Transistor, the full name: semiconductor transistor, is a semiconductor device that controls current. Transistor
can be used to amplify weak signal, or works as a switch. It has three electrodes(PINs): base (b), collector (c)
and emitter (e). When there is current passing between "be", "ce" will allow several-fold current (transistor
magnification) pass, at this point, transistor works in the amplifying area. When current between "be" exceeds
a certain value, "ce" will not allow current to increase any longer, at this point, transistor works in the saturation
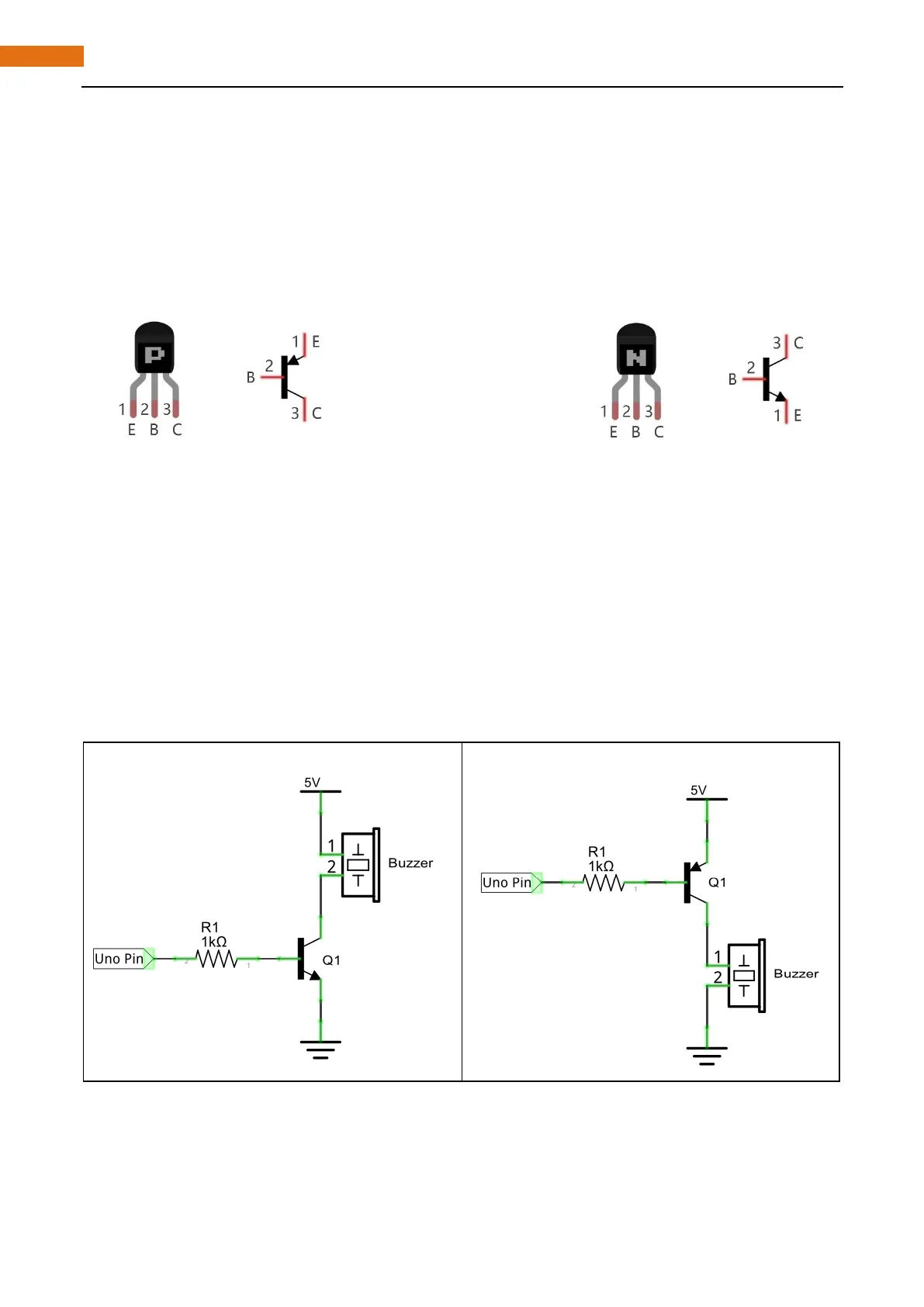
area. Transistor has two types shown below: PNP and NPN,
PNP transistor NPN transistor
In our kit, the PNP transistor is marked with 8550, and the NPN transistor is marked with 8050.
According to the transistor's characteristics, it is often used as a switch in digital circuits. For micro-controller's
capacity of output current is very weak, we will use transistor to amplify current and drive large-current
components.
When use NPN transistor to drive buzzer, we often adopt the following method. If GPIO outputs high level,
current will flow through R1, the transistor gets conducted, and the buzzer make a sound. If GPIO outputs
low level, no current flows through R1, the transistor will not be conducted, and buzzer will not sound.
When use PNP transistor to drive buzzer, we often adopt the following method. If GPIO outputs low level,
current will flow through R1, the transistor gets conducted, buzzer make a sound. If GPIO outputs high level,
no current flows through R1, the transistor will not be conducted, and buzzer will not sound.
 Loading...
Loading...