68
ber of ways in which the work bits can be used. Whenever difficulties arise in
programming a control action, consideration should be given to work bits and
how they might be used to simplify programming.
Work bits are often used with the OUTPUT, OUTPUT NOT, DIFFERENTIATE
UP, DIFFERENTIATE DOWN, and KEEP instructions. The work bit is used
first as the operand for one of these instructions so that later it can be used
as a condition that will determine how other instructions will be executed.
Work bits can also be used with other instructions, e.g., with the SHIFT REG-
ISTER instruction (SFT(33)). An example of the use of work words and bits
with the SHIFT REGISTER instruction is provided 3-7-20 SHIFT REGISTER
- SFT(33).
Although they are not always specifically referred to as work bits, many of the
bits used in the examples later in this section use work bits. Understanding
the use of these bits is essential to effective programming.
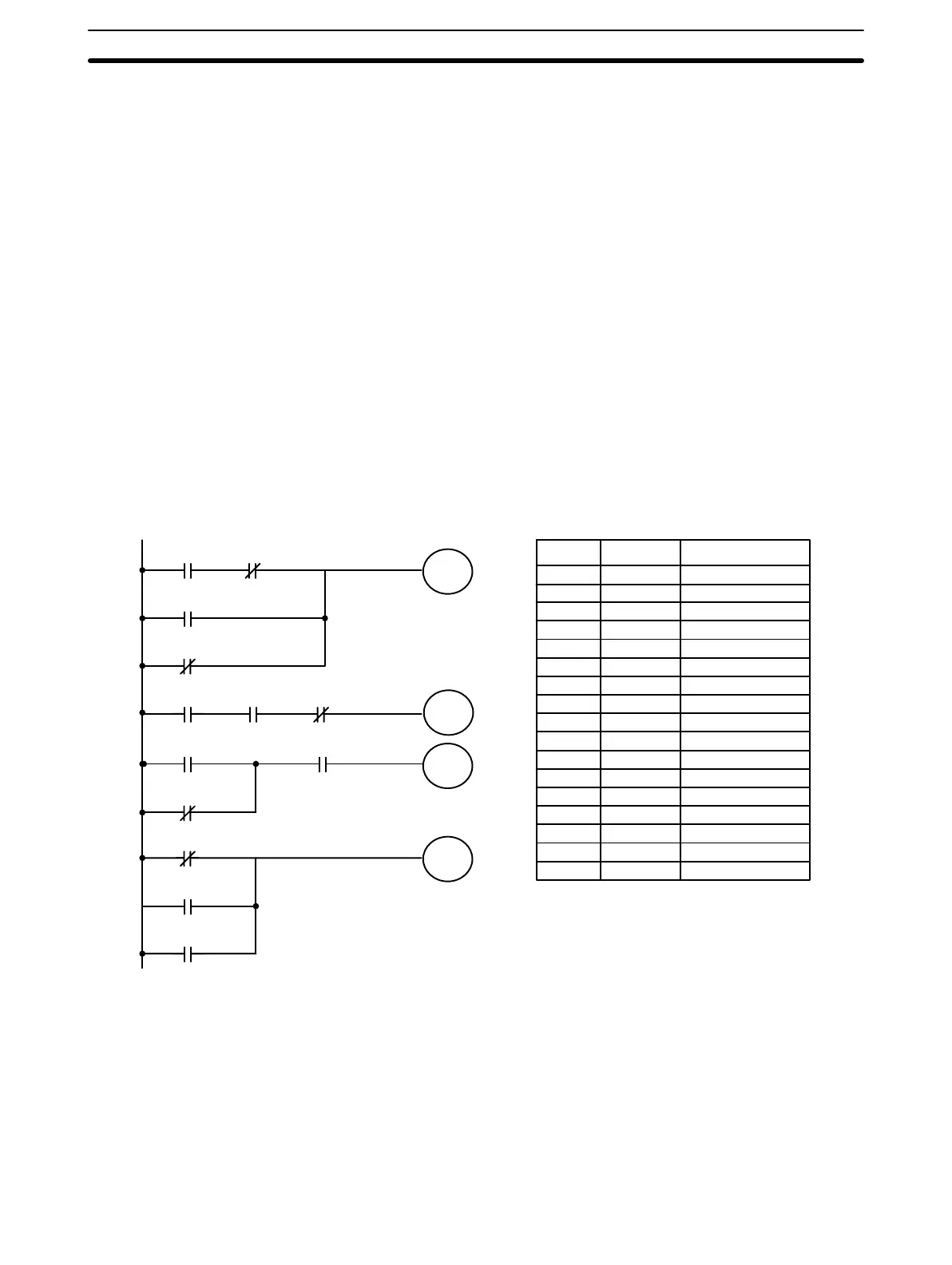
Work bits can be used to simplify programming when a certain combination
of conditions is repeatedly used in combination with other conditions. In the
following example, bit 0000, bit 0001, bit 0002, and bit 0003 are combined in
a logic block that stores the resulting execution condition as the status of bit
0103. Bit 0103 is then combined with various other conditions to determine
output conditions for bit 0000, bit 0001, and bit 0002, i.e., to turn the outputs
allocated to these bits ON or OFF.
0000
0003
0001
0004
0002
0005
0004
0009
0008
00050103
0103
0103
0103
0100
0101
0102
Address Instruction Operands
000 LD 0000
001 AND NOT 0001
002 OR 0002
003 OR NOT 0003
004 OUT 0103
005 LD 0103
006 AND 0004
007 AND NOT 0005
008 OUT 0100
009 LD 0103
010 OR NOT 0004
011 AND 0005
012 OUT 0101
013 LD NOT 0103
014 OR 0008
015 OR 0009
016 OUT 0102
Differentiated Conditions Work bits can also be used if differential treatment is necessary for some, but
not all, of the conditions required for execution of an instruction. In this exam-
ple, bit 0100 must be left ON continuously as long as bit 0001 is ON and both
bit 0002 and bit 0003 are OFF, or as long as bit 0004 is ON and bit 0005 is
OFF. It must be turned ON for only one scan each time bit 0000 turns ON
(unless one of the preceding conditions is keeping it ON continuously).
This action is easily programmed by using bit 0200 as a work bit as the oper-
and of the DIFFERENTIATE UP instruction (DIFU(10)). When bit 0000 turns
ON, bit 0100 will be turned ON for one scan and then be turned OFF the next
Reducing Complex
Conditions
Advanced Programming Section 3-6
 Loading...
Loading...











