controlled, depending on make and model of the
seat. See
Fig. 5.17.
4.
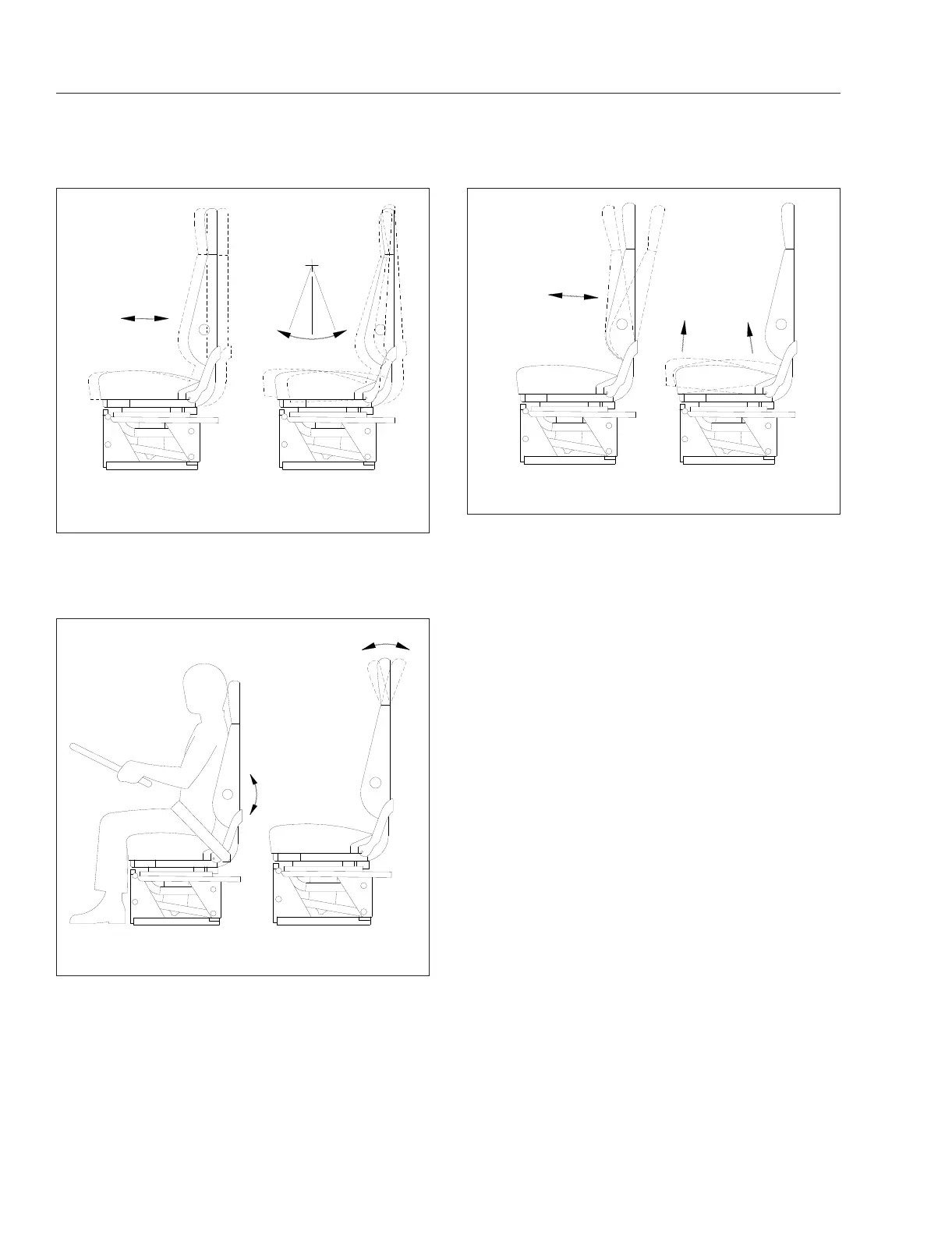
Headrest: When this adjustment is made, the
upper part of the back cushion changes angle to
provide head and upper back support. See
Fig. 5.17.
5.
Backrest Tilt: This adjustment pivots the backrest
forward or backward. See
Fig. 5.18.
6.
Seat Cushion Tilt: This adjustment raises or
lowers the front and/or back of the seat bottom
cushion. This adjustment is easier to perform
when all weight is removed from the seat. See
Fig. 5.18.
7.
Seat Tilt: When this adjustment is made, the seat
assembly, both backrest and seat cushion, tilts
forward or backward. See
Fig. 5.18.
8.
Ride Height Adjustment: The entire seat moves
up or down when adjusting the ride height. The
adjustment is either manual or air controlled,
depending on the make and model of the seat.
See
Fig. 5.19.
9.
Damper: While sitting on the seat, a leveling
valve sets the seat in the center of the ride zone.
When the damper is adjusted properly under
normal driving conditions, the seat should not top
or bottom against the limits of the vertical travel.
10.
Ride Firmness: A firmer ride gives a better feel
for the road but less protection against
unevenness in the road surface. A softer ride
smooths out the bumps.
Sitting Posture
Before driving, adjust the seat to support good sitting
posture as shown in
Fig. 5.20. Good posture
supports the safe operation of the vehicle and the
driver’s fitness and comfort. When correctly seated,
all instruments and controls should be within easy
10/05/2001
f910482
A
B
A. Seat Slide (forward/back) Adjustment
B. Isolator Feature
Fig. 5.16, Seat Slide Adjustment and Isolator Feature
10/05/2001
A
B
f910483
A. Lumbar Support B. Headrest Adjustment
Fig. 5.17, Lumbar Support and Headrest Adjustment
A
B
10/05/2001
f910484
A. Backrest Tilt B. Seat Cushion Tilt
Fig. 5.18, Cushion Tilt Adjustments
Cab Features
5.9
 Loading...
Loading...











