417D/424D
Users Manual
18
The result shows in the summary line as the room triangle
area.
6. Push for 2 seconds to get the second results as the angle
between d1 and d2, the triangle circumference, and the area.
Indirect Measurement
The Meter can calculate distances with Pythagoras’ theorem.
With this function, you can find a distance with two auxiliary
measurements, such as building height or width measurements.
It is helpful to use a tripod for a height measurement that uses
two or three measurements.
Note
Make sure that you use the correct sequence of
measurement:
• All target points must be in a horizontal or vertical plane.
• For the best results, turn the Meter about a set point. An
example of this is with the endpiece fully open and the
Meter on a wall.
• Make sure that the first measurement and the
measurement distance are at 90
°
angles.
• The minimum/maximum tracking is very helpful for 90
°
angle measurements. See Minimum/Maximum Tracking.
To find a distance with two measurements (Pythagoras 1):
1. Push 1x.y shows on the display.
2. Point the laser at the top point (1). See Figure 12.
Figure 12. Pythagoras 1
3. Push .
4. Point the laser at the second target (2).
Make sure that the Meter is perpendicular to the wall.
5. Push for the second distance measurement.
The Meter shows the height in the summary line. The
distance of the second measurement shows in the
secondary line.
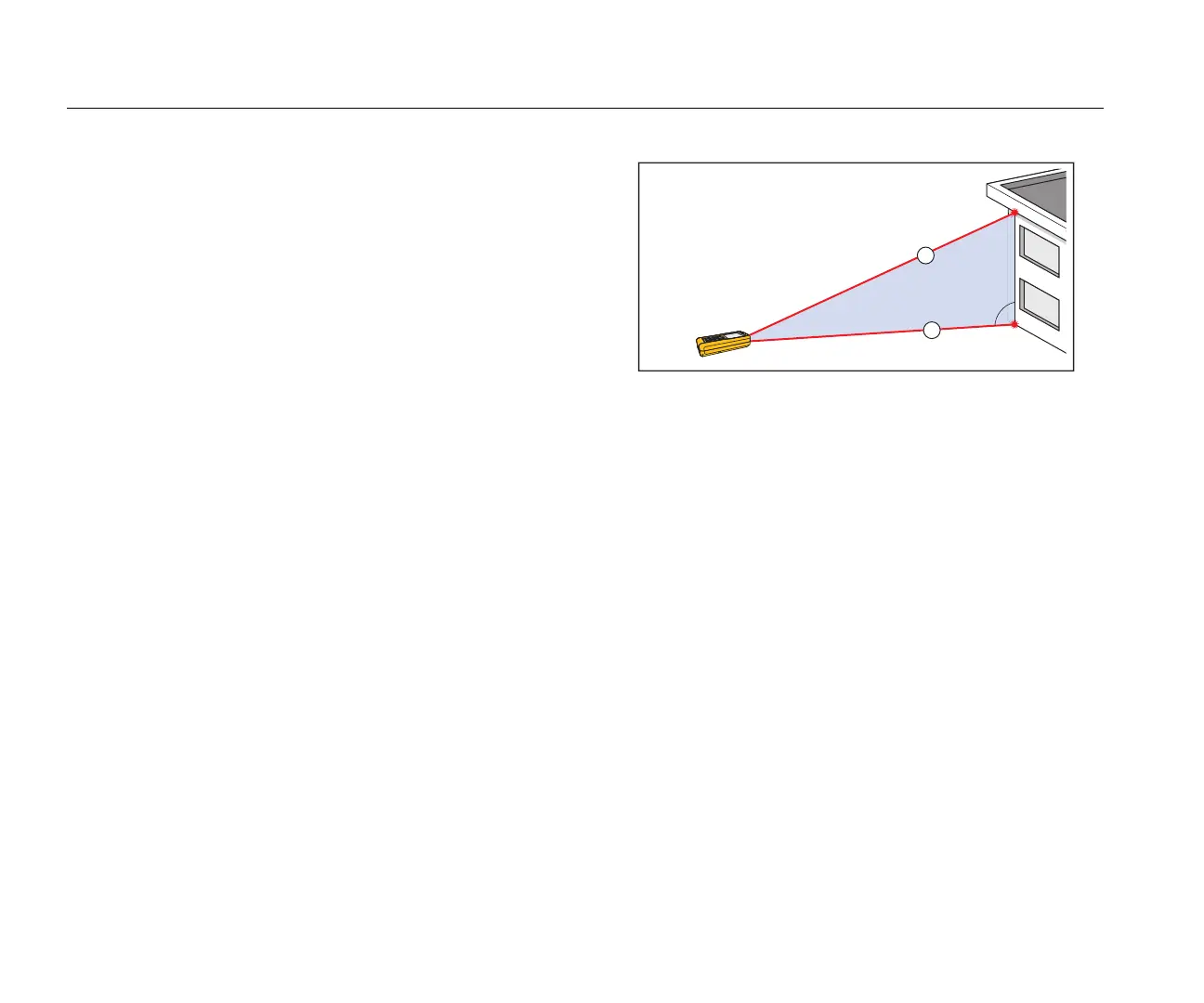
To find a total distance with three measurements (Pythagoras 2):
1. Push 2x. z shows on the display.
2. Point the laser at the first target. See Figure 13.
 Loading...
Loading...