4
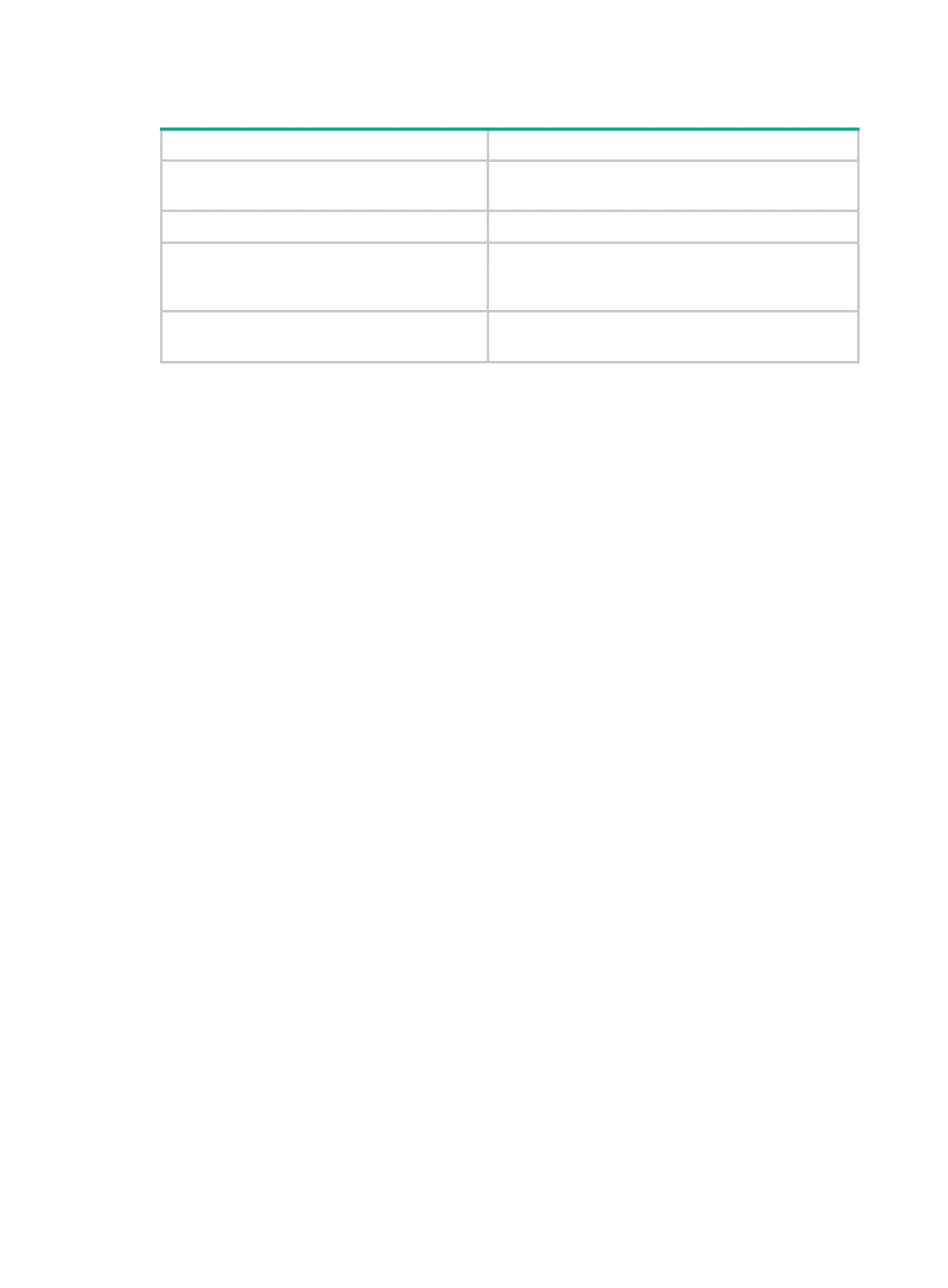
Table 1 Comparing TV program transmission and multicast transmission
TV program transmission Multicast transmission
A TV station transmits a TV program through a
channel.
A multicast source sends multicast data to a multicast
group.
A user tunes the TV set to the channel. A receiver joins the multicast group.
The user starts to watch the TV program
transmitted by the TV station on the channel.
The receiver starts to receive the multicast data sent by
the source to the multicast group.
The user turns off the TV set or tunes to another
channel.
The receiver leaves the multicast group or joins another
group.
Common notations in multicast
The following notations are commonly used in multicast transmission:
• (*, G)—Rendezvous point tree (RPT), or a multicast packet that any multicast source sends to
multicast group G. The asterisk (*) represents any multicast source, and "G" represents a
specific multicast group.
• (S, G)—Shortest path tree (SPT), or a multicast packet that multicast source "S" sends to
multicast group "G." "S" represents a specific multicast source, and "G" represents a specific
multicast group.
Multicast benefits and applications
Multicast benefits
• Enhanced efficiency—Reduces the processor load of information source servers and network
devices.
• Optimal performance—Reduces redundant traffic.
• Distributed application—Enables point-to-multipoint applications at the price of minimum
network resources.
Multicast applications
• Multimedia and streaming applications, such as web TV, web radio, and real-time video/audio
conferencing
• Communication for training and cooperative operations, such as distance learning and
telemedicine
• Data warehouse and financial applications (stock quotes)
• Any other point-to-multipoint application for data distribution
Multicast models
Based on how the receivers treat the multicast sources, the multicast models include any-source
multicast (ASM), source-filtered multicast (SFM), and source-specific multicast (SSM).
ASM model
In the ASM model, any multicast sources can send information to a multicast group. Receivers can
join a multicast group and get multicast information addressed to that multicast group from any

 Loading...
Loading...














