24 Port Gigabit Ethernet PoE Switch – User Manual Page 47 of 72
________________________________________________________________________
©2014 MICROSENS GmbH & Co. KG – Hamm/Germany www.microsens.com
3-2-14. SNMP
Any Network Management System (NMS) running the Simple Network Management
Protocol (SNMP) can manage devices equipped with SNMP agent, provided that the Man-
agement Information Base (MIB) is installed correctly on the managed devices. It is a
protocol used to govern the transfer of information between SNMP manager and agent
and traverses the Object Identity (OID) of the management Information Base (MIB), de-
scribed in the form of SMI syntax. SNMP agent is running on the switch to response the
request issued by SNMP manager.
Basically, it is passive except issuing the trap information. The switch supports a
switch to turn on or off the SNMP agent. If you set the field SNMP “Enable”, SNMP agent
will be started up. If the field SNMP is set “Disable”, SNMP agent will be de-activated, the
related Community Name, Trap Host IP Address, Trap and all MIB counters will be ig-
nored.
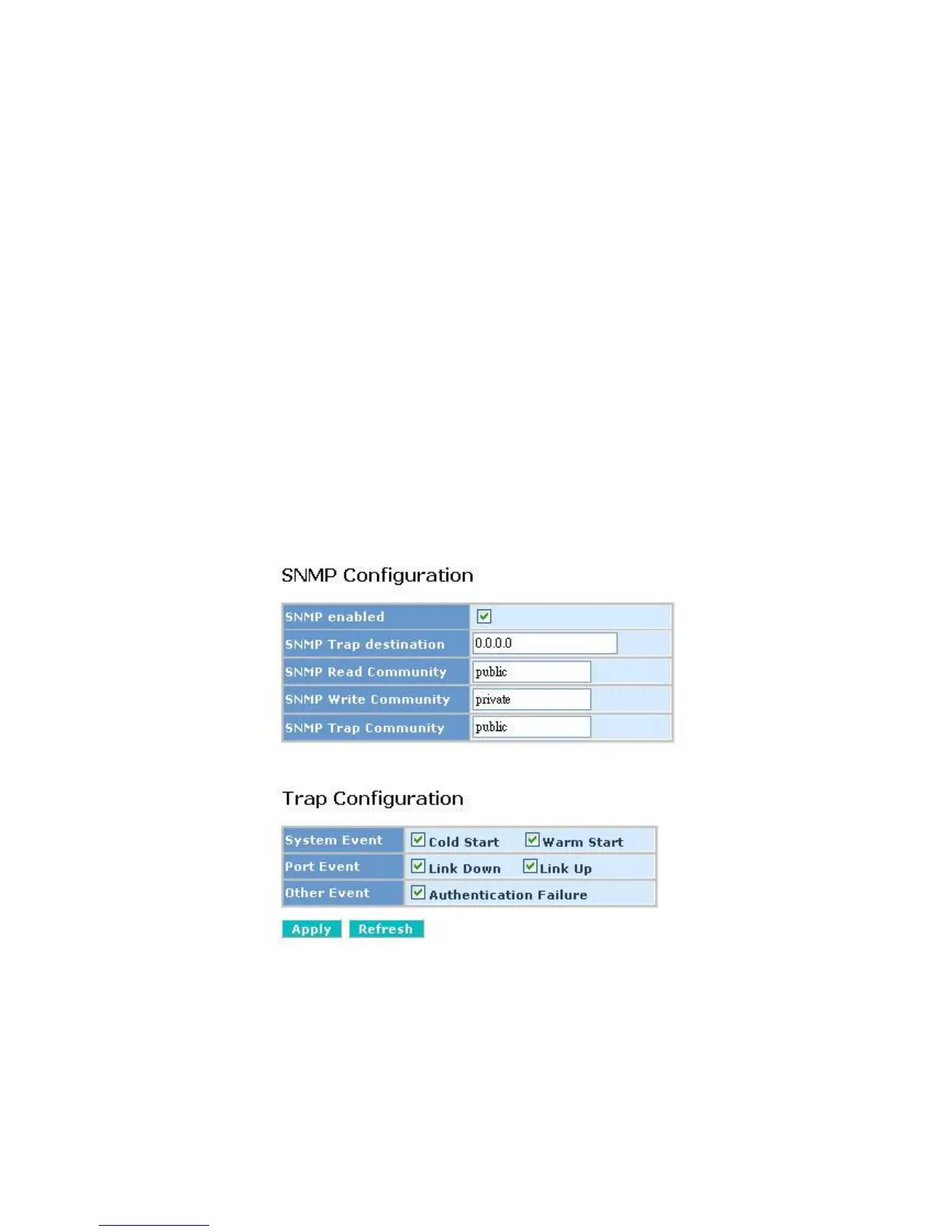
Function name
SNMP Configuration
Function description
This function is used to configure SNMP settings, community name, trap host and
public traps as well as the throttle of SNMP. A SNMP manager must pass the authentica-
tion by identifying both community names, and then it can access the MIB information of
the target device. So, both parties must have the same community name. Once complet-
ing the setting, click <Apply> button, the setting takes effect.
Fig. 3-21 SNMP Configuration
Parameters description:
SNMP enable:
The term SNMP enable here is used for the activation or de-activation of SNMP.
Default is “Disabled”.
Read/Write/Trap Community:
Community name is used as password for authenticating if the requesting net-
work management unit belongs to the same community group. If they both don’t
 Loading...
Loading...