IP Routing Concepts 85
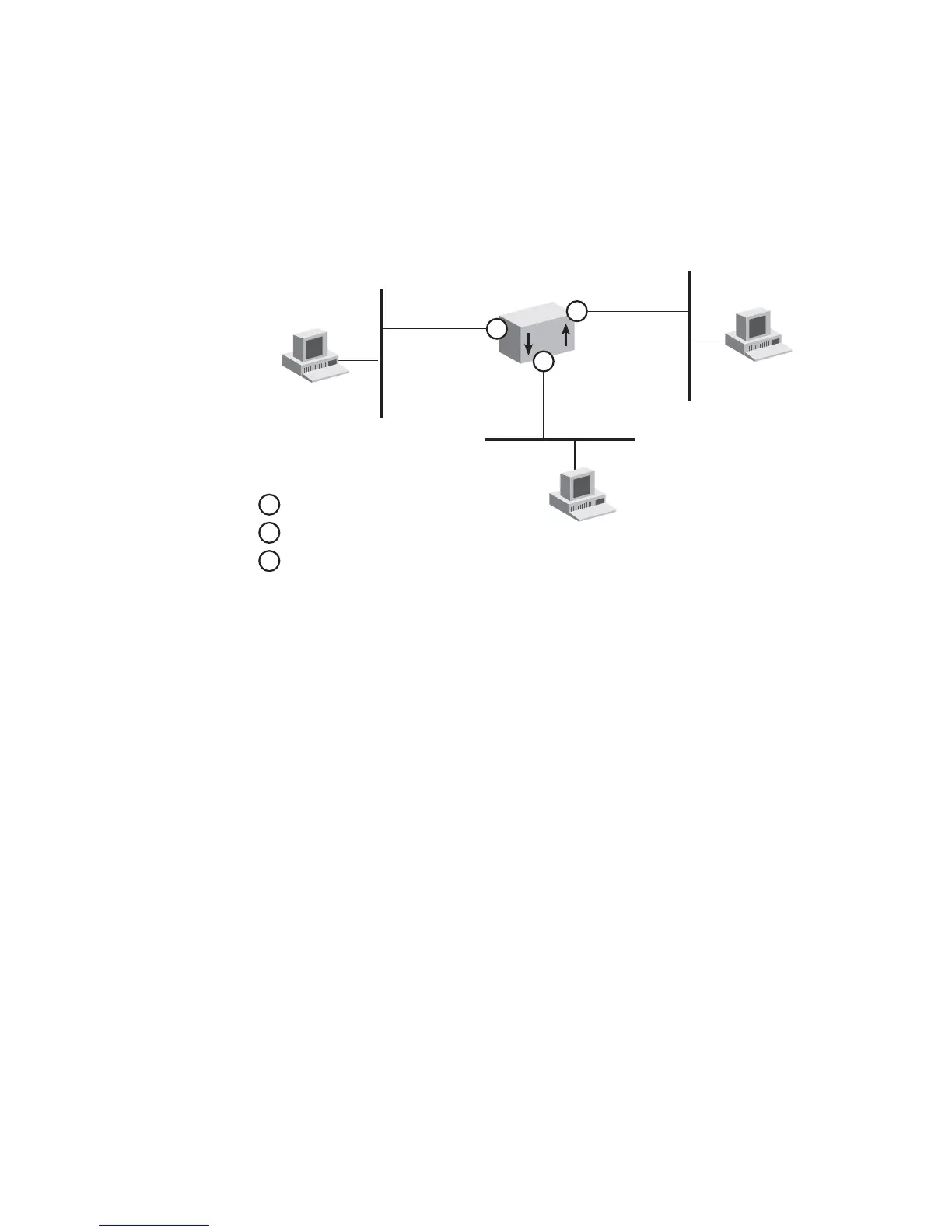
Figure 23 Routing Interfaces
Routing Tables With a routing table, a router or host determines how to send a packet
toward its ultimate destination. The routing table contains an entry for
every learned and locally defined network. The size of the routing table is
dynamic and can hold at most 2000 entries.
A router or host uses the routing table when the destination IP address of
the packet is not on a network or subnetwork to which it is directly
connected. The routing table provides the IP address of a router that can
forward the packet toward its destination.
The routing table consists of the following elements:
■ Destination IP address — The destination network, subnetwork, or
host.
■ Subnet mask — The subnet mask for the destination network.
■ Metric — A measure of the distance to the destination. In the Routing
Information Protocol (RIP), the metric is the number of hops through
routers.
■ Gateway — The IP address of the router interface through which the
packet travels on its next hop.
■ Status — Information that the routing protocol has about the route,
such as how the route was put into the routing table.
L3
158.101.1.2
Network 1
158.101.1.1
158.101.2.2
Network 2
158.101.3.2
Network 3
158.101.2.1
158.101.3.1
Router
1
2
3
= Interface 1
= Interface 2
= Interface 3
1
2
3
 Loading...
Loading...











