26
The gas supply shall have a maximum inlet pressure of less than 14" water column (350 mm), ½ pound
pressure (3.5 kPa), and a minimum of 3.5" water column. The entire piping system, gas meter and
regulator must be sized properly to prevent pressure drop greater than 0.5" WC as stated in the National
Fuel Gas Code. This information is listed on the rating plate.
It is very important that you are connected to
the type of gas as noted on the rating plate:
"LP" for liquefied petroleum, propane gas, or
"Nat" for natural or city gas. All gas
connections must be approved by the local
gas supplier or utility, in addition to the
governing authority, prior to turning the gas
supply on.
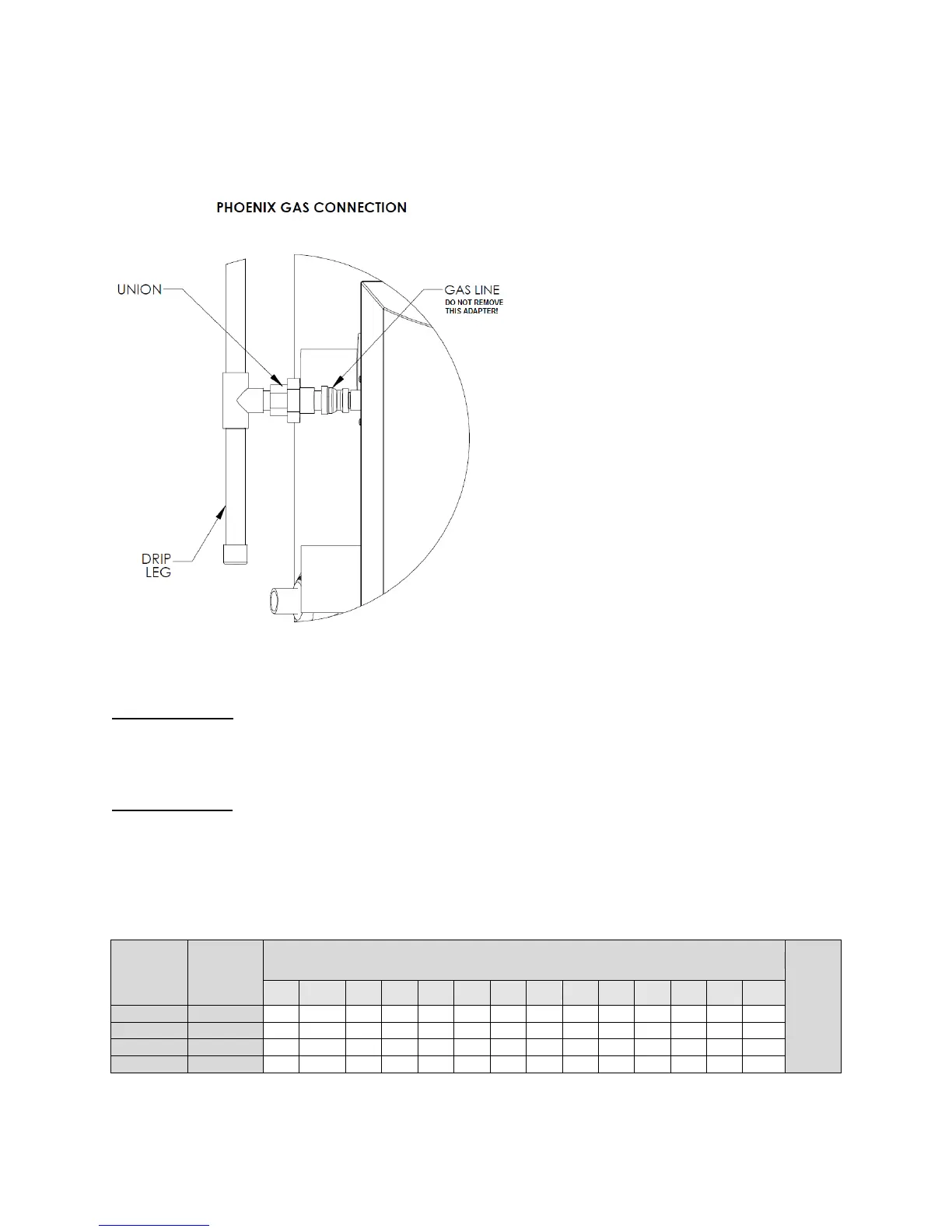
Do not remove the adaptor in Figure 12! It is
mandatory that this fitting is used for
connection to a field fabricated drip leg per the
National Fuel Gas Code. You must ensure
that the entire gas line to the connection at the
water heater is no smaller than ¾".
Once all inspections have been performed,
the piping must be leak tested. If the leak test
requirement is a higher test pressure than the
maximum gas inlet pressure, you must isolate
the heater from the gas line to continue leak
testing. To do this, you must turn off the
factory and field-installed gas cocks. This will
minimize the possibility of damaging the gas
valve. Failure to do so may damage the gas
valve. In the event the gas valve is exposed to a pressure greater than ½ PSI, 14" water column, the gas
valve must be replaced. Never use an open flame (match, lighter, etc.) to check gas connections.
A. GAS PIPING
Run the gas supply line in accordance with all applicable codes. Locate and install manual shutoff valves
in accordance with local and state requirements.
B. GAS TABLE
Refer to the table below to size the supply piping to minimize pressure drop between meter or regulator
and unit.
Maximum capacity of pipe in cubic feet of gas per hour for gas pressures of .5 psi or less and a pressure
drop of .3 inch water column.
Iron Pipe
Size
Internal
Diameter
(Inches)
Length of Pipe (Feet)
BTU’s
Per
Hour x
1,000
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 125 150 175 200
278 190 152 130 115 105 96 90 84 79 72 64 59 55
520 350 285 245 215 195 180 170 160 150 130 120 110 100
1,600
1,100 890 760 670 610 560 530 490 460 410 380 350 320
Table 3 – Source – ANSI Z223.1
 Loading...
Loading...









