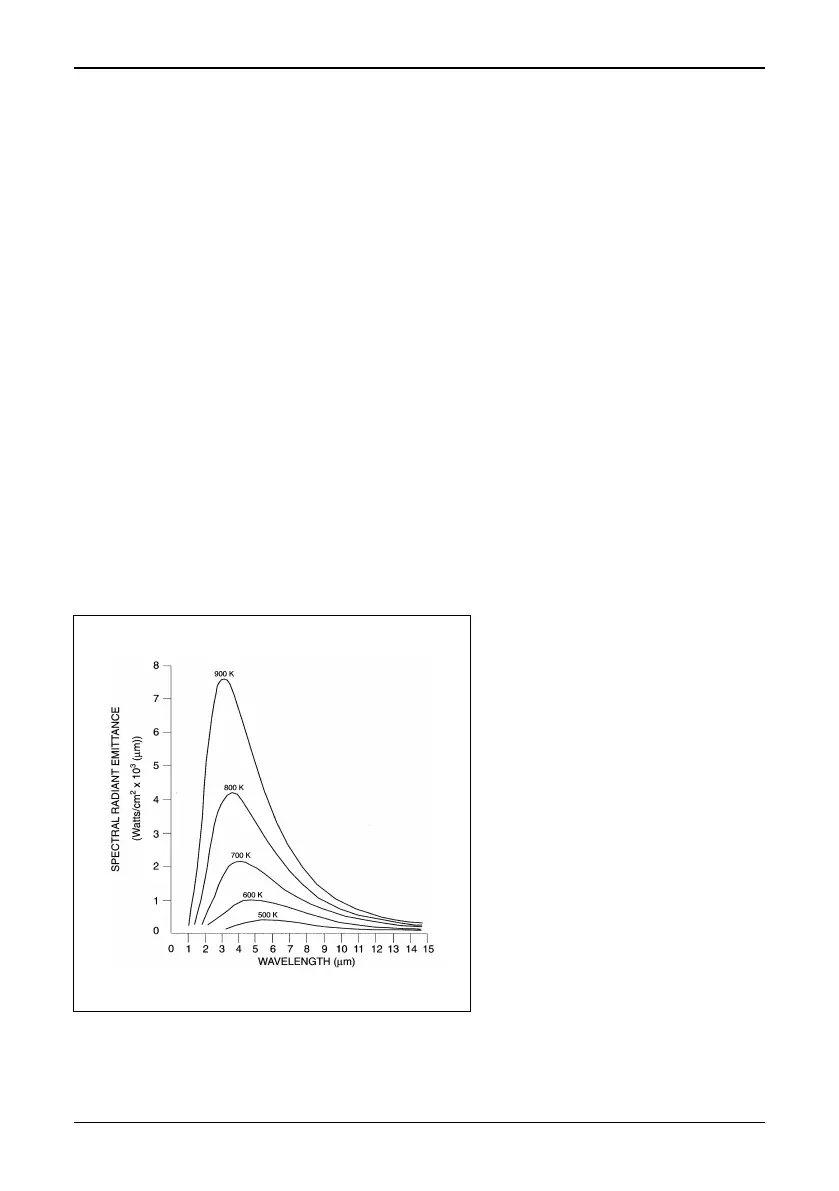
Planck’s formula, when plotted graphically for various temperatures, produces a
family of curves. Following any particular Planck curve, the spectral emittance is
zero at
λ = 0, then increases rapidly to a maximum at a wavelength λ
max
and after
passing it approaches zero again at very long wavelengths. The higher the temper-
ature, the shorter the wavelength at which maximum occurs.
Figure 9.2 Blackbody spectral radiant emittance according to Planck’s law,
plotted for various absolute temperatures.
Wλ
b
2πhc
2
λ
5
hcλkT⁄
1
()
---------------------------------------10
6–
× Wattm
2
µm⁄[]=

 Loading...
Loading...