What is STP? 37
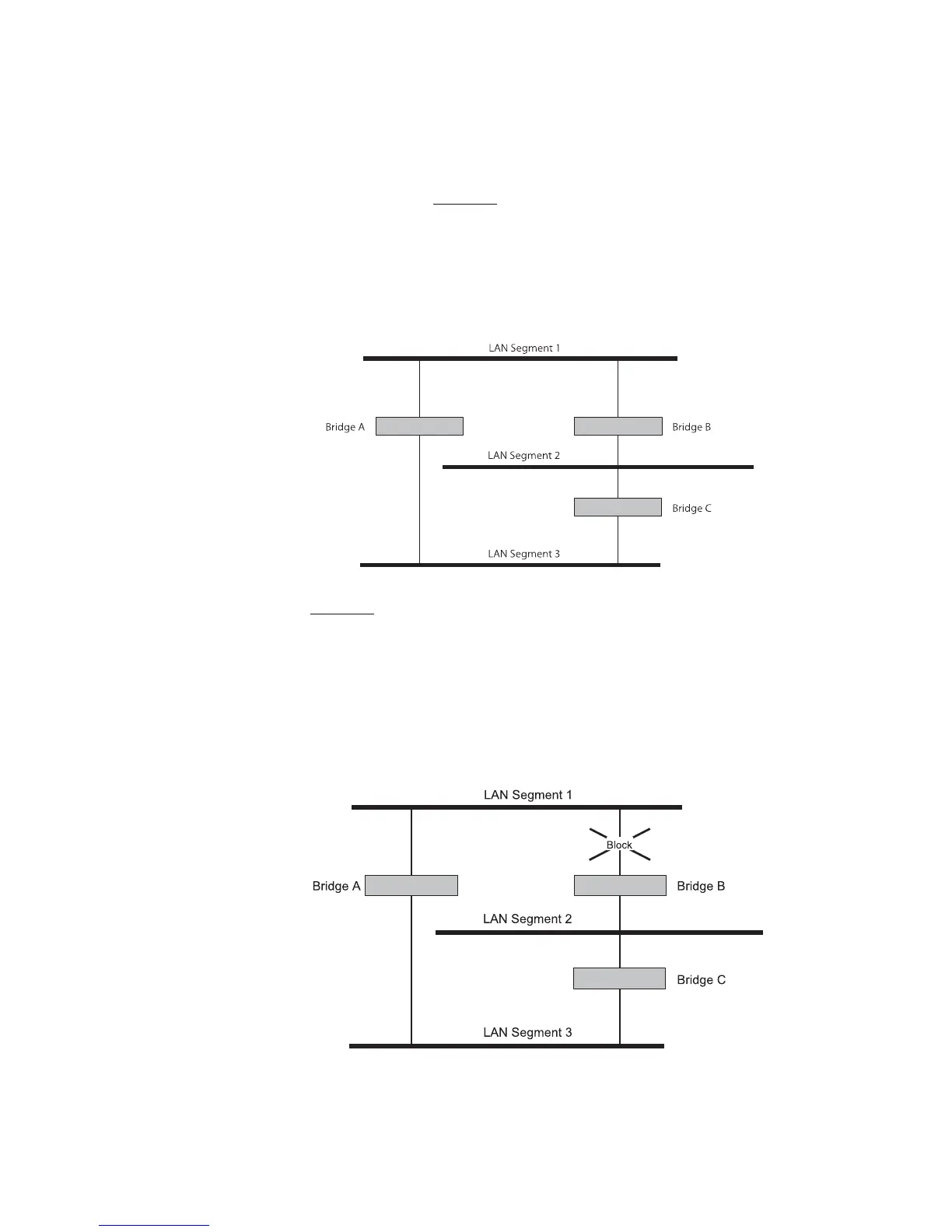
As an example, Figure 5 shows a network containing three LAN segments
separated by three bridges. With this configuration, each segment can
communicate with the others using two paths. Without STP enabled, this
configuration creates loops that cause the network to overload.
Figure 5 A network configuration that creates loops
Figure 6 shows the result of enabling STP on the bridges in the
configuration. STP detects the duplicate paths and prevents, or blocks,
one of them from forwarding traffic, so this configuration will work
satisfactorily. STP has determined that traffic from LAN segment 2 to LAN
segment 1 can only flow through Bridges C and A, because, for example,
this path has a greater bandwidth and is therefore more efficient.
Figure 6 Traffic flowing through Bridges C and A
 Loading...
Loading...











