4: Sample Experiments
Relative Irradiance Experiments
Irradiance is the amount of energy at each wavelength from a radiant sample. In relative terms, it is the
fraction of energy from the sample compared to the energy collected from a lamp with a blackbody
energy distribution, normalized to one at the energy maximum. Relative irradiance is calculated by the
following equation:
S
λ
- D
λ
I
λ
= B
λ
(
R
λ
- D
λ
)
Where:
B
λ
= the relative energy of the reference (calculated from the color temperature) at wavelength λ
S
λ
= the sample intensity at wavelength λ
D
λ
= the dark intensity at wavelength λ
R
λ
= the reference intensity at wavelength λ
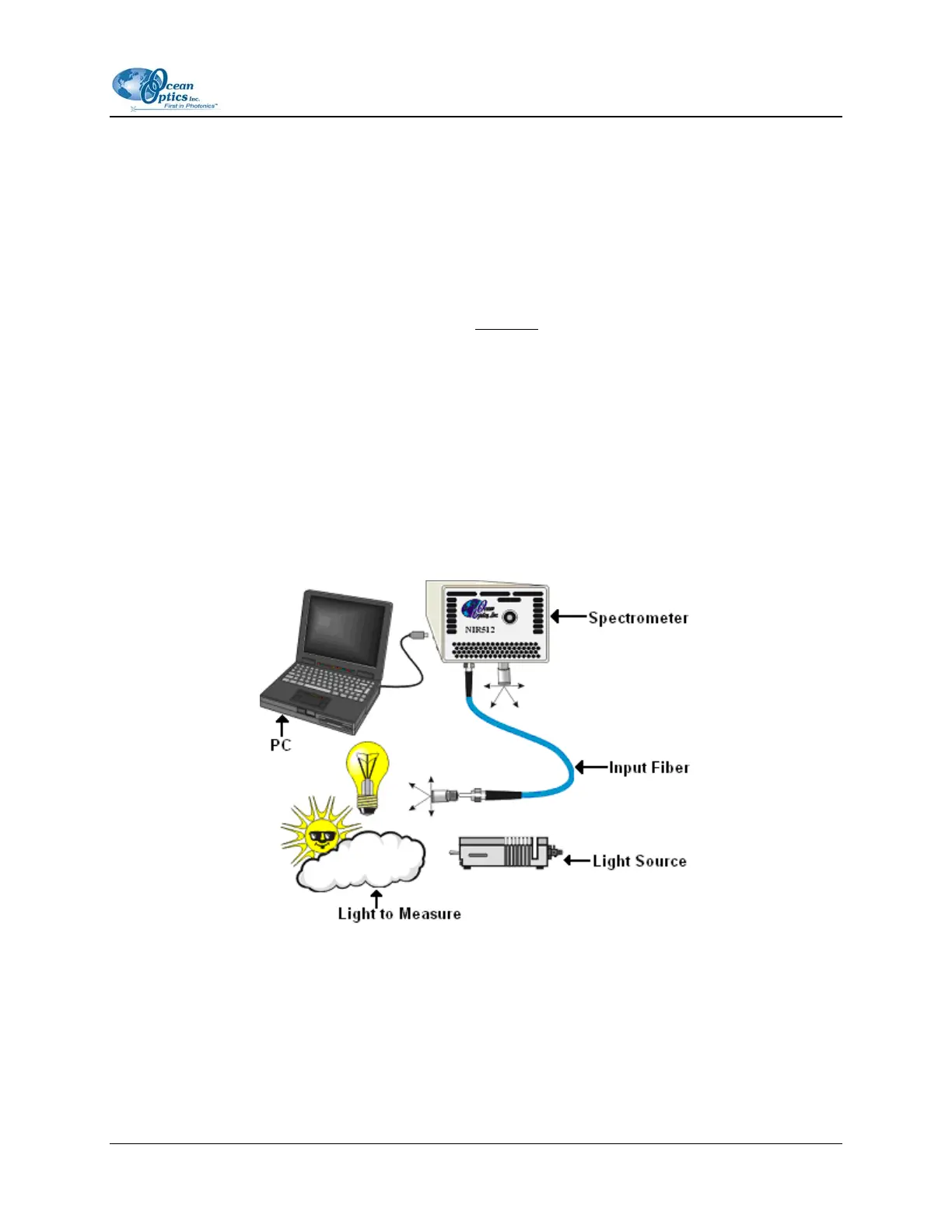
The figure below shows a typical Relative Irradiance setup.
Common applications include characterizing the light output of LEDs, incandescent lamps, and other
radiant energy sources such as sunlight. Also included in relative irradiance measurements is
fluorescence, in which case the spectrometer measures the energy given off by materials that have been
excited by light at a shorter wavelength.
197-00000-512-02-0305 25
 Loading...
Loading...