BATTERY
CHARGING
CIRCUIT
INTEGRAL
CONTROLLER
(l.C.)
The Integral Controller (l.C.) is
an
encapsulated, solid-state
unit that supplies a
DC
charging voltage to the generator's
starting battery
while
the generator
is
opening.
Charging Voltage:
~.o
. 14.0 volts DC
Charging Amperage: 0 • 10.0 amps
DC
A separate
group
of stator
windings
supplies AC
voltage
to
a
bridge rectifier
which
converts the
AC
current
to
supply
the
I.C.
unit.
The
I.C.
unit senses the
needs
of
the starting battery
and supplies a DC charge
when
one is needed
..
If
you
.suspect
that the I.C. unit is
faulty
(that is,
if
the battery's
charge
is
low),
check the
charging
circuit
and
it's components
as
described
in
the
following
steps. Check all connections for
cleanliness and tightness including the ground before
replacing
the
r.c.
unit.
NOTE:
When
the
generator is first
started,
the l
C.
unit
will
produce a low
charging
rate.
'This
charging
rate will
rise
as
the
generator is
operated.
·
The Integral Controller
is
mounted inside the generator
hous-
ing
in the 12:00
position.
There
is
a voltage output
adjustment
on
the
controller that will allow a DC voltage output
adjust-
ment
of±
2
volts.
NOTE:
New
four
wire
controllers eliminate the ballast resistor
circuit
since the ballast resistor's
function
is
now
handled
·
internally.
Whenever
replacing
an
early stylr controller with
the
~wer
four
wire
model,
remove
the ballast resistor
and
its
wiring.
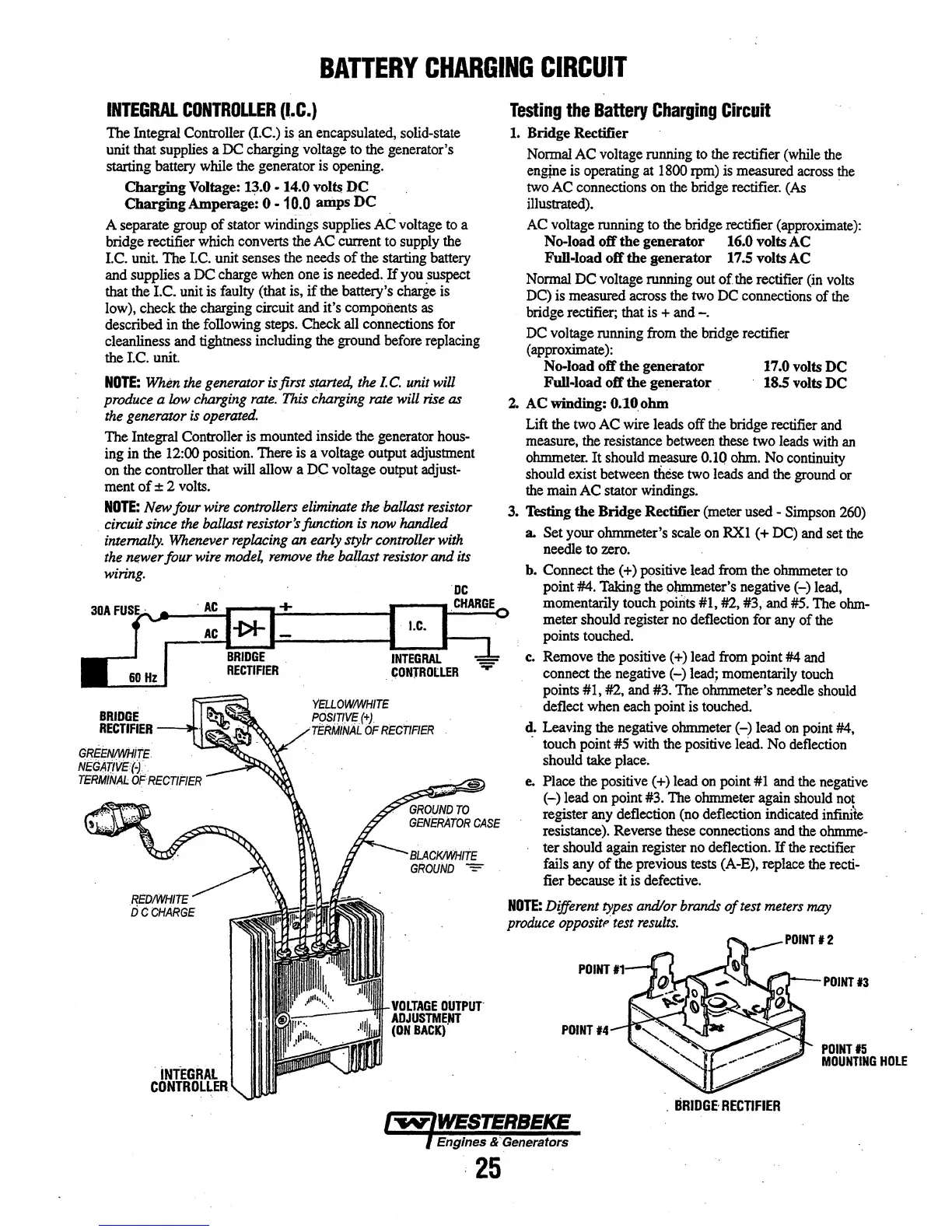
BRIDGE
RECTIFIER
--*~
GREEN!MlitE.
