Installation and Connection 2-6
2
2-3-3 Connection of Control Terminals
Table 2-3-2 shows the functions of the control
circuit terminals. The method of connecting
control function terminals varies according to
the function setting. Refer to the connection
method for the function.
Table 2-3-2 Functions of control circuit terminals
Classifi- Terminal
cation symbol Terminal name Description of function
13 Potentiometer power +10 Vdc power supply for frequency setting POT.
supply (POT: 1 to 5 kohm).
12 Voltage input (1) The frequency is set according to the external
analog input voltage command.
• 0 to +10 Vdc / 0 to 100%
• Reversible operation using +/- signal: 0 to +/-10
Vdc / 0 to 100%
Analog • Inverse mode operation: +10 to 0 Vdc / 0 to 100%
input (2) The PID control feedback signal is input.
* Input resistance: 22 kOhm
C1 Current input (1) The frequency is set according to the analog
input current command.
• 4 to 20 mAdc / 0 to 100%
• Inverse mode operation: 20 to 4 mAdc / 0 to 100%
(2) The PID control feedback signal is input.
* Input resistance 250 ohm
11 Common Common for analog signals
FWD Forward operation Forward operation with FWD-P24 ON and
command deceleration and stop with FWD-P24 OFF.
REV Reverse operation Reverse operation with REV-P24 ON and
command deceleration-stop with REV-P24 OFF.
X1 Digital input 1 A coast-to-stop command from an external
X2 Digital input 2
device, external alarm, alarm reset, multi-step
X3 Digital input 3
frequency selection and other functions can be
X4 Digital input 4
assigned to the X1 through X5 terminals. Refer to
X5 Digital input 5
the terminal function E01 to 05 setting method in
section 5-2 Detail Description of Each Function.
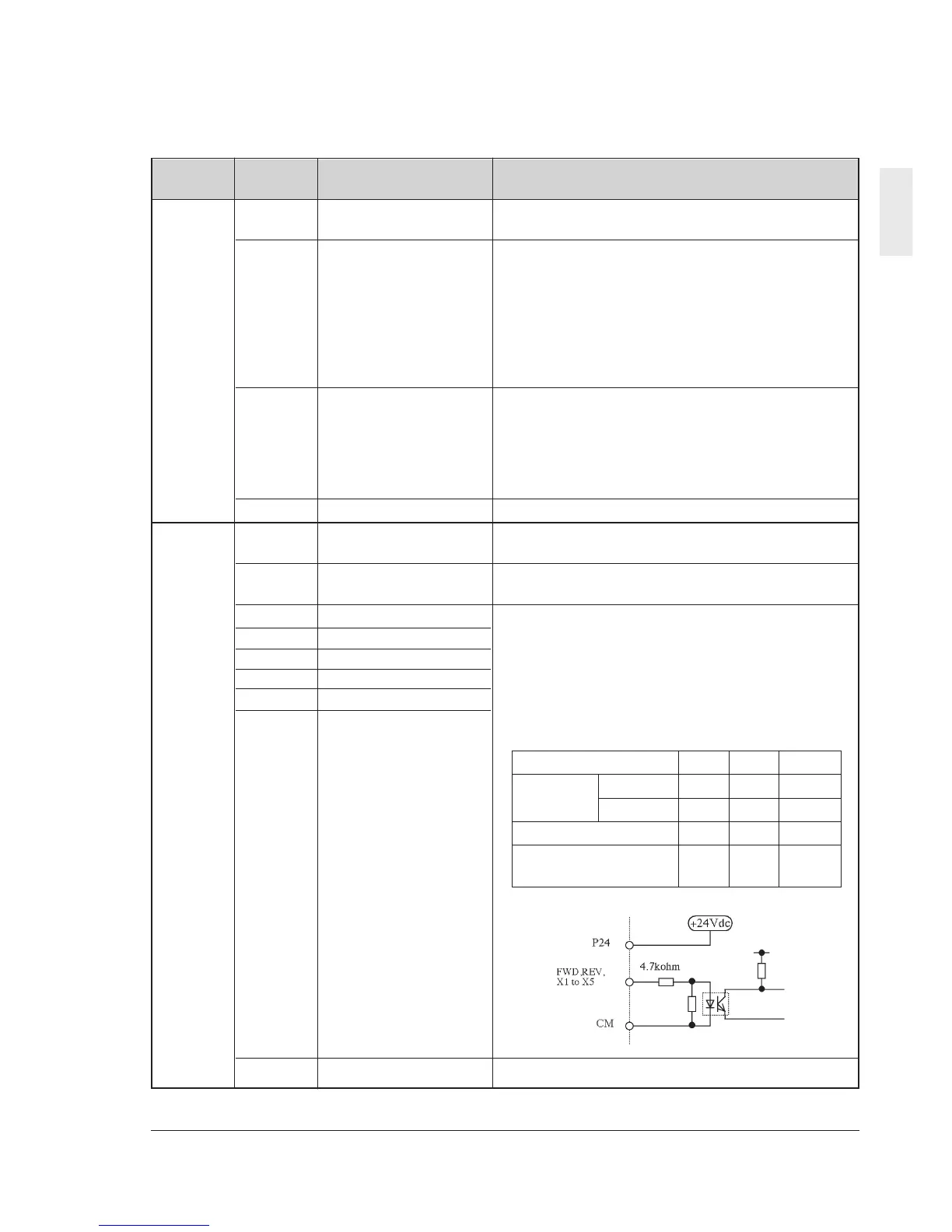
<Digital input circuit specification>
Digital
input
CM Common Common for digital input
Item min. typ. Max
Operation Level OFF 0V - 2V
voltage Level ON 22V 24V 27V
Operation current at ON - 4.2mA 6mA
Allowable leakage
current at OFF
- - 0.5mA
 Loading...
Loading...