Specifications
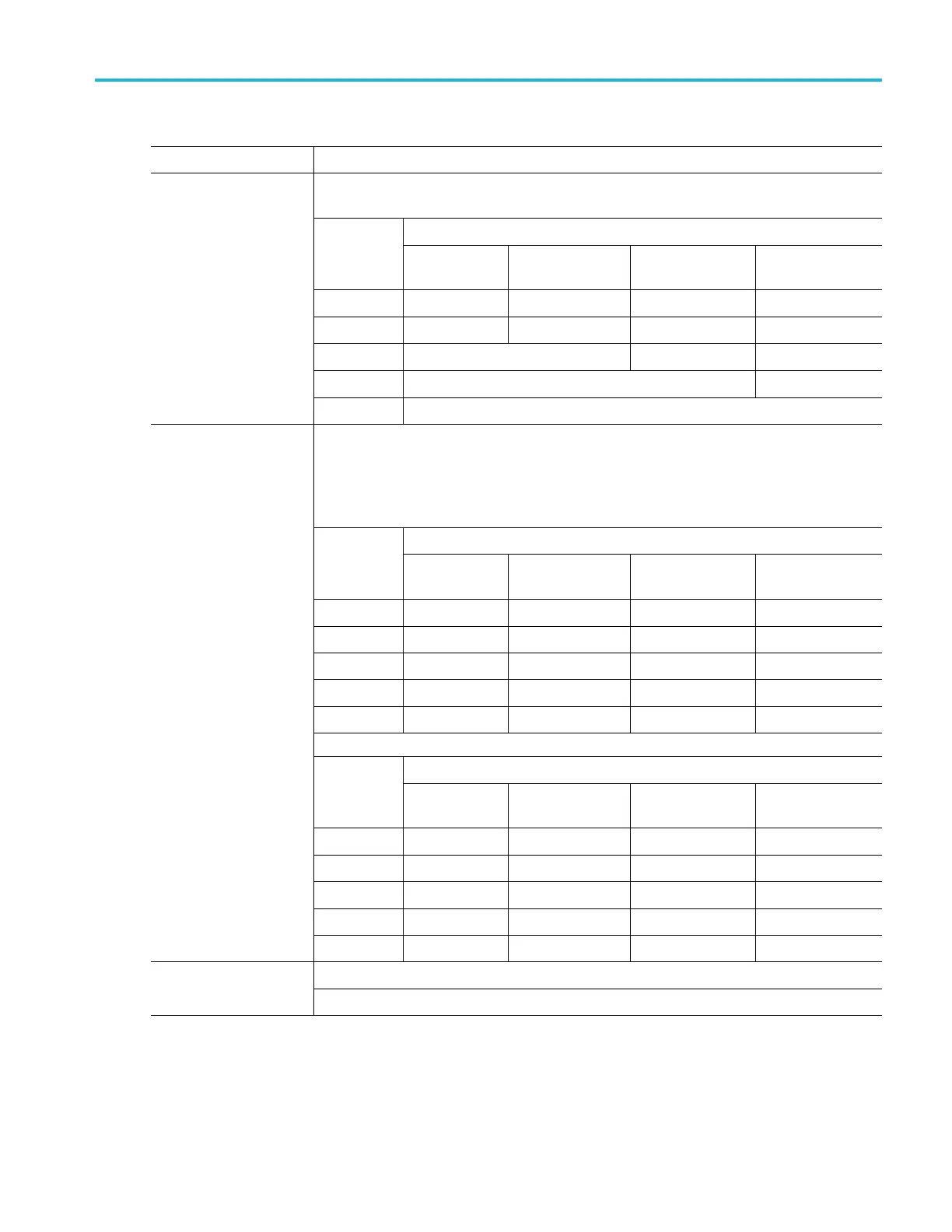
Table 1: Analog channel input and vertical specifications (cont.)
Characteristic Description
The limits stated below are for ambient temperature of 30 °C and the bandwidth selection set to
FULL. Reduce the upper bandwidth frequency by 1% for each °C above 30 °C.
Vertical Scale Setting
Instrument
Bandwidth
100 mV/div to
100 V/div
50 mV/div to
99.8 mV/div
20 mV/div to
49.8 mV/div
10 mV/div to
19.9 mV/div
1 GHz DC to 1.00 GHz DC to 400 MHz DC to 250 MHz DC to 150 MHz
500 MHz
DC to 500 MHz DC to 400 MHz DC to 250 MHz DC to 150 MHz
350 MHz
DC to 350 MHz DC to 250 MHz DC to 150 MHz
200 MHz
DC to 200 MHz DC to 150 MHz
Analog Bandwidth, 1 M
with Standard Probe,
typical
100 MHz
DC to 100 MHz
The formula is calculated by measuring –3 dB bandwidth of the oscilloscope. The formula accounts
for the rise time contribution of the oscilloscope independent of the rise time of the signal source.
All values in the above table are in pS. 1 GHz BW models assume the TPP1000 probe. 500 MHz
and 350 MHz models assume the TPP0500B probe. 200 MHz and 100 MHz models assume
the TPP0250 probe.
Vertical Scale Setting (50 )
Instrument
Bandwidth
1 mV/div to
1.99 mV/div
2 mV/div to
4.98 mV/div
5mV/divto
9.98 mV/div
10 mV/div to 1 V/div
1GHz
2,666 ps 1,333 ps 800 ps 400 ps
500 MHz 2,666 ps 1,333 ps 800 ps 800 ps
350 MHz 2,666 ps 1,333 ps 1,143 ps 1,143 ps
200 MHz 2,666 ps 2,000 ps 2,000 ps 2,000 ps
100 MHz 4,000 ps 4,000 ps 4,000 ps 4,000 ps
Vertical Scale Setting (TPPXXX0 probe)
Instrument
Bandwidth
10 mV to
19.9 mV
20 mV to 49.8 m V 50 mV to 99.8 mV 100 mV to 100 V
1GHz
2,666 ps 1,600 ps 1,000 ps 400 ps
500 MHz 2,666 ps 1,600 ps 1,000 ps 800 ps
350 MHz 2,666 ps 1,600 ps 1,143 ps 1,143 ps
200 MHz 2,666 ps 2,000 ps 2,000 ps 2,000 ps
Calculated rise time,
typical
100 MHz 4,000 ps 4,000 ps 4,000 ps 4,000 ps
For instruments with 1 GHz, 500 MHz or 350 MHz analog bandwidth: 20 MHz, 250 MHz, and Full
Analog bandwidth limit
filter selections
For instruments with 200 MHz and 100 MHz analog bandwidth: 20 MHz and Full
MDO3000 Series S pecifications and Performance Verification 5
 Loading...
Loading...