13
1.3.3.
2.
Time
measurements
Time measurements
of signals are
determined
in conjunction with the trigger
level function in a similar
way to
frequency
measurements.
The input signal
is applied via the
voltage
attenuator to one input of the
comparator
A502.
The selected
trigger level
is
applied
to the other
input.
When
the amplitude of
the signal exceeds
that of the selected
trigger level, an output
pulse
from the
com-
parator is applied
direct to the
microprocessor.
Two
trigger modes are
possible for the time
measurement function:
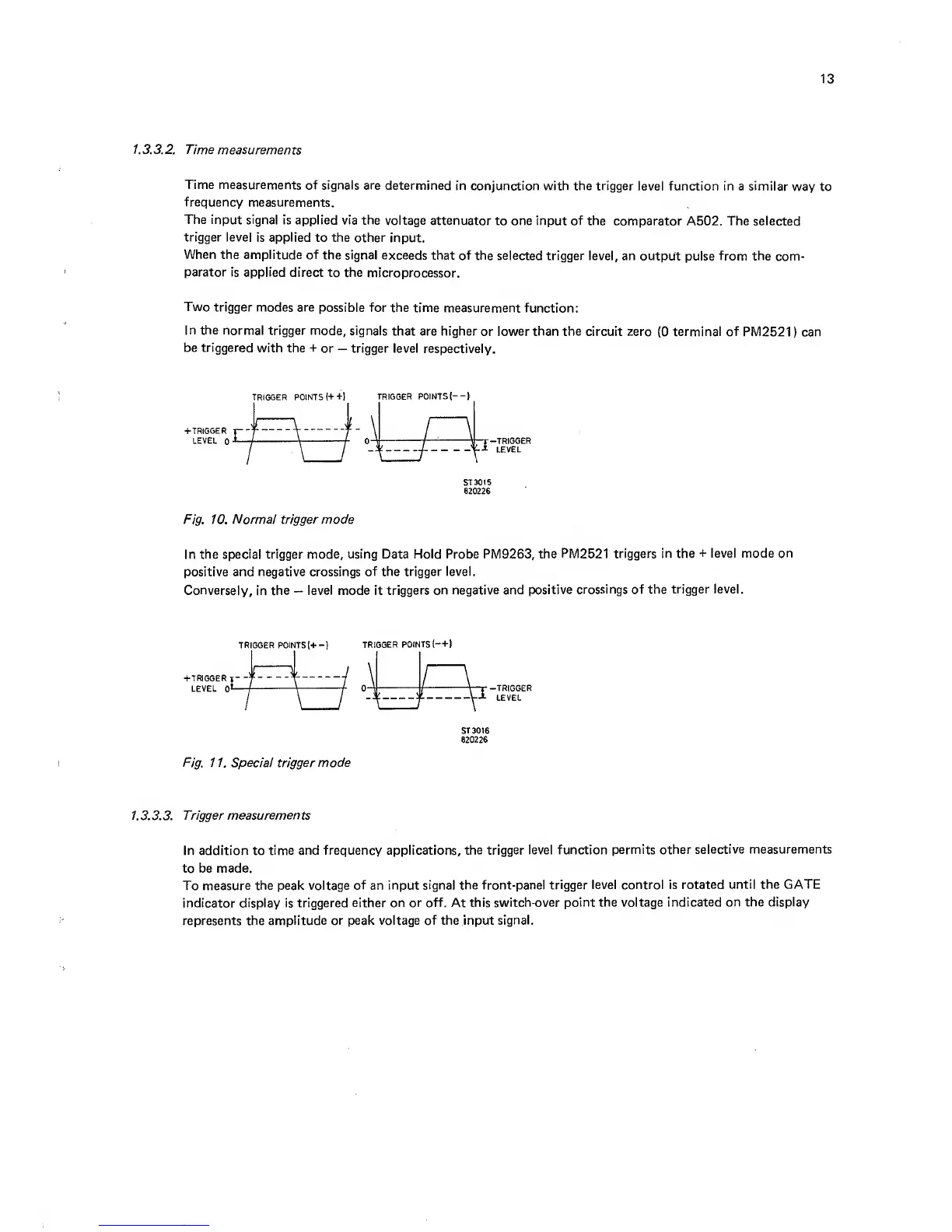
In the
normal trigger mode,
signals
that are higher
or
lower than the
circuit zero
(0
terminal of
PM2521
)
can
be triggered
with the
-i-
or
—
trigger level respectively.
•(-TRIGGER
LEVEL
0
TRIGGER
POINTS
(+-(1
TRIGGER
POINTS!
)
ST
301
6
S20226
Fig.
10.
Normal trigger mode
In the special
trigger mode, using Data Hold
Probe
PM9263,
the PM2521 triggers in the
-i-
level mode
on
positive and negative
crossings of the trigger
level.
Conversely,
in
the
—
level mode it
triggers on
negative and positive
crossings of the
trigger level.
•(TRIGGER
1
LEVEL
O'
TRIGGER
POINTS!-!--)
TRIGGER
points!—
(-1
A
1
\
°-i
:
i
1
'
p:
A 1
V
TRIGGER
LEVEL
ST 3016
820226
Fig.
1
1.
Special trigger mode
1. 3.3.3.
Trigger
measurements
In addition to
time and frequency applications,
the trigger level
function permits other
selective measurements
to be made.
To
measure the peak voltage
of
an input
signal the front-panel
trigger level control is
rotated until the GATE
indicator display is
triggered either
on
or off.
At
this switch-over
point the voltage
indicated on the display
represents the
amplitude or peak voltage of the input
signal.
 Loading...
Loading...