Network Operation
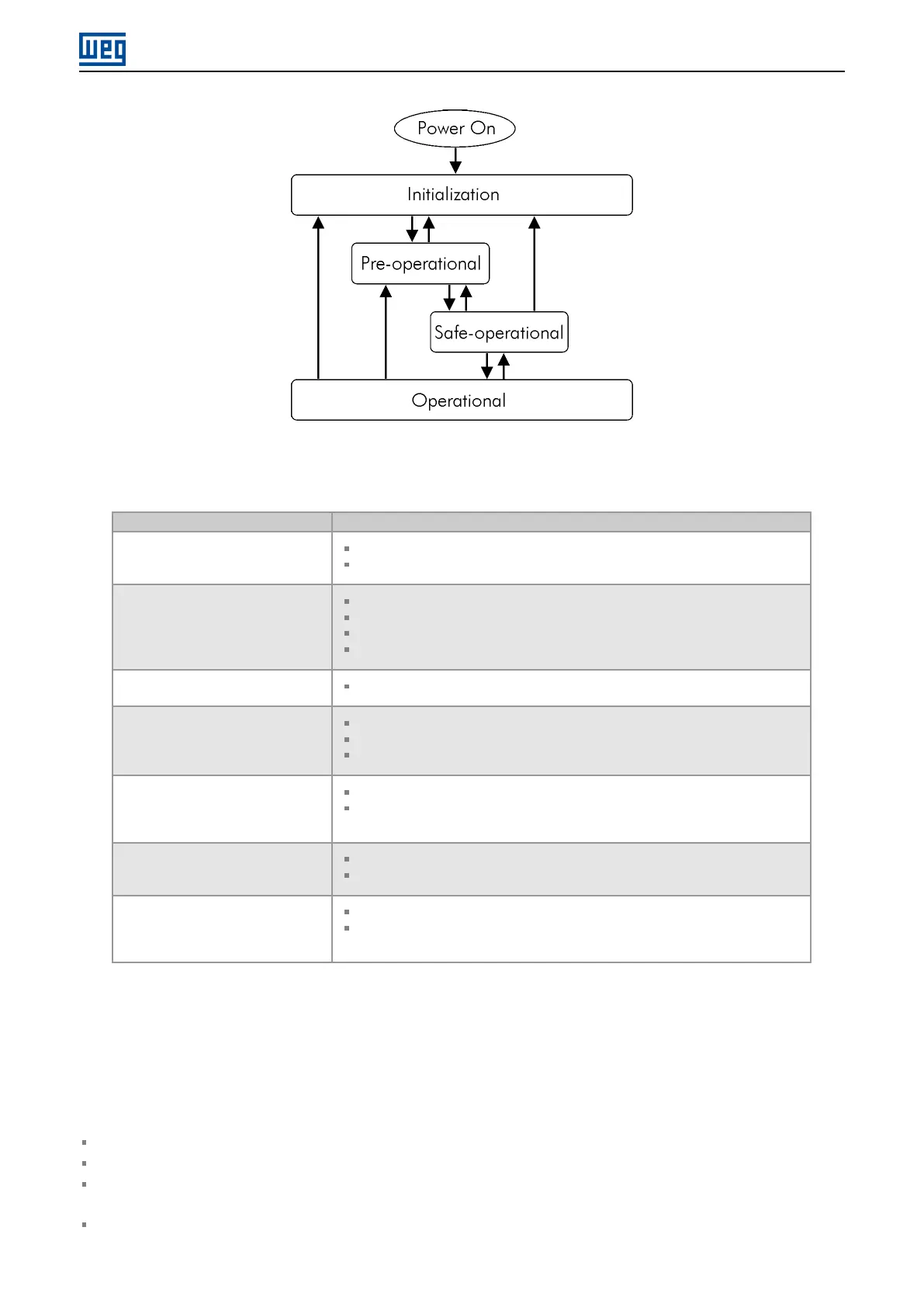
Figure 6.2: EtherCAT state machine
Table 6.1: States and transitions for EtherCAT state machine
State / Transition Description
Initialization
Standard state after initialization.
Mailbox communication or process data exchange is not allowed.
Initialization → Pre-operational
Master configures logical address for slave.
Master configures mailbox Sync Manager.
Master initiates synchronizations with slaves (Distributed Clock).
Master requests pre-operational state.
Pre-operational
Mailbox communication is possible, but no process data communication.
Pre-operational → Safe-operational
Master configures Sync Manager and FMMU for process data.
Master sends commands via SDO for slave configuration, including PDO mapping.
Master requests safe-operational state.
Safe-operational
Mailbox communication is possible.
Slave sends input process data to master, but output data from master to slave
remains with initial values.
Safe-operational → Operational
Master sends valid output values.
Master requests operational state.
Operational
Mailbox communication is possible.
Process data communication (inputs and outputs) is possible, according to PDO
mapping.
6.3 SYNC MANAGERS
Sync Managers are responsible for controlling access to data sent and received over the network, and ensure data
consistency. There are 4 Sync Managers, each one responsible for managing a different data type:
Sync Manager 0: responsible for writing mailbox data.
Sync Manager 1: responsible for reading mailbox data.
Sync Manager 2: control access to RxPDO data. Object 1C12h is used to indicate which RxPDO this Sync
Manager is associated with.
Sync Manager 3: control access to TxPDO data. Object 1C13h is used to indicate which TxPDO this Sync
Manager is associated with.
CFW11 | 22
 Loading...
Loading...