Functional description
16
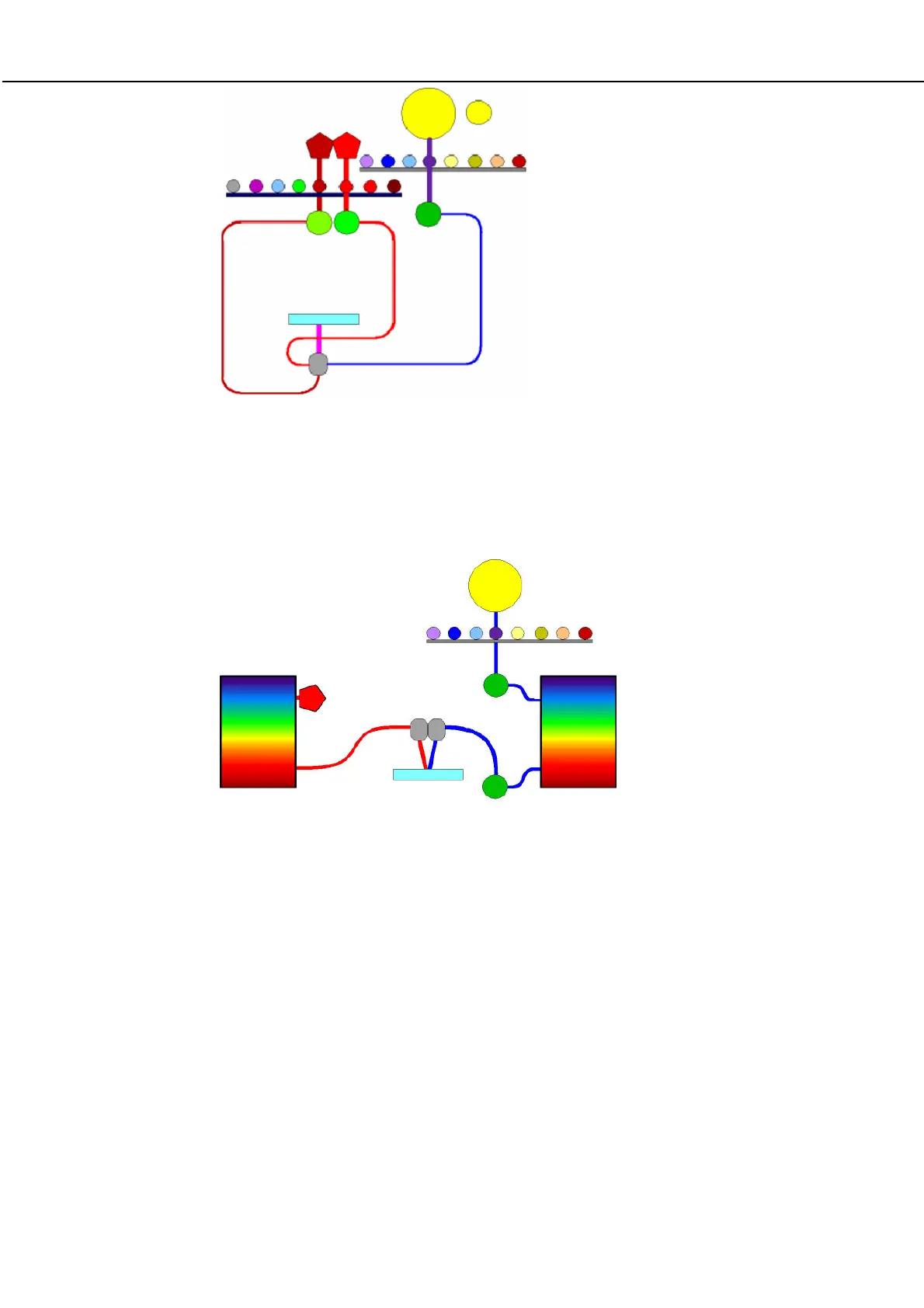
Figure 11. Excitation from below/Dual reading from below
Using the quad monochromator option, excitation light from the lamp is
directed through the excitation double monochromator into the sample. The
emission light is then directed through the emission double monochromator
to the detector.
Figure 12. FI measurement using the EnVision™ monochromator option
Monochromator function relies on the direction of a beam of polychromatic
light onto a diffraction grating. The grating separates the incident
polychromatic beam into its constituent wavelength components, sending
each wavelength into a different direction so that a narrow band of
wavelengths can be collected. Double monochromators contain two
diffraction gratings. The use of monochromators provides the benefit that
wavelength can be selected steplessly through the workstation software.
Although monochromators relieve you of the need to have filters for every
label, a broad waveband cut-off filter is still required in order to block
harmonic multiple orders of the wavelength chosen. A total of three cut-off
filters covers the entire range of wavelengths supported by the instrument.

 Loading...
Loading...