Dual TCP/IP Configuration Examples
E-4 StorageTek SL8500 Library Guide
3.
Specify a second
LMUADDR
parameter to define the dual TCP/IPs. ELS
automatically determines whether the connection is dual TCP/IP or dual LMU.
4. Take the ACS offline, issue the
LMUPDEF
command, and bring the ACS back online
to pick up the revised
LMUPATH
statement that includes the second connection.
For more information, see the ELS documentation.
Dual TCP/IP Configuration Examples
■ ACSLS Dual TCP/IP and Shared Subnets Example
■ ACSLS Dual TCP/IP Through a Public Network Example
■ ACSLS High Availability Dual TCP/IP Example
■ See also "Redundant Electronics Configuration Examples" on page D-2 for an
example of RE and dual TCP/IP.
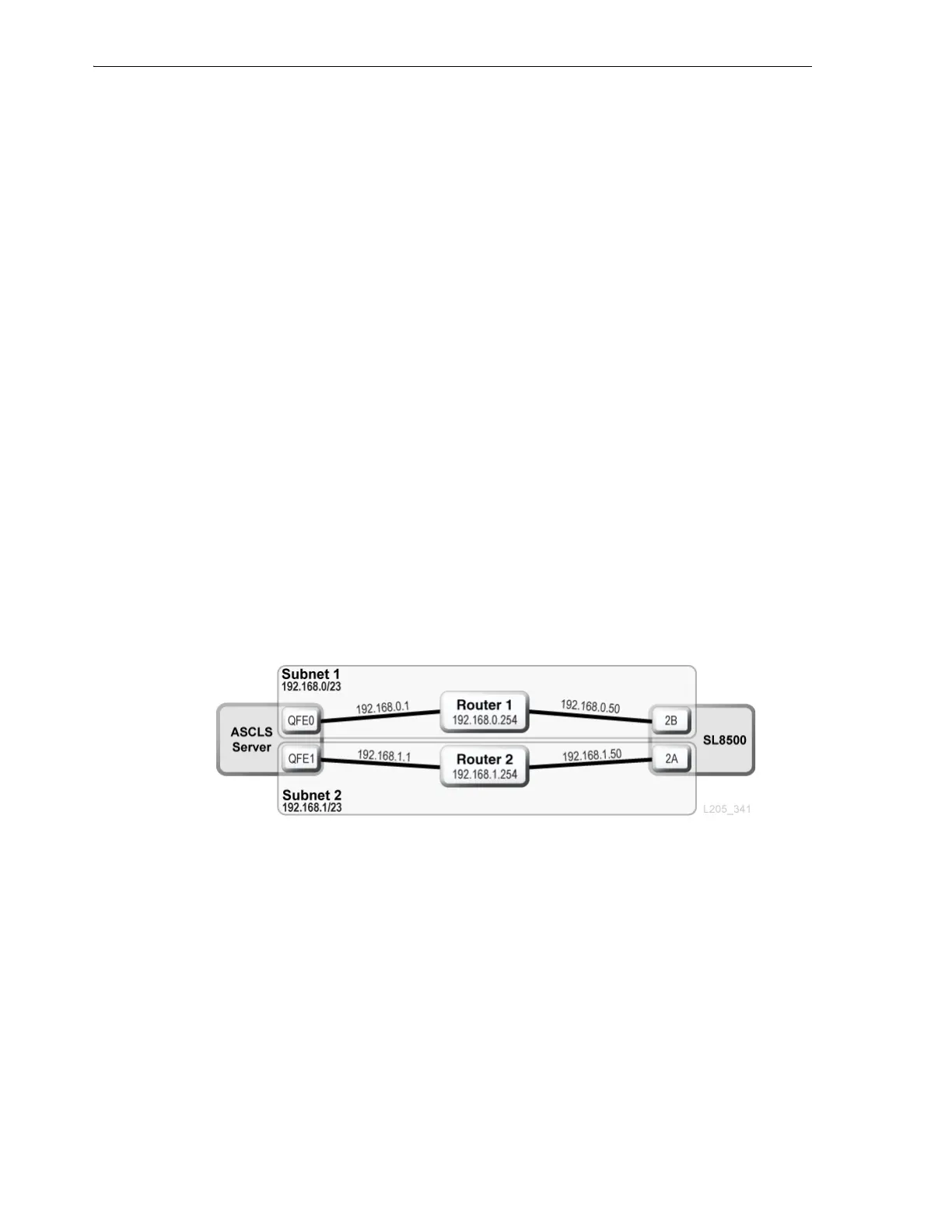
ACSLS Dual TCP/IP and Shared Subnets Example
In this example, the ACSLS server and the library share two separate subnets. The
SL8500 uses a one-to-one relationship with the network interfaces on the ACSLS
server. The network interface card on subnet 192.168.0/23 connects to port 2B and the
network interface card on subnet 192.168.1/23 connects to port 2A.
Routing
Force a relationship by using the UNIX
route
commands. For more information, see
the ACSLS Administrator's Guide.
Figure E–1 ACSLS Dual TCP/IP with Shared Subnets
ACSLS Dual TCP/IP Through a Public Network Example
In this example, the ACSLS server contains two network interfaces that reside on two
separate subnets. Both interfaces pass through a public network and into two different
subnets before connecting to the SL8500 library. This configuration uses the same
commands as in the first example.

 Loading...
Loading...











