Instruction Reference Manual 53
Description
• IOI: The IOI prefix allows the use of existing memory access instructions as internal I/O
instructions. When prefixed, a 16-bit memory instruction accesses the I/O space at the address
specified by the lower byte of the 16-bit address. With IOI, the upper byte of a 16-bit address is
ignored since internal I/O peripherals are mapped within the first 256-bytes of the I/O address
space. Writes to internal I/O registers require two clocks rather than the three required for mem-
ory write operations.
• IOE: The IOE prefix allows the use of existing memory access instructions as external I/O
instructions. Unlike internal I/O peripherals, external I/O devices can be mapped within 8K of
the available 64K address space. Therefore, prefixed 16-bit memory access instructions can be
used more appropriately for external I/O operations. By default, writes are inhibited for external
I/O operations and fifteen wait states are added for I/O accesses.
WARNING: If an I/O prefixed instruction is immediately followed by one of these 12 special one byte
memory access instructions, a bug in the Rabbit 2000 causes I/O access to occur instead of memory access:
This bug can be avoided by putting a NOP instruction between an I/O instruction and any of the aforemen-
tioned instructions. Dynamic C versions 6.57 and later will automatically compensate for the bug. This bug
is not present in the Rabbit 3000.
Examples
The following instruction loads the contents of A into the internal I/O register at address location 030h:
IOI LD (030h), A
These next instructions read a word from external I/O address 0A002:
LD IX, 0A000h
IOE LD HL, (IX+2)
IOE
IOI
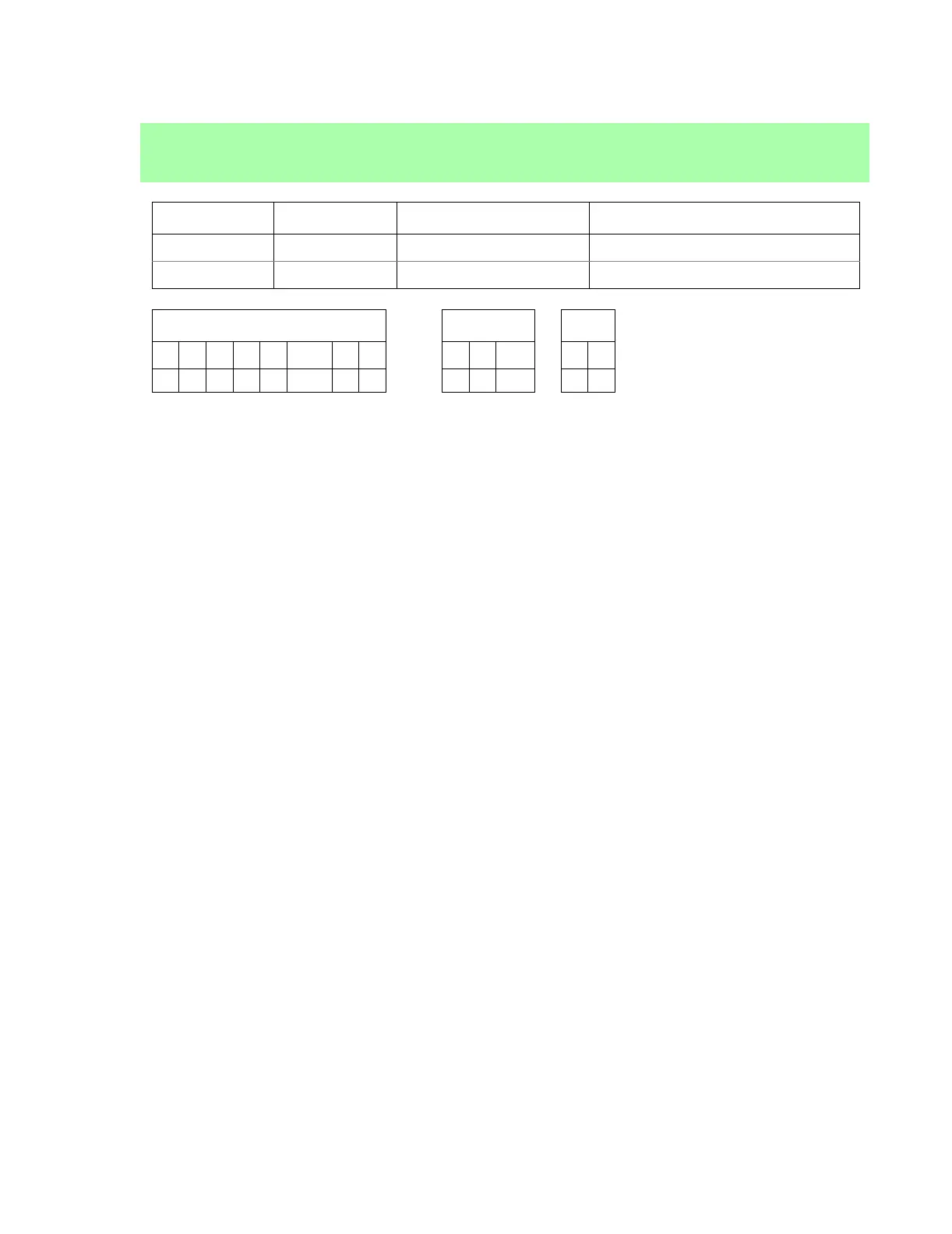
Opcode Instruction Clocks Operation
DB IOE 2 I/O external prefix
D3 IOI 2 I/O internal prefix
Flags ALTD I/O
S Z L/V C F R SP S D
- - - -
ADC A,(HL)
ADD A,(HL)
AND (HL)
CP (HL)
OR (HL)
SBC A,(HL)
SUB (HL)
XOR (HL)
DEC (HL)
INC (HL)
LD r,(HL)
LD (HL),r
 Loading...
Loading...