In subfunction setup (), GPIO.setmode (GPIO.BOARD) is used to set the serial number of the GPIO, which is
based on physical location of the pin. So, GPIO17 and GPIO18 correspond to pin11 and pin12 respectively in
the circuit. Then set ledPin to output mode, buttonPin to input mode with a pull resistor.
ledPin = 11 # define the ledPin
buttonPin = 12 # define the buttonPin
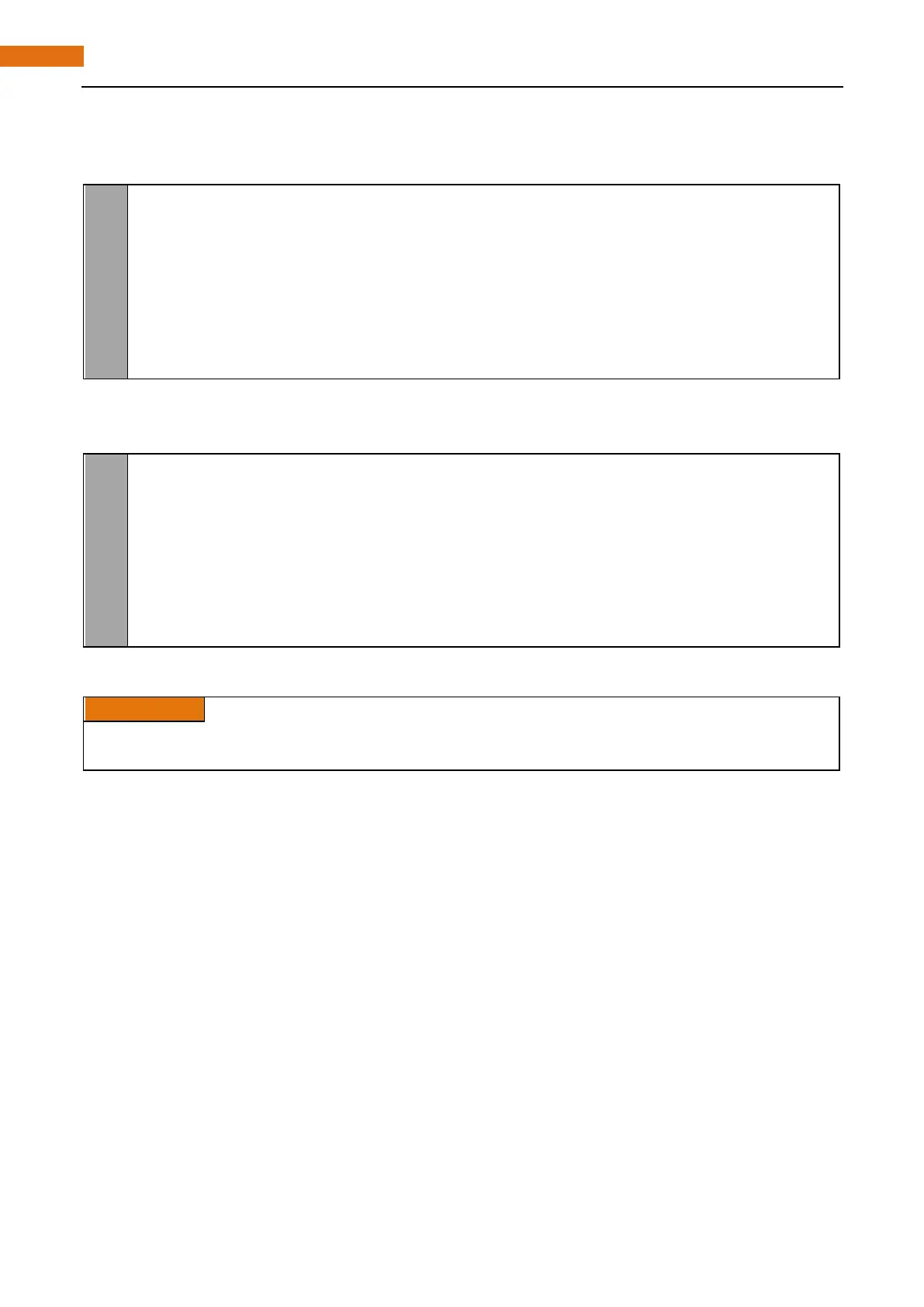
def setup():
p rint ('Program is starting...')
GPIO. setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # Numbers GPIOs by physical location
GPIO. setup(ledPin, GPIO. OUT) # Set ledPin's mode is output
GPIO. setup(buttonPin, GPIO. IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP) # Set buttonPin's mode is
input, and pull up to high level(3.3V)
In the loop function while dead circulation, continue to judge whether the key is pressed. When the button is
pressed, the GPIO.input(buttonPin) will return low level, then the result of “if” is true, ledPin outputs high level,
LED is turned on. Or, LED will be turned off.
w hile Tr ue:
if GPIO.input(buttonPin)==GPIO.LOW:
GPIO.output(ledPin,GPIO.HIGH)
print ('led on ...')
else :
GPIO.output(ledPin,GPIO.LOW)
print ('led off ...')
Execute the function destroy (), close the program and release the resource.
About function GPIO.input ():
This function returns the value read at the given pin. It will be “HIGH” or “LOW”(1 or 0) depending on the
logic level at the pin.
 Loading...
Loading...