9
1. Introduction
1-7-3. Directory structure of media
The directory structure of each medium is as follows.
WXDAT
1
TEST0001
2
Aaaaa001.dat
3
Aaaaa001.hdr
3
(Aaaaa001.wav)
TEST0002
Bbbbb001.dat
Aaaaa002.hdr
Aaaaa002.dat
1
WXDAT
This directory is made automatically when the medium is
formatted. When the medium is inserted in an WX-7000, this
directory is made automatically if it does not already exist.
2
TEST0001
Name of the directory entered in DIRECTORY, which is in the
dialog box displayed by choosing FILE and then RECORDING
FILE.
3
Aaaaa001.dat
Aaaaa001.hdr
Aaaaa001.wav
Data, header and voice memo files (if voice memos were
recorded) created for a single ID
1-7-4. Data file
16-bit data converted from analog to digital is recorded as 2-byte
integer values from –32768 to +32767 while 24-bit converted data
is recorded as 4-byte integer values from –8388608 to +8388607.
Negative numbers are shown using two’s-complement notation.
The byte order is from the lowest to the highest (Intel format).
The data order is from the first sampling channel to the second sam-
pling channel and so on until the last sampling channel. This order is
called the INTERLACED format, and the format name is recorded in
STORAGE_MODE in the header file.
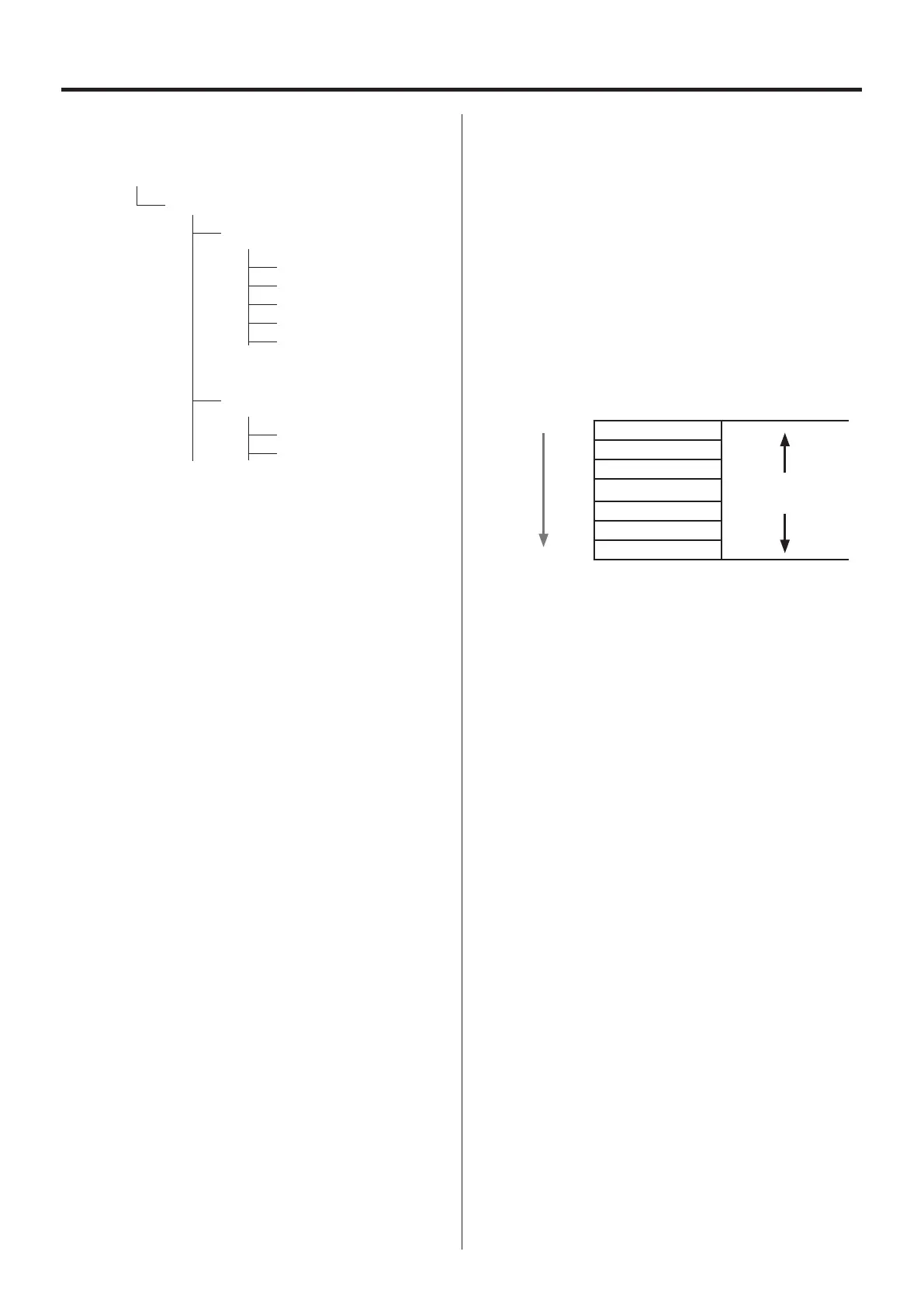
The structure of a data file is as follows. In this document, a collec-
tion of data as shown in the example is called a “scan”. A data file is
made of repeated scans.
Example of data for one scan recorded at 6 kHz sampling frequency
Data order
ch1
ch2
ch3
:
1/6000
ch14
ch15
ch16
1-7-5. Converting data to physical quantities
16-bit data converted from analog to digital is recorded as integer
values from –32768 to +32767 and the value would be ±25000
when the input is ±100% in the input range settings. 24-bit
converted data is recorded as integer values from –8388608 to
+8388607 and the value would be ±6400000 when the input is
±100% in the input range settings.
The input value is obtained from the following formula:
Input value = (A/D conversion value of the data file) × SLOPE +
Y_OFFSET
o See “Explanations of header file” on page 11 for information
about SLOPE and Y_OFFSET.

 Loading...
Loading...