32
DETAILED INSTRUCTIONS
An absence of the dicrotic notch, a smaller amplitude, a decreased
slope and a rounding of the systolic peak are the initial signs of a
possible abnormality – the measured ABI value is lower than the
one with normal pulse waveform.
A flattened PVR waveform or a PVR without the typical shape is an
indicator of severe PAD. The absence of the pulsations caused by
occlusions in the artery makes it impossible to calculate the ankle
pressures. Instead of the ABI value, the device will display a ‘PAD’
result, indicating severe disease. The result is confirmed with a
non-typical, flattened PVR waveform similar to the one below.
PULSE
WAVEFORM
5.5.2
The MESI ABPI MD uses the PADsense™ pattern recognition
algorithm to automatically interpret the acquired pulse waveform
and calculate the ABI with the result. However, to help the user
better understand the performed ABI measurement, this pulse
waveform is available on the result screen.
Combining both the ABI result and pulse waveform represents the
best practice in evaluating the presence and severity of Peripheral
Arterial Disease (PAD).
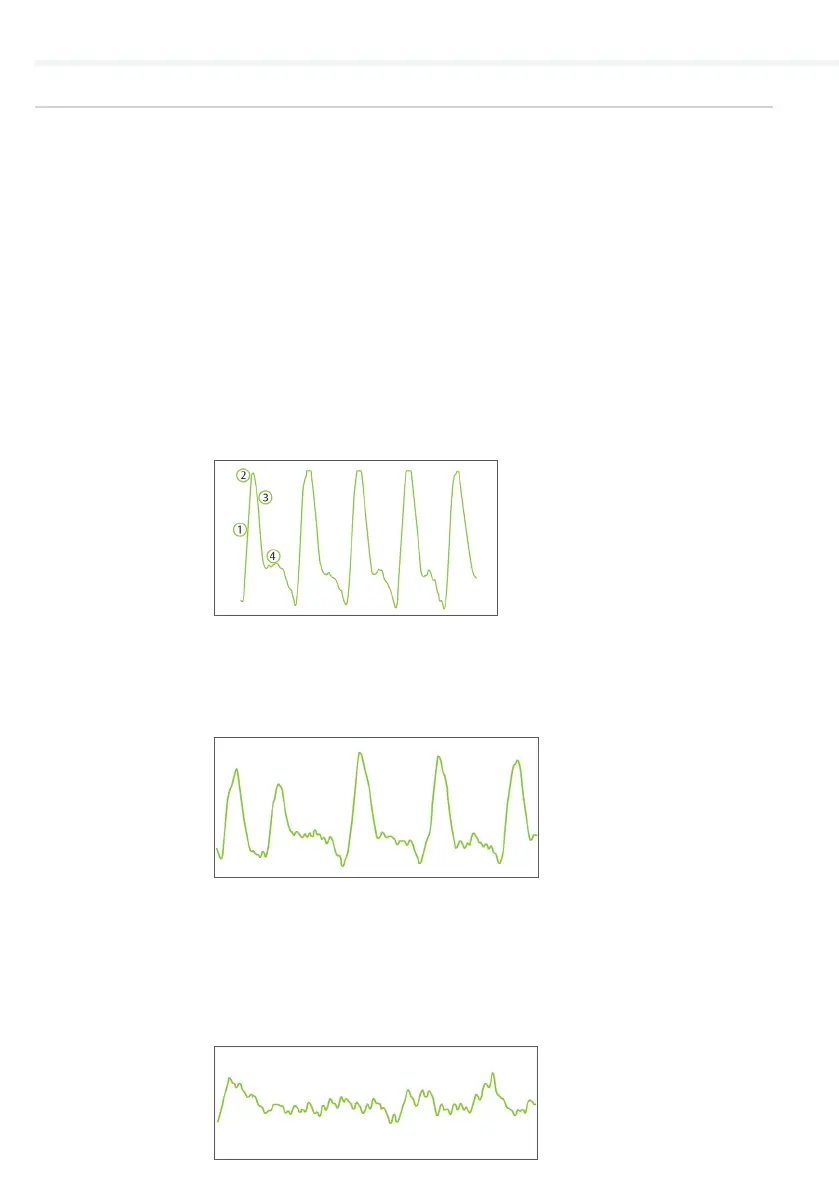
Normal pulse waveform will display:
(1) a rapid rise in the upstroke during systole,
(2) a very sharp peak,
(3) a gradual downstroke,
(4) the presence of the dicrotic notch.
 Loading...
Loading...