Clocks
12/29 AN2586 Rev 8
3 Clocks
Three different clock sources can be used to drive the system clock (SYSCLK):
• HSI oscillator clock (high-speed internal clock signal)
• HSE oscillator clock (high-speed external clock signal)
• PLL clock
The devices have two secondary clock sources:
• 40 kHz low-speed internal RC (LSI RC), driving the independent watchdog and,
optionally, the RTC used for Auto-wakeup from the Stop/Standby modes.
• 32.768 kHz low-speed external crystal (LSE crystal), optionally driving the real-time
clock (RTCCLK)
Each clock source can be switched on or off independently when it is not used, to optimize
the power consumption.
Refer to the reference manuals for the description of the clock tree:
• RM0008 for STM32F101xx, STM32F102xx, STM32F103xx and STM32F105xx/107xx
microcontrollers
• RM0041 for STM32F100xx value line microcontrollers
3.1 HSE OSC clock
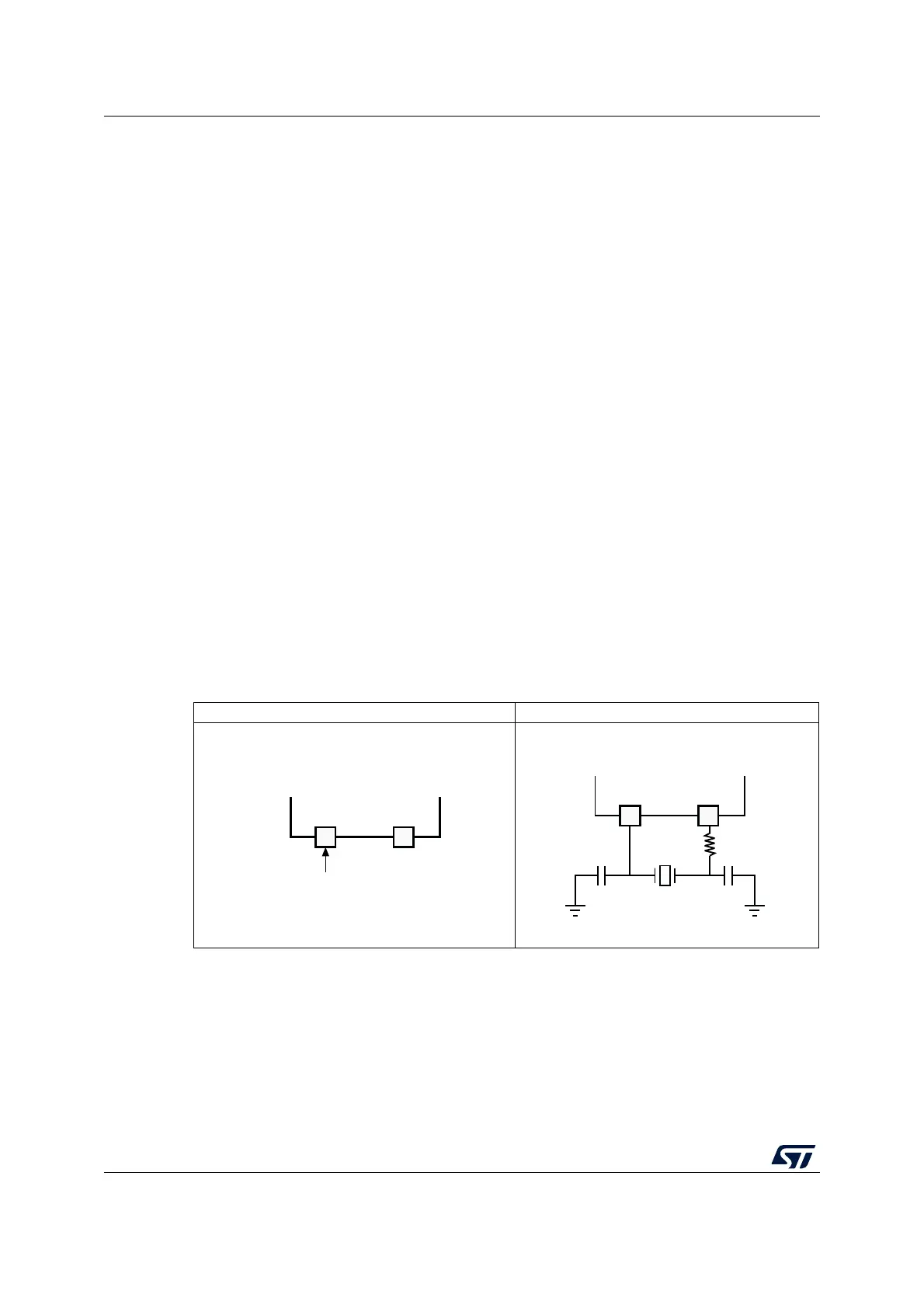
The high-speed external clock signal (HSE) can be generated from two clock sources:
• HSE external crystal/ceramic resonator (see Figure 7)
• HSE user external clock (see Figure 6)
1. The value of R
EXT
depends upon the crystal characteristics. Typical value is in the range of 5 to 6 R
S
(resonator series resistance).
2. Load capacitance C
L
has the following formula: C
L
= C
L1
x C
L2
/ (C
L1
+ C
L2
) + C
stray
, where: C
stray
is the
pin capacitance and board or trace PCB-related capacitance. Typically, it is between 2 and 7 pF. Refer to
Section 6 to minimize its value.
Figure 6. External clock Figure 7. Crystal/ceramic resonators
OSC_OUTOSC_IN
External source
(Hi-Z)
ai14369
Hardware configuration
OSC_OUTOSC_IN
ai14370
STM32F10xxx
R
EXT
(1)
C
L1
C
L2
Hardware configuration

 Loading...
Loading...