CHAPTER 12: DESCRIPTION OF PARAMETER SETTINGS
129 63-4528—04
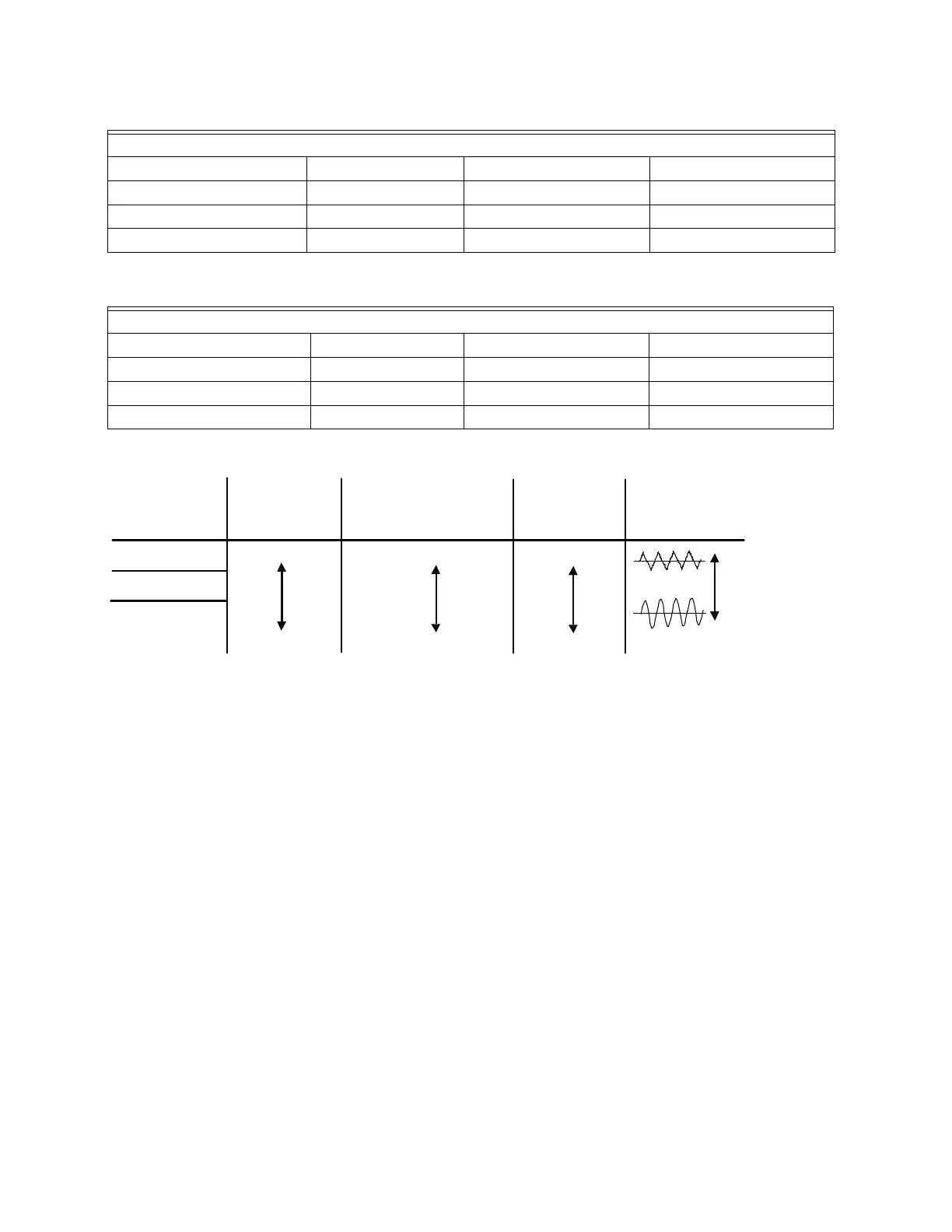
• From the table, we see that the PWM carrier frequency has a significant influence on the electromagnetic noise, VFD heat
dissipation, and motor acoustic noise. Therefore, if the surrounding noise is greater than the motor noise, lower the carrier
frequency is good to reduce the temperature rise. Although it is quiet operation in the higher carrier frequency, the entire wiring
and interference resistance should be considered.
• When the carrier frequency is higher than the factory setting, it needs to protect by decreasing the carrier frequency. See
Pr.06-46 for the related setting and details.
230V series
Models 1-20HP [0.75-15kW] 25-60HP [18.5-45kW] 75-125HP [55-90kW]
Settings 02~15kHz 02~10kHz 02~09kHz
Normal Duty Factory Setting 8kHz 6kHz 4kHz
Heavy Duty Factory Setting 8 kHz 6 kHz 4 kHz
460V series
Models 1-25HP [0.75-18.5kW] 30-100HP [22-75kW] 125-536HP [90-400kW]
Settings 02~15kHz 02~10kHz 02~09kHz
Normal Duty Factory Setting 2kHz 2kHz 2kHz
Heavy Duty Factory Setting 8 kHz 6 kHz 4 kHz
00 - 13 PLC Command Mask
Factory Setting: Read Only
Settings Bit 0: Control command controls by PLC
Bit 1: Frequency command controls by PLC
Bit 2: Reserved
Bit 3: Reserved
a
00 - 14 Source of the MASTER Frequency Command (AUTO)
Factory Setting: 0
Settings 0: Digital keypad
1: RS-485 serial communication
1kHz
8kHz
15kHz
Carrier
Frequency
Acoustic
Noise
Noise or Leakage
Current
Heat
Dissipation
Current
Wave
Significant
Minimal
Minimal
Minimal
Significant
Significant
 Loading...
Loading...