Advanced IP Routing Options 97
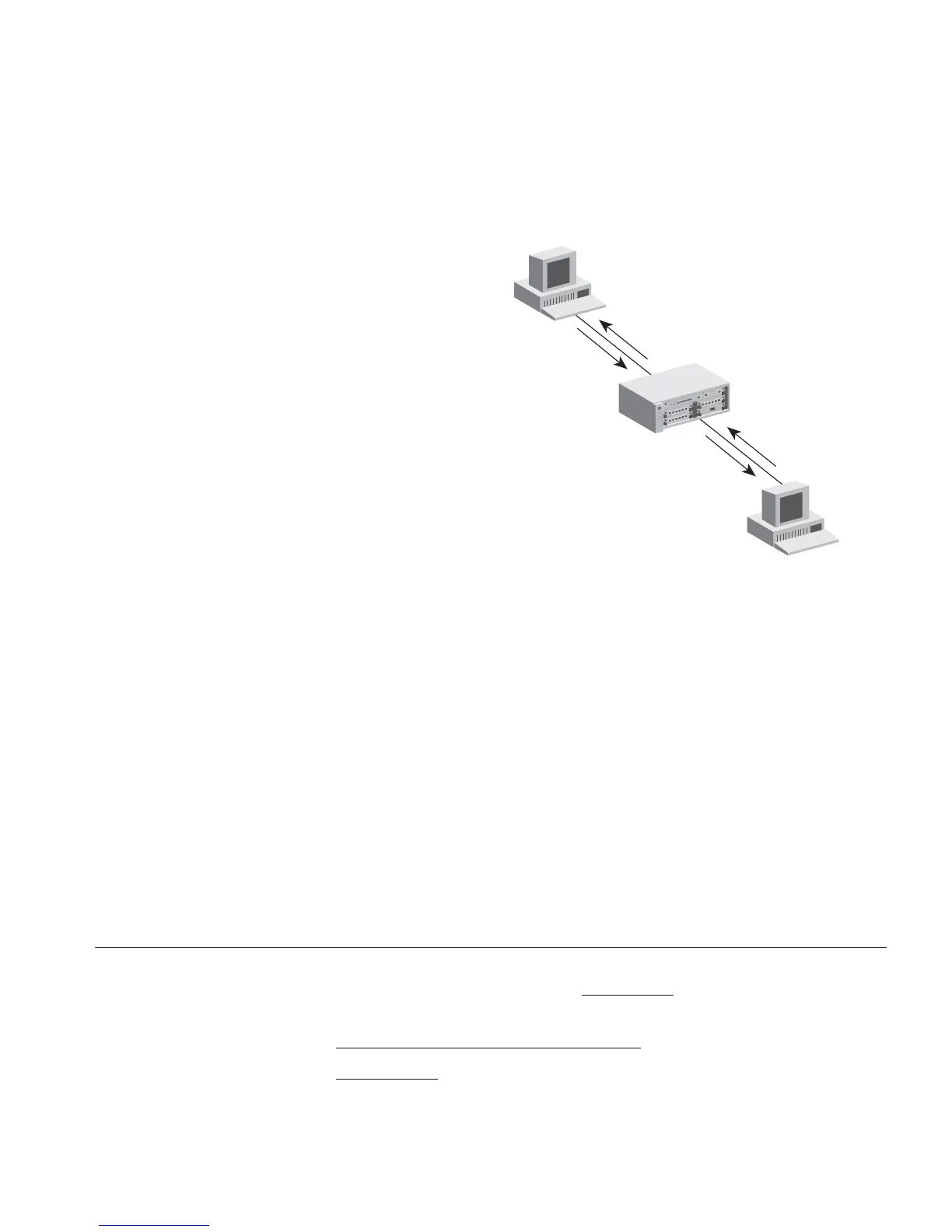
Figure 28 ARP Proxy
Internet Control
Message Protocol
(ICMP)
Because a router knows only about the next network hop, it is not aware
of problems that may be closer to the destination. Destinations may be
unreachable if:
■ Hardware is temporarily out of service.
■ You specified a nonexistent destination address.
■ The routers do not have a route to the destination network.
To help routers and hosts discover problems in packet transmission, a
mechanism called Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) reports
errors back to the source when routing problems occur. With ICMP, you
can determine whether a delivery failure resulted from a local or a remote
problem.
Advanced IP
Routing Options
Your Switch has several features which further extend the networking
capabilities of the device. Refer to Appendix D
for more information on
the following:
■ Variable Length Subnet Masks (VLSMs)
■ Supernetting
Server A
Server B
158.101.1.2
(255.255.0.0)
158.101.2.1
(255.255.0.0)
158.101.2.2
(255.255.0.0)
With Proxy ARP enabled
the MAC address of Server B
is returned to Server A because
the subnetworks are transparent
With proxy ARP enabled the
MAC address for the switch
is returned to Server A when
it ARP's for the IP address of
Server B

 Loading...
Loading...











