5
69
RAID 0 (Stripe)
RAID0readsandwritessectorsofdatainterleavedamongmultipledrives.Ifanydisk
member fails, it affects the entire array. The disk array data capacity is equal to the
number of drive members times the capacity of the smallest member. The striping
blocksizecanbesetfrom4KBto128KB.RAID0doesnotsupportfaulttolerance.
RAID 1 (Mirror)
RAID 1 writes duplicate data onto a pair of drives and reads both sets of data in
parallel. If one of the mirrored drives suffers a mechanical failure or does not respond,
the remaining drive will continue to function. Due to redundancy, the drive capacity of
the array is the capacity of the smallest drive. Under a RAID 1 setup, an extra drive
called the “spare drive” can be attached. Such a drive will be activated to replace a
failed drive that is part of a mirrored array. Due to the fault tolerance, if any RAID 1
drive fails, data access will not be affected as long as there are other working drives in
the array.
RAID 5 (Parity)
RAID5providesdatastripingatthebytelevelandalsostripeserrorcorrection
information.Thisresultsinexcellentperformanceandgoodfaulttolerance.Level5is
one of the most popular implementations of RAID.
RAID 10 (0+1)
RAID10isacombinationofstripingandmirroring.Thiscongurationprovidesoptimal
speed and reliability, but you need four SATA hard disks.
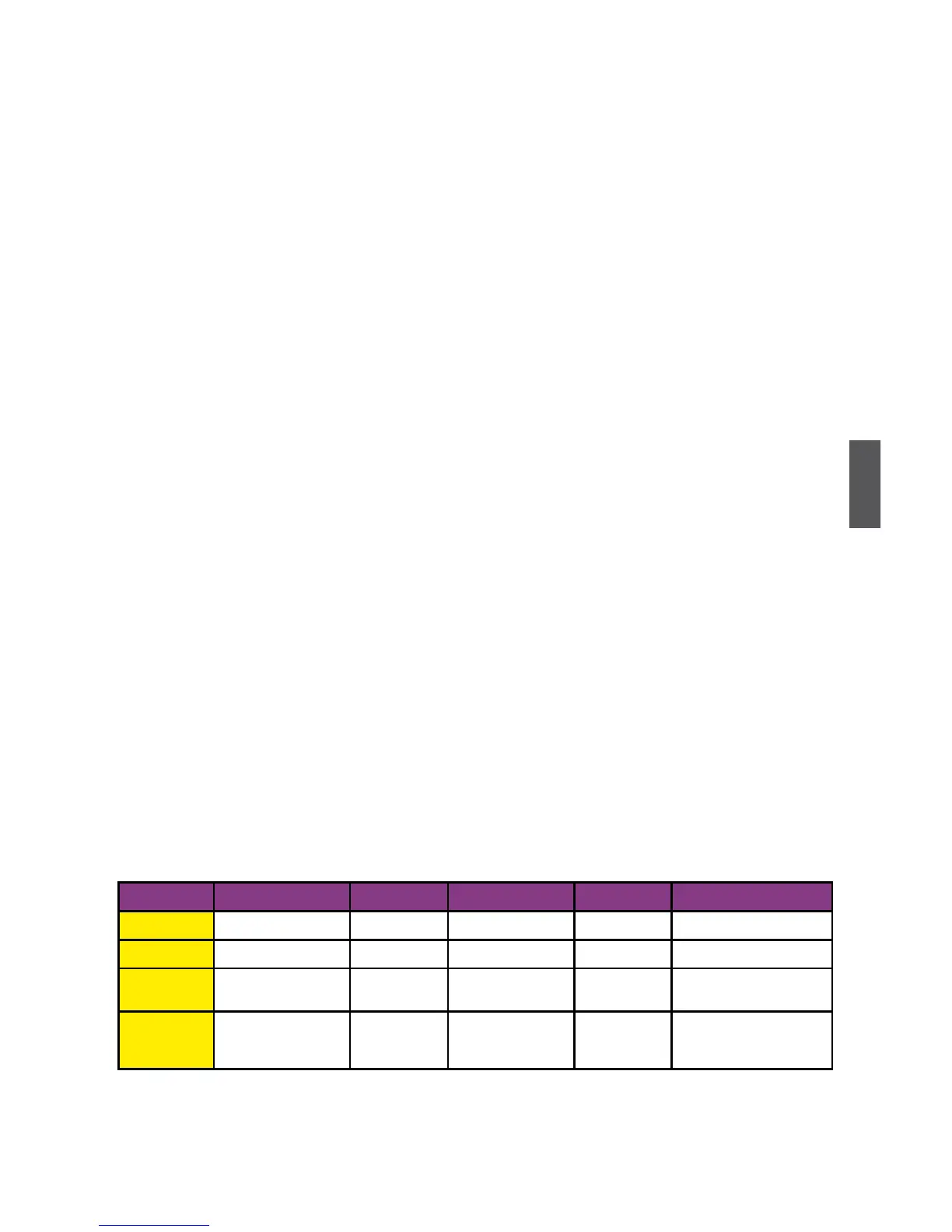
Comparison Table :
Solution Hard Disks No. Capacity Performance Reliability Application
RAID0 >=2 All Highest Dangerous Look for speed
RAID1 2 50% Read faster Excellent 100%Databackup
RAID5 >=3 N-1 Read faster
Write slower
Good Limited budget
RAID10 >=4
(Even number)
Smallest
*2
High Excellent Unlimited budget

 Loading...
Loading...











