35
Shelving EQ (High Shelf shown)
InA Input A HSF:1-<::
1k00Hz Q=3.0 0.0dB
Remember–tochangefiltertypes,pressBYPASSto
bypassthefilter,andthenuseENTERtoselectthefilter
type.
TheshelvingEQhasadjustablefrequency,‘Q’(or
Bandwidth)andGaincontrols.Theseaffectarangeof
frequenciesfromtheturnoverfreqencyasshowninthe
graph.Forahighshelf,frequenciesabovetheturnover
frequencywillbeaffected.Foralowshelf,frequencies
belowtheturnoverfrequencywillbeaffected.
Variouslevelsofcutandboostareshowntotheleft,
alongwithvarious‘Q’settings(gainboostsonlyare
showbelow).
Rememberthat‘Q’is1/Bandwidth,sothehigherthe
‘Q’,thelowertheBandwidth,andthesmallertherange
offrequenciesaffected.
Notethat‘Q’settingsabove0.75willresultinslight
overshootinthefilterresponse(asseenatthehigh
est
settingtotheright). Thisisnormalbehaviouranddoes
notindicateinstability.
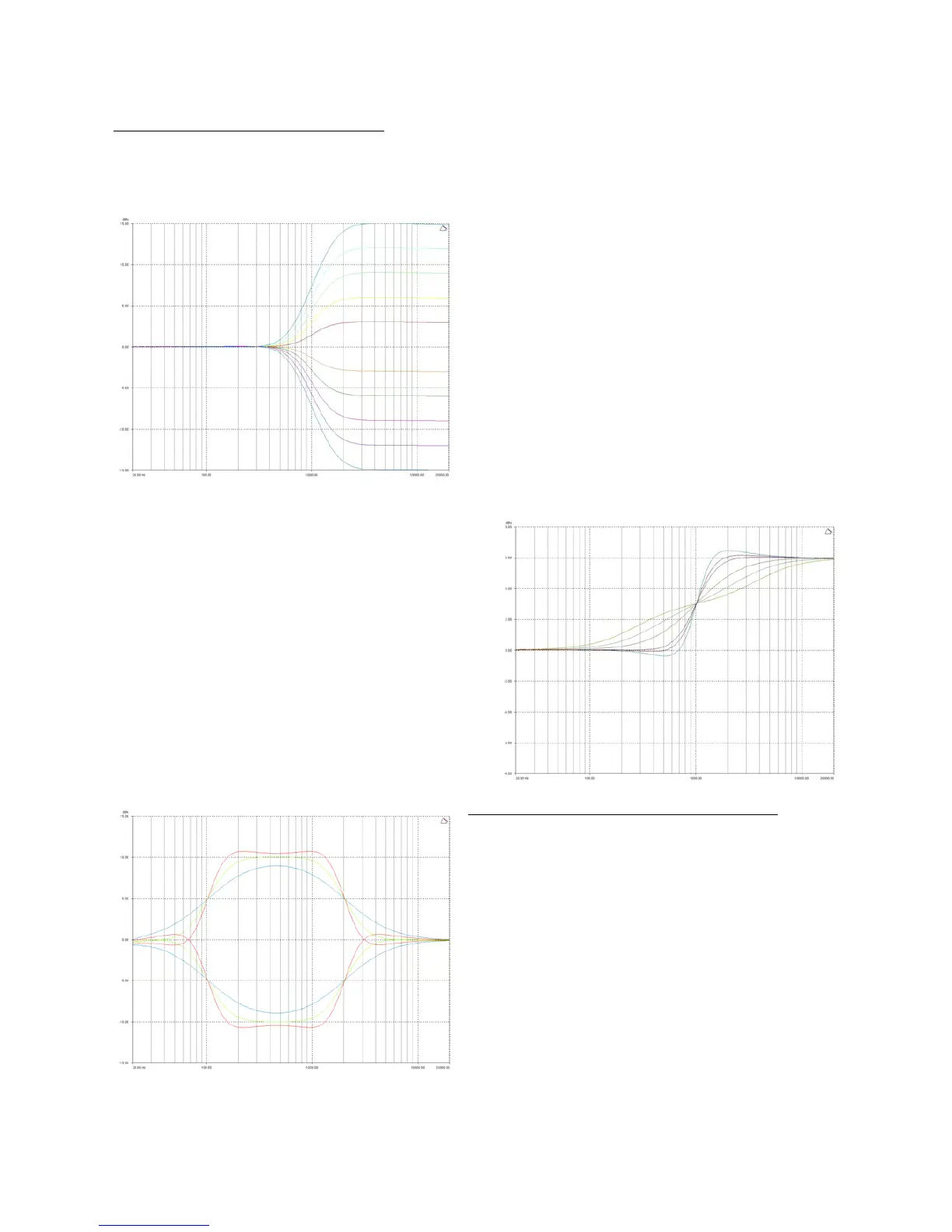
Creating a Flat-topped EQ Response
Tocreateaflat‐toppedEQfilterresponsesuchasthat
showntotheleft,usetwoEQbands,BOTHconfigured
aslowshelves.ForanoverallBOOST,settheLower
frequencyfiltertoBOOSTthedesiredamount,andthe
UpperfrequencyfiltertoCUTbythesameamount.
Thisexa
mpleshowsonefilterat100Hzandtheotherat
2kHz,withthe100Hzfilterat–10dB,andthe2kHz
filterat+10dB.Varyingthe‘Q’affectstheslopeofthe
response–valuesabove0.75willcauseovershootas
shown.
Assymetricalresponsesmaybeachievedbyadjustingthe‘Q’ofeachfilterindependantly.
 Loading...
Loading...