SAMLEX AMERICA INC. | 23
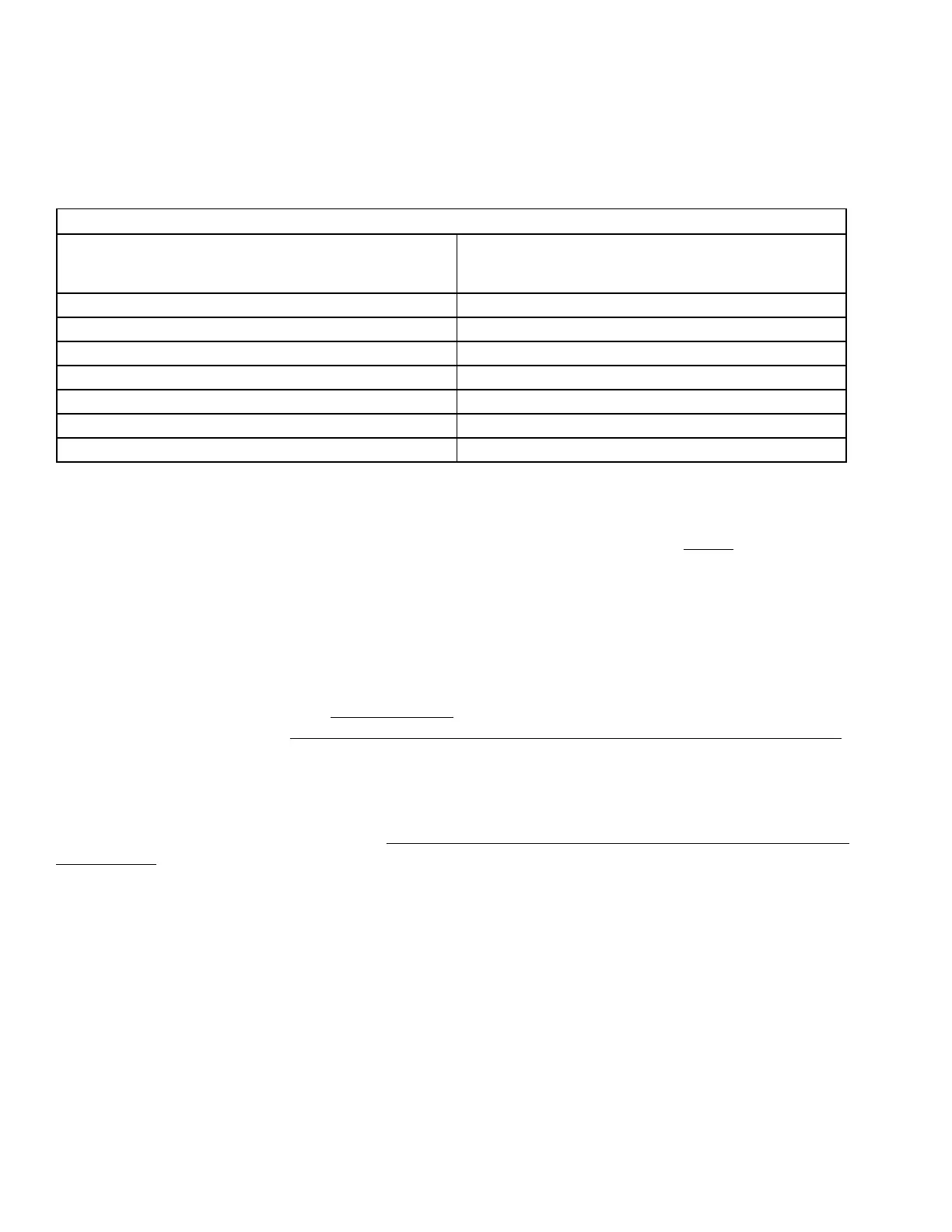
1.4.10.4 Table 1.4.2 gives some examples of typical C-rates of Discharge and applications:
TABLE 1.4.2 TYPICAL “C-rates” OF DISCHARGE
C-rate of Discharge
(Column 1)
Examples of C-rate of Discharge
for 100 Ah capacity battery
(Column 2)
2C 200A
1C 100A
C/5 or 0.2C (Inverter application) 20A
C/8 or 0.125C (UPS application) 12.5A
C/10 or 0.1C (Telecom application) 10A
C/20 or 0.05C (Automotive application) 5A
C/100 or 0.01C 1A
1.4.11 Charge / Discharge Curves to Determine State of Charge of Lead Acid Battery Based on its
Terminal Voltage and C-rates of Charge / Discharge
1.4.11.1 Fig 1.4.1 shows examples of State of Charge / Discharge Curves for different C-rates for typical 12V / 24V
Lead Acid Battery at 80°F / 26.7°C. These curves are used to determine the State of Charge / Discharge of the battery
based on its terminal voltage.
The Y-Axis shows the terminal voltage of the battery. The X-Axis shows % State of Charge. % State of Discharge can
be converted to % State of Charge using formula:
• % State of Charge = (100% -% State of Discharge) e.g. 80% State of Discharge = 100%-80% = 20% State of Charge
1.4.11.2 Example of Determining State of Charge (using Fig 1.4.1) when Charging 12V, 100Ah Battery at
C-rate of 0.1C or C/10 or 10A: Refer to Charge Curve marked C\10 of the upper 4 curves marked “CHARGE”. States
of Charge at different battery terminal voltages will be: (a) At 5.3V = 100% charged; (b) At 14.3V = 90% charged; (c)
At 13.5V = 70% charged; (d) At 12.5V = 15% charged
1.4.11.3 Example of Determining State of Discharge (using Fig 1.4.1) when Discharging 12V, 100Ah
Battery at C-rate of 0.33C or C/3 or 33.3A: Refer to Charge Curve marked C\3 of the lower 4 curves marked
“DISCHARGE”. States of Discharge at different battery terminal voltages will be: [a] At 9.5V = 100% discharged (0%
charged); [b] At 10.4V = 80% discharged (20% charged): [c] At 11.5V = 28% discharged (72% charged) and [d]
11.75V = 0% discharged (100% charged)
SECTION 1.4 | General Information – Battery Related
 Loading...
Loading...