1.22
Operation Manual
© 2013 Prism Media Products Ltd
Revision 1.00Prism Sound Lyra
5 Lyra hardware
This section describes in detail the capabilities of the Lyra hardware.
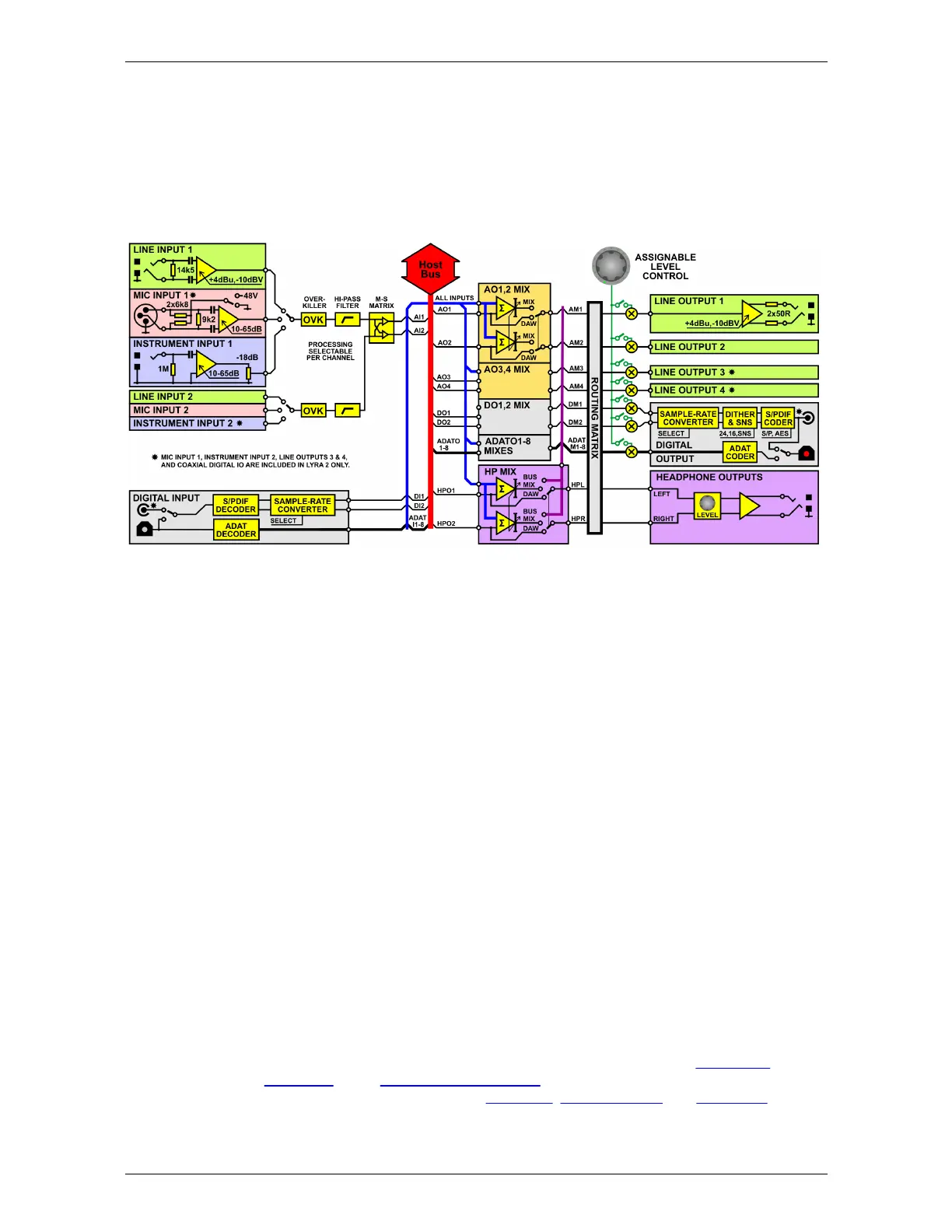
5.1 Signal path architecture
The figure above is a simplified block diagram of the Lyra audio signal paths.
Lyra is basically a sound card, with all inputs made available to the host computer via the USB bus,
and all outputs likewise driven from the USB bus. However, Lyra's signal paths contain a range of
enhanced processing and mixing functions, which are described in the following sections.
5.1.1 Analogue inputs
Both analogue input channels feature balanced line inputs on TRS jacks, with dual switchable
sensitivity to allow connection to professional or consumer line-level sources. The '+4dBu' setting
accommodates professional signals with a nominal level of +4dBu and allows a maximum level of
+18dBu (0dBFS). The '-10dBV' setting accommodates consumer signals with a nominal level of
-10dBV and allows a maximum level of +6dBu (0dBFS).Unbalanced sources are automatically
accommodated.
Both input channels of Lyra 2 (but only input 2 of Lyra 1) have balanced XLR microphone inputs, with
gains variable from 10dB to 65dB in accurate 1dB steps, and with individually switchable phantom
power. A -20dB pad may also be selected if required.
Both input channels of Lyra 2 (but only input 1 of Lyra 1) have high-impedance front-panel
unbalanced 6.3mm instrument ('DI') jacks, also with fine and accurate gain control.
Selection of input modes may be automatic: where mic input mode is over-ridden by the insertion of
a line jack, and both are over-ridden by the insertion of an instrument jack. Alternatively, input
selection may be set manually irrespective of which jacks are inserted.
The input mode and phantom power state of the input channels is indicated on the front panel of the
unit, and also in the Inputs tab of the Lyra Control Panel app. Line, mic and instrument gains are
also adjusted in the Inputs tab, as is selection of the Overkiller, high-pass filter and MS matrix
functions described in the following sections.
 Loading...
Loading...