38
Tools
NOTES:
Porous mould materials such as wood and plaster should be properly sealed to prevent the vacuum pump
from sucking out any moisture or sawdust, loose plaster etc. The vacuum circuit may quickly become blocked
with dust or slurry if moulds are not properly sealed.
As the plastic cools after forming it will contract, gripping the tool tightly. If the tool has been made with
sloping sides and has a good surface finish it will release more easily. Where the draft angle must be kept to
a minimum a release agent may be used to assist release.
Sealed moulds will usually release more easily. Silicon based release agents may be used on more difficult
moulds. Silicon based release agents are rapidly absorbed by porous (unsealed) moulds, rendering them
ineffective.
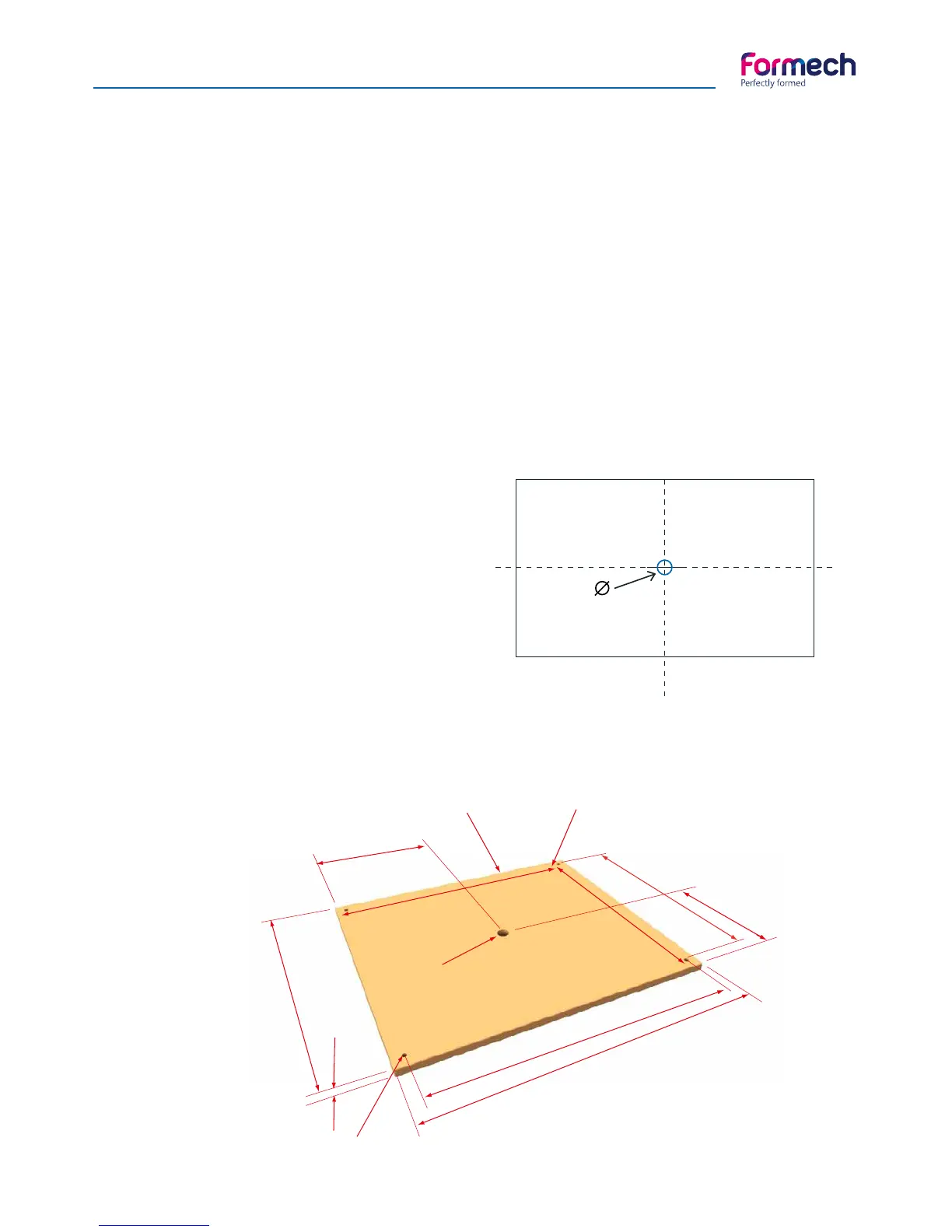
The baseboard can be made from either MDF or aluminium and needs to be 12.00mm (1/2”) thick. The
vacuum hole can be 19.00 – 20.00mm (3/4”) diameter and needs to be positioned in the center of the table.
19-20mm
The baseboard has to be 4/5mm shorter in
both directions than the forming aperture
of the machine e.g. Forming aperture
482mm x 432mm = baseboard size
478mm x 428mm.
477mm (18.78”)
427mm (16.81”)
Make board 4mm ( 0.15”) smaller than reducing
window aperture front to back and left to right
213.5mm (8.40”)
12mm (1/2”)
238.5mm (9.38”)
Use four M6 cap head set screws
or M6 CSK machine screws x 19mm (3/4”)
long to bolt the board to the table (platen)
442mm (17.40”)
392mm (15.43”)
7mm (.275”) Diameter holes
R10mm (0.39”)
508DT and 508FS standard base board
R2mm (0.078”) radius on top edge
all round to stop MDF from flaking
508DT/FS standard baseboard
Make board 4mm (0.15“) smaller than full size
aperture front to back and left to right
 Loading...
Loading...