IG-267-EN versión 01; 07/04/2017
24
Protection functions General Instructions
ekor.rpa
4.3.2. Neutral and sensitive neutral directional units
The neutral and sensitive neutral directional units include
two different criteria to determine direction: Directional
criterion and wattmetric criterion. The criterion is selected
through a setting in the unit itself.
Angular criterion
The angular criterion of the neutral and sensitive neutral
directional units is based on the phase difference between
the polarisation signal (-3V
o
) and the residual current signal
(3I
o
).
The polarisation signal used is the 180° out-of-phase
residual voltage, i.e.- 3V
o
.
The settings for the neutral and sensitive neutral directional
unit, which apply to the angular criteria, are:
• Characteristic neutral angle: Characteristic angle (from
- 90.0° to 90.0°). In distributions with earthed neutral,
this often corresponds to the earth impedance angle.
• Minimum neutral voltage: Minimum polarisation
voltage (from 0.5 kV to 72.0 kV). Polarisation voltage
value as of which the directional unit considers the
angle reliable, and is capable of determining a direction.
• Indeterminate zone: Indeterminate zone angle (from
0.0° to 90.0°). Setting to establish the indetermination
zone which is close to the zero torque line.
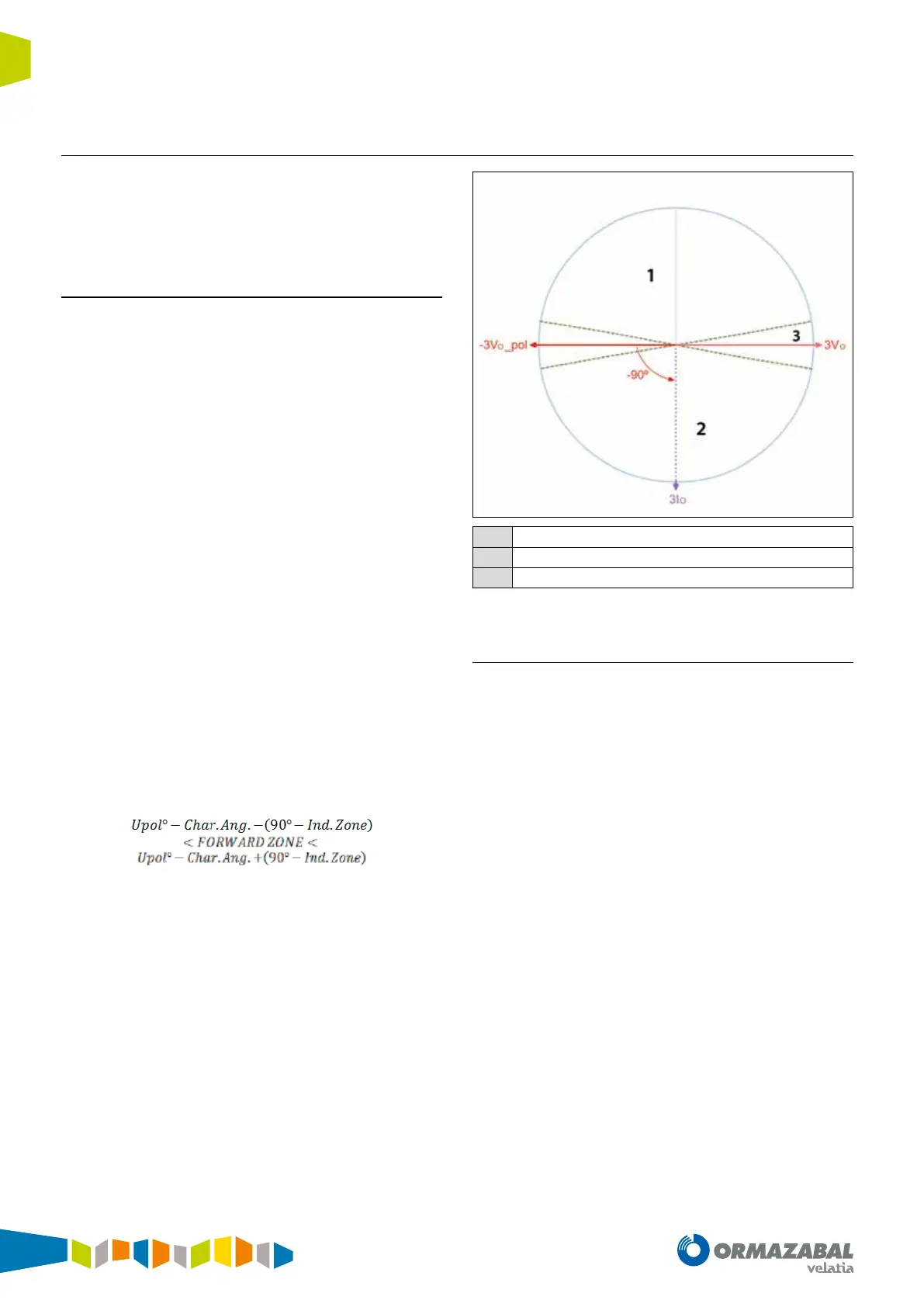
The direction indicated by the units can be Forward, Reverse
or ndef (undefined).
The Forward direction zone is delimited by the following
formula:
The Reverse direction zone will be the opposite of the
Forward zone. In other words, the above formula needs to
be turned around 180° in order to achieve the expression
which delimits the Reverse direction zone.
The directional units will indicate ndef direction if in the
indeterminate zone or polarisation voltage is below the V
min
setting.
The figure below shows an example of operation for the
neutral directional unit:
1
Reserve
2
Forward
3
Indeterminate zone
Figure 4.4. Neutral directional unit
Wattmetric criterion
The wattmetric criterion of the neutral and sensitive neutral
directional units is based on the phase difference between
the polarisation signal (- 3V
o
) and the residual current signal
(3l
o
), along with the magnitude of the residual active power.
The settings for the neutral and sensitive neutral directional
unit, which apply to the wattmetric criteria, are:
• Minimum neutral active power: Minimum residual
active power. Minimum residual active power value (in
absolute value), as of which direction other than ndef
(i.e. Forward or Reverse) can be considered. Variable
ranges in accordance with current transformers used.
• Minimum neutral voltage: Minimum polarisation
voltage (from 0.5 kV to 72.0 kV). Polarisation voltage
value as of which the directional unit considers the
angle reliable, and is capable of determining a direction.
• Indeterminate zone: Indeterminate zone angle (from
0.0° to 90.0°). Angle formed by the 90° axis and the line
which delimits the indeterminate zone.
The direction indicated by the units can be Forward, Reverse
or ndef (undefined).

 Loading...
Loading...