45
4. Contamination due to dirt entering the engine through the atmospheric air and
bad fuel.
5. Other additive depletion due to reaction which will affect the performance of oil.
The engine oil becomes inefcient after the recommend hours. Hence, it is
necessary to replace.
6.1.5 Oil performance classication system
Following are the organizations designing and approving oil classication and
specication standards.
API (American Petroleum Institute)
ACEA (Association des Constructeurs Europeans d’Automobiles - European)
ASTM (American Society for Testing Materials)
JASO (Japanese Automobile Standards Organization)
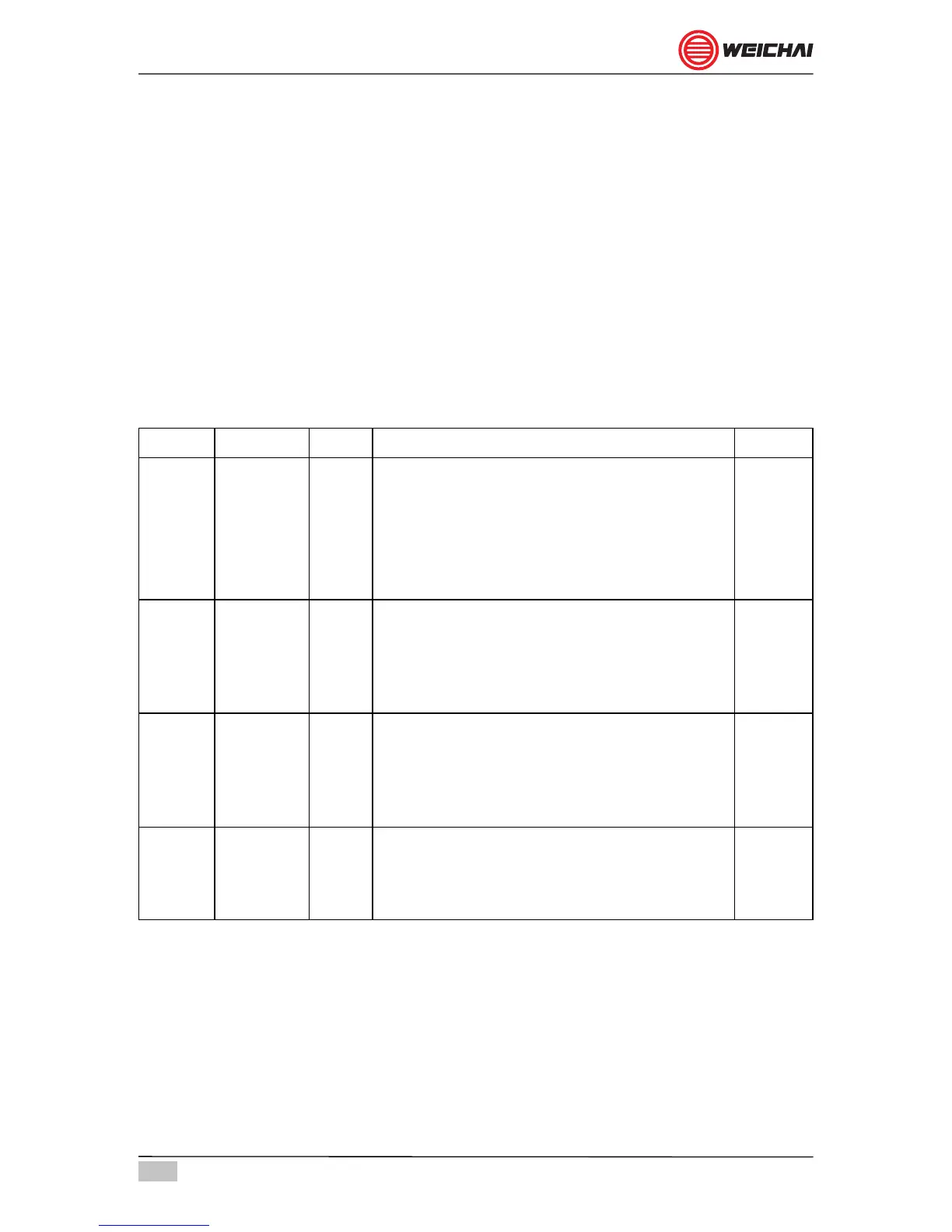
Sr. No Category Year Service Status
1 CJ-4 2006
For high speed, four stroke engines to meet
2007 emission standards. Use diesel fuels
ranging in sulphur content up to 500 ppm
(0.05% by weight Current). DPF and other
emission device compatible. API CJ-4 oils
are backward compatible.
2 CI-4 2002
For high-speed 4 stroke engines to meet
exhaust emission standards implemented
in 2002. EGR and diesel fuels sulphur up to
0.5%. Can be used in place of CD, CF, CF-4
and CH-4 oils.
Current
3 CH-4 1996
For high-speed, four stroke engines
designed to meet 1998 exhaust emission
standards. Diesel fuels sulphur content up to
0.5% weight. Can be used in place of CD,
CE, CF-4, and CG-4 oils.
Current
4 CF 1994
For off-load, indirect injected and other diesel
engines including those using fuel with over
0.5% sulphur. Can be used in place of CD
oils.
Current
Table 6.1
6.1.6 SAE viscosity recommendations
The viscosity of oil is a measure of its resistance to ow. The Society of Auto-
motive Engineers has classied engine oils in viscosity grades:
• Oils that meet the low temperature [0°F (-18°C)] requirement, carry a grade
designation with a “W” sufx.
• Oils that meet both the low and high temperature requirements are referred to
as multi grade or multi viscosity grade oils.

 Loading...
Loading...