Configuration RS-485 Configuration
4-6
Two-wire Mode
In two-wire mode, the MSS operates in half duplex: one pair of wires shares transmit and receive signals,
and an optional third wire can be used for shield/ground. The main advantage of using two-wire mode is
reduced cabling costs.
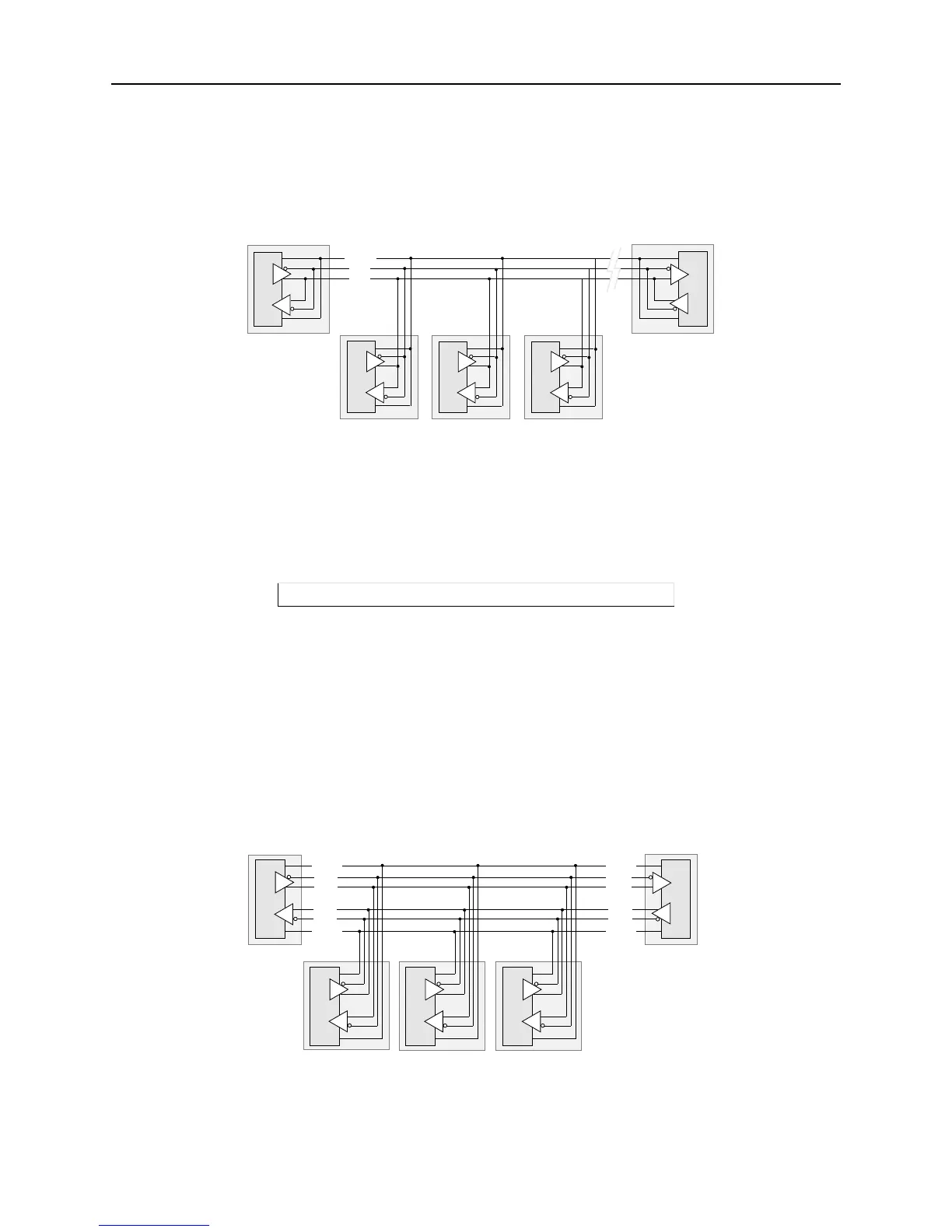
Figure 4-9: Example Two-wire Mode Network
In a two-wire RS-485 network, the MSS must turn its transmitter on when it is ready to send data and then
off for a certain period of time after the data has been sent so that the line is available to receive again. At
most baud rate settings, the timing delay is typically one character length with a maximum of 1.5 character
lengths.
Figure 4-10: Enabling Two-Wire RS-485 Mode
Note:
For two-wire mode, the TXDrive setting must be set to Automatic (see TXDrive on page 4-
7). If you enable two-wire mode and TXDrive is set for Always, the MSS will return an
error.
Four-wire Mode
In four-wire mode, the MSS operates in full duplex: one pair of wires functions as the transmit pair, another
pair of wires functions as the receive pair, and there is a shield/ground wire for each pair. The MSS is able
to send and receive data simultaneously. In a four-wire RS-485 network, one device acts as a master while
the other devices are slaves. The advantages of four-wire mode are double the throughput of two-wire mode
and a guaranteed open path to each slave device’s receiver.
Figure 4-11: Example Four-Wire Mode Network
Local>> CHANGE RS485 PORT 3 MODE 2WIRE
TX-
TX+
TX
RX
Shield
-
-
+
+
-
+
+
-
RX
TX
Shield
Shield
Shield
-
+
-
+
TX
RX
Sh
Sh
-
+
-
+
TX
RX
Sh
Sh
-
+
-
+
TX
RX
Sh
Sh
¥
¥
¥
Shield
Slave Slave Slave
Slave
Master
(MSS)
TX
RX
RX
TX
TX-
TX+
RX+
RX-
Shield
Shield
RX-
RX+
TX+
TX-
Shield
Shield
Sh
-
-
+
+
TX
RX
Sh
Sh
-
-
+
+
TX
RX
Sh
Sh
-
-
+
+
TX
RX
Sh
Master
(MSS)
Slave Slave Slave
Slave

 Loading...
Loading...