Acquisition Control 12
Keysight InfiniiVision 3000 X-Series Oscilloscopes User's Guide 187
So, in practice, an oscilloscope's sample rate should be four or more times its
bandwidth: f
S
= 4f
BW
. This way, there is less aliasing, and aliased frequency
components have a greater amount of attenuation.
Note that 1 GHz bandwidth 3000 X-Series oscilloscope models have more of a
brick-wall type frequency response (also known a flat response) than the Gaussian
response of lower bandwidth 3000 X-Series oscilloscope models. To understand
the characteristics of each type of oscilloscope frequency response, see
Understanding Oscilloscope Frequency Response and Its Effect on Rise-Time
Accuracy, Keysight Application Note 1420
(http://literature.cdn.keysight.com/litweb/pdf/5988-8008EN.pdf).
See Also Evaluating Oscilloscope Sample Rates vs. Sampling Fidelity: How to Make the
Most Accurate Digital Measurements, Keysight Application Note 1587
(http://literature.cdn.keysight.com/litweb/pdf/5989-5732EN.pdf)
Oscilloscope Rise Time
Closely related to an oscilloscope's bandwidth specification is its rise time
specification. Oscilloscopes with a Gaussian-type frequency response have an
approximate rise time of 0.35/f
BW
based on a 10% to 90% criterion.
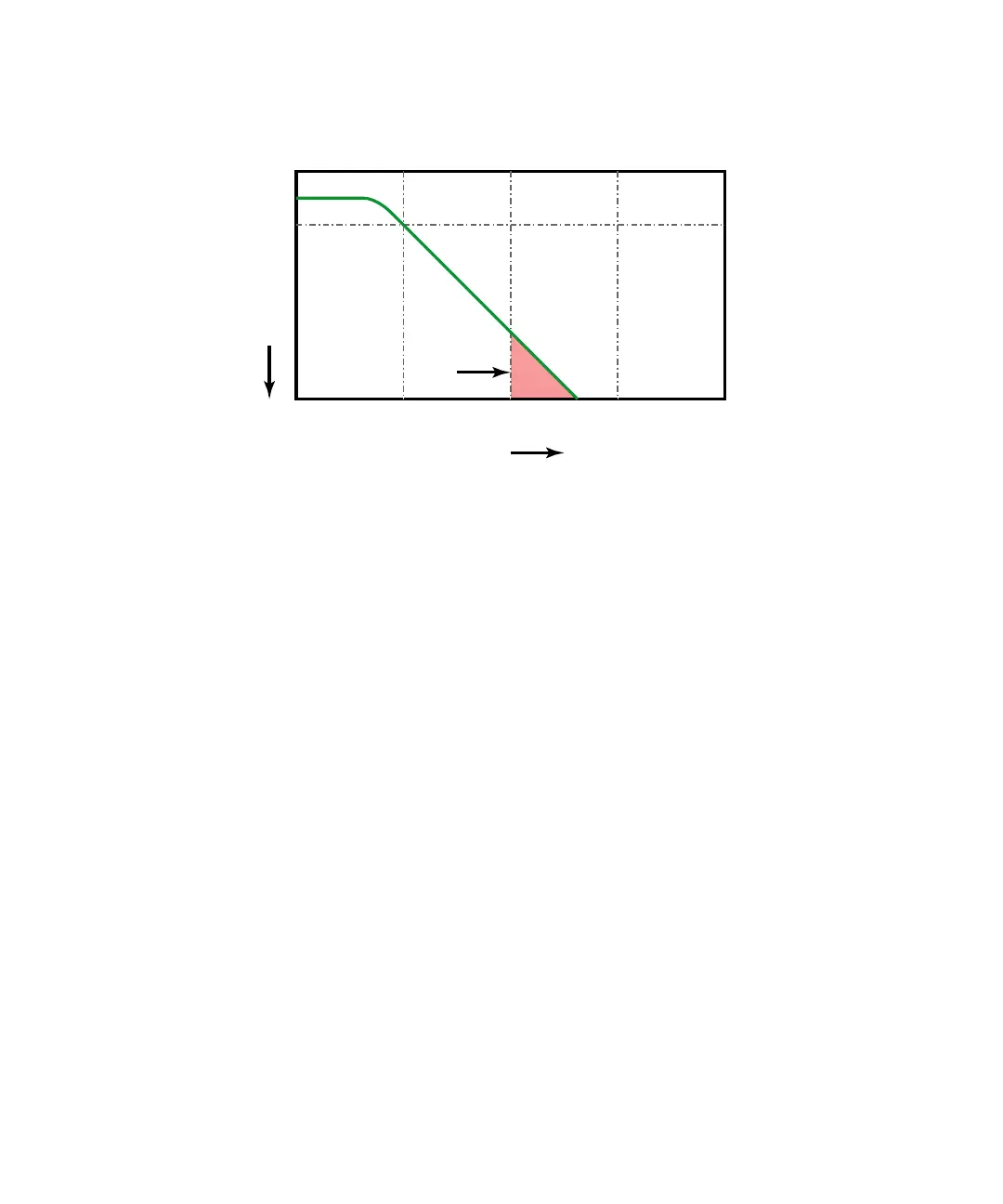
Figure 35 Sample Rate and Oscilloscope Bandwidth
Limiting oscilloscope bandwidth (f
BW
) to 1/4 the sample rate (f
S
/4)
reduces frequency components above the Nyquist frequency (f
N).
[
H
[
C
[
H
$)
"(Y7
6iiZcjVi^dc
6a^VhZY[gZfjZcXn
XdbedcZcih
;gZfjZcXn
%Y7
 Loading...
Loading...