Configuration 802.11 Configuration
4-14
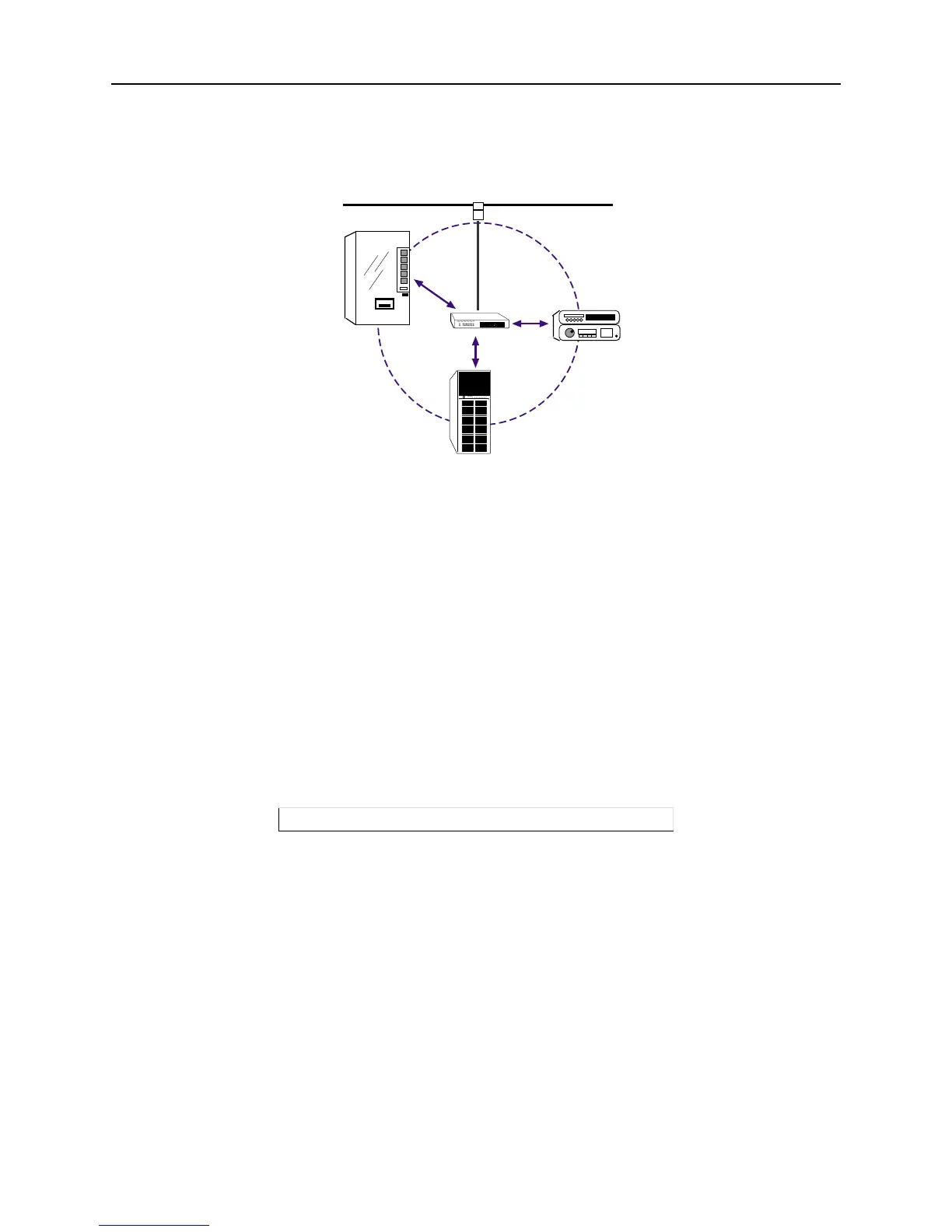
BSS Basic Service Set (or Cell), a group of wireless devices that speak directly with
each other. A BSS may consist of at most one AP.
Figure 4-34: Simple Wireless Network BSS
ESS Extended Service Set, a network consisting of one or more BSSs that share the
same ESSID. An ESS can contain multiple APs.
IBSS Independent Basic Service Set, a BSS with no APs. Devices work in an ad-hoc
networking mode.
WEP Wireless Equivalent Privacy, a form of encryption for wireless communication.
Enabling 802.11 Networking
The MSS has 802.11 networking enabled by default. This allows the MSS to check for a compatible
wireless networking card at startup. If a compatible card is present, the MSS will use the wireless network
and ignore any wired Ethernet settings. If no compatible PC card is present, the MSS will use the 10/
100BASE-T or 100BASE-FX Ethernet interface.
If you want the MSS to only look for a wired Ethernet connection, you must disable 802.11.
Figure 4-35: Disabling 802.11
Note:
You must reboot the MSS after enabling or disabling 802.11 networking.
Region
When using 802.11 networking, you must make sure the MSS is configured for the correct regulatory
region. Configuring this option incorrectly may cause the MSS to broadcast on frequencies that are illegal
in your area. The factory default setting is correct for the United States; users in other countries should
change it to a value appropriate for their area before attempting 802.11 operation.
Recognized regions are:
FCC United States (the default)
IC Canada
Local>> CHANGE 80211 DISABLED
AP
BSS

 Loading...
Loading...