(homing high speed). After encountering the rising edge of the Z signal, it decelerates and reverses
according to the set value of P9-14 (homing acceleration and deceleration time), accelerates to P9-13
(homing low speed) and searches for the Z signal at low speed in forward direction. Next, the homing
action is divided into two cases:
(a1) Mechanical offset (P9-19, P9-20) is 0:
In the process of forward acceleration or forward constant speed operation, stop immediately when
encountering the rising edge of the other side of the motor Z signal.
(a2) Mechanical offset (P9-19, P9-20) is not 0:
In the process of positive acceleration or positive constant speed operation, stop the machine
immediately when encountering the rising edge on the other side of the motor Z signal. After the motor
is completely stopped, the motor will walk a quantitative pulse (P9-19, P9-20) at the speed set by P9-12
(homing high speed) according to the set number and direction of mechanical offset pulses (either
positive direction or negative direction), then the motor stops.
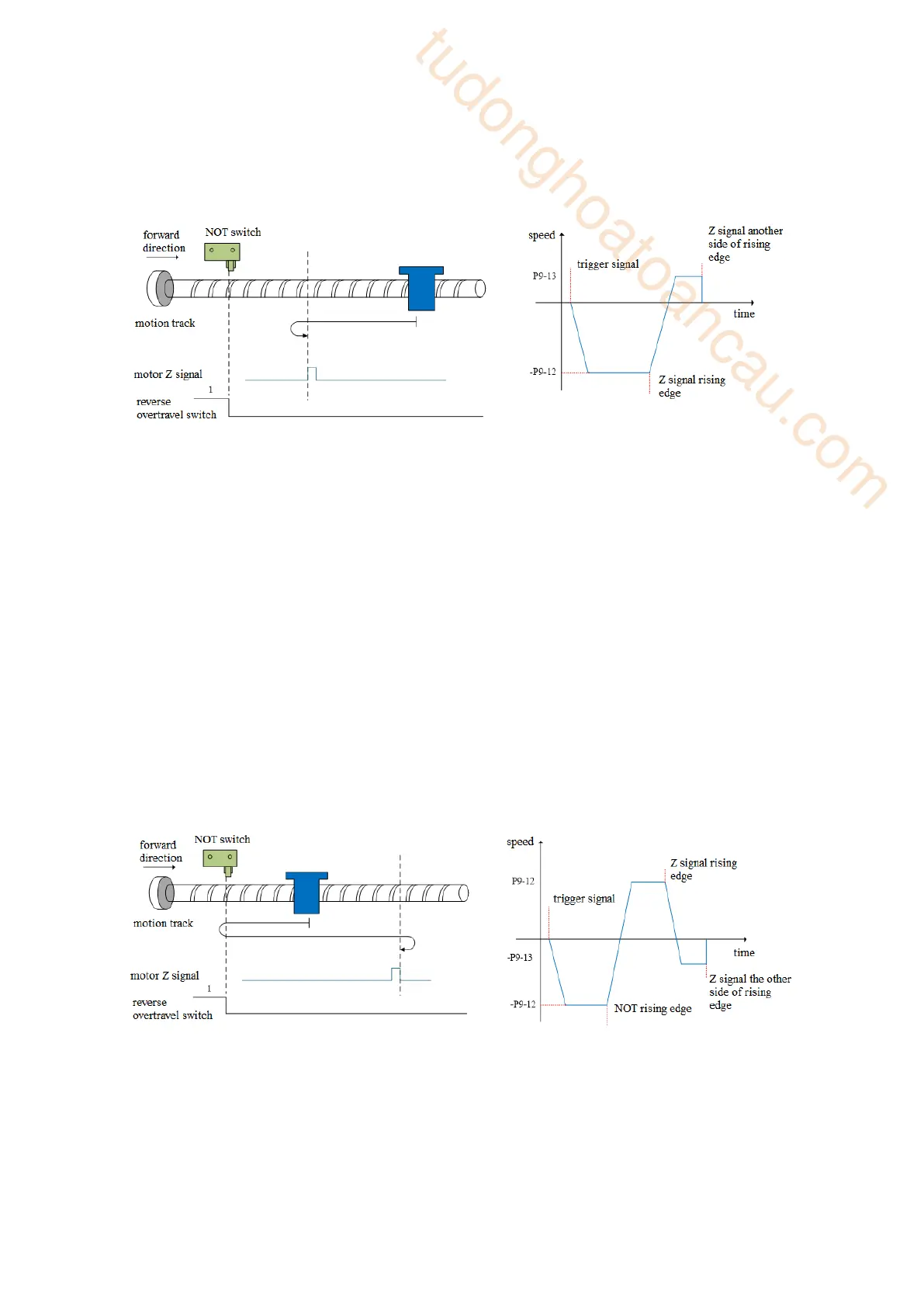
(b) When the motor starts to move, the Z signal is invalid or valid (P5-64 = 0-invalid, 1-valid), and
the reverse overtravel switch is triggered in the process (NOT)
The servo motor searches for the Z signal at high speed -P9-12 (homing high speed) in reverse
direction. After encountering the reverse overtravel switch, the driver decelerates and reverses
according to P9-14, and then searches for the Z signal at high speed P9-12 (homing high speed) in
forward direction until encountering the rising edge of the Z signal, and gradually decelerates and
reverses (i.e. restores the reverse direction) according to the set value of P9-14 (homing acceleration
and deceleration time). The servo motor searches the rising edge on the other side of the Z signal at low
speed -P9-13 (homing low speed) in reverse direction. Next, the homing action is divided into two
cases:
(b1) Mechanical offset (P9-19, P9-20) is 0:
In the process of reverse acceleration or reverse constant speed operation, stop immediately when
encountering the rising edge of the other side of the Z signal.
(b2) Mechanical offset (P9-19, P9-20) is not 0:
In the process of reverse acceleration or reverse constant speed operation, stop immediately when
encountering the rising edge on the other side of the motor Z signal. After the motor is completely
stopped, the motor will walk a quantitative pulse (P9-19, P9-20) at the speed set by P9-12 (homing
high speed) according to the set number and direction of mechanical offset pulses (either positive
direction or negative direction), then the motor stops.
5. Homing mode 4——forward homing, deceleration point and origin are forward

 Loading...
Loading...