NEGATIVE({.
TERMINAL
oFRECTIFIER
BRIDGE
RECTIFIER
.
iNTEGRAL
CONTROLLER
INTEGRAL
.
CONTROLLER
YELLOW/WHITE
~~W~l°6F
RECTIFIER
Testing
the
Battery
Charging
Circuit
1.
Bridge Rectifier
Normal
AC
voltage
running
to
the
rectifier
(while
the
engine is operating at
1800
zpm)
is
measured
across
the
two
AC
connections
on
the
bridge
rectifier. (As
illustrated).
AC
voltage
running
to
the
bridge
rectifier
(approximate):
No-load off the generator 16.0 volts AC
Full-load off the generator
17.S
volts AC
Normal
DC voltage
running
out of.the rectifier
(in
volts
DC)
is measured across
the
two
DC
connections
of
the
bridge
rectifier; that is + and
-.
DC
voltage running
from
the
bridge
rectifier
(approximate):
No-load off the generator 17.0 volts DC
Full-load off the generator . · 18.5 volts DC
2. AC winding: 0.10.obm
Lift the
two
AC
wire leads off
the
bridge rectifier
and
measure,
the resistance
between
these
two
leads
with
an
ohmmeter.
It
should
measure
0.10
ohm.
No
continuity
should exist
between
these
two
leads
and the
ground
or
the
main
AC stator
windings.
3.
Testing the Bridge Rectifier (meter
used
-
Simpson
260)
a. Set your ohmmeter's scale
on
RXl (+DC)
and
set
the
needle
to
z.ero.
b. Connect
the
(
+)
positive lead
from
the
ohmmeter
to
point
#4.
Taking
the
ob:mmeter's
negative (-)
lead,
momentarily touch
poirits
#1,
#2,
#3,
and
#5. The
ohm-
meter should register
no
deflection for
any
of the
points
touched.
c.
Remove
the
positive ( +) lead
from
point #4
and
connect
the
negative(-)
lead;
momentarily
touch
points
#1,
#2,
and
#3.
The
ohmmeter's
needle
should
deflect
when
each
point
is
touched.
d.
Leaving
the
negative ohmmeter (-) lead
on
point
#4,
·
touch
point
#S
with
the positive
lead.
No
deflection
should take place.
e.
Place
the
positive ( +)
lead
on
point
#1
and
the
negative
(-) lead
on
point #3.
The
ohmmeter
again
should
not
register
any
deflection
{no
deflection
indicated
infinite
resistance). Reverse
these
connections
and
the
ohmme-
ter should
again
register
no
deflection.
If
the
rectifier
fails
any of the previous
tests
(A-E),
replace
the
recti-
fier because it
is
defective.
NOTE:
Different types and/or
brands
of
test
meters
may
produce
oppositf'.
test
results.
POINTl4
.
BRIDGE
RECTIFIER
POINTl3
POINTl5
MOUNTING
HOLE
Engines &·Generators
;
25

 Loading...
Loading...