Select the specific VAP profile (in this case, “RF Card A : VAP-1”). The basic settings of the VAP are
collected in the profile as follows:
VAP: Disable or Enable this VAP.
Profile Name: Name of the VAP profile for identity / management purposes.
ESSID: Extended Service Set Identifier (ESSID) serves as an identifier for clients to associate
with the specific VAP.
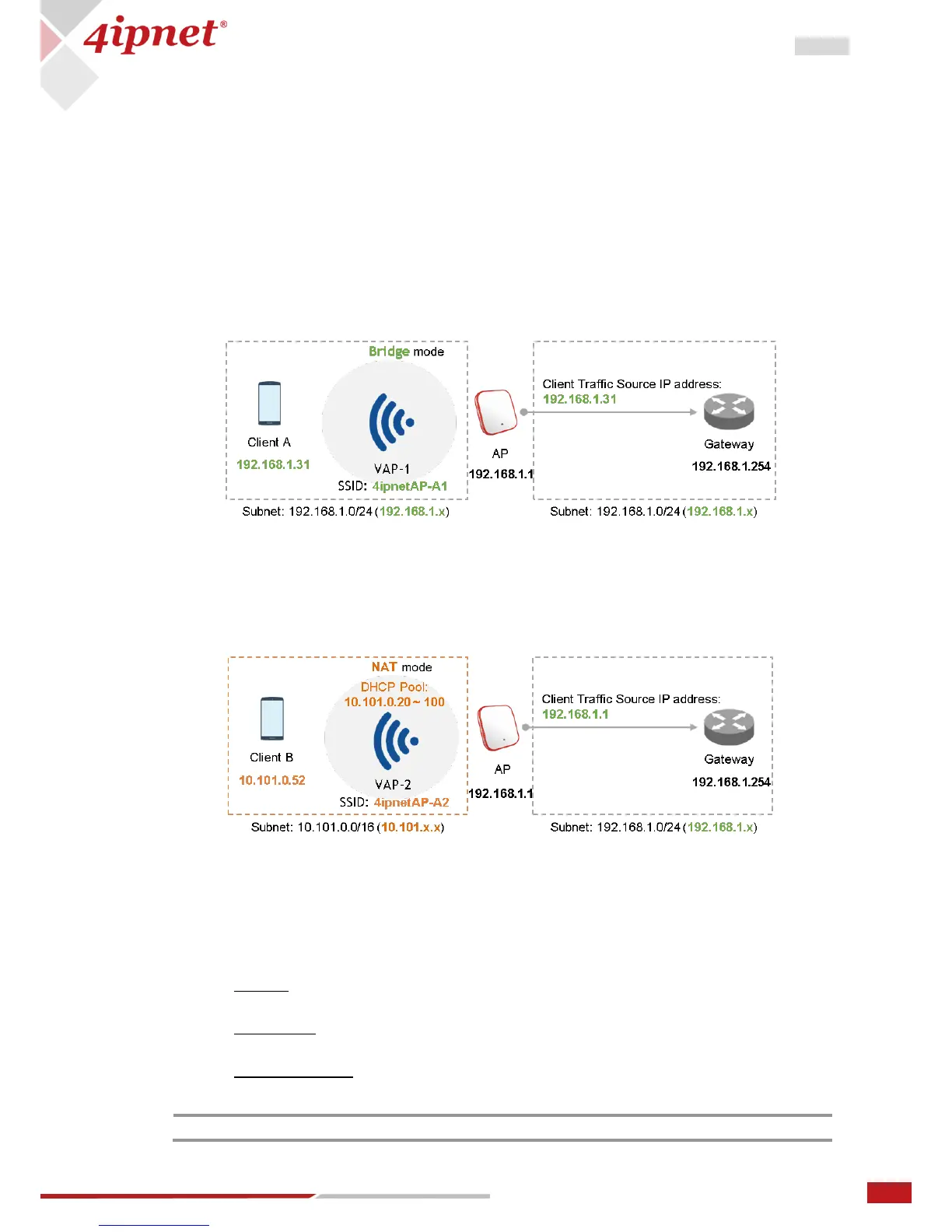
Network Mode:
Bridge mode – the VAP operates transparently (i.e. no NAT, no DHCP) such that client
devices will be assigned a dynamic IP address from a DHCP server on the LAN side. The
source IP address of client traffic seen by the uplink gateway/switch will remain the
original IP address of the client (in this case, 192.168.1.31, as shown in the diagram
below).
NAT mode – the VAP operates like a Network Address Translation (NAT) device with a
built-in DHCP server on this SSID such that client devices will be assigned a dynamic IP
address from the configured DHCP pool on this SSID. After NAT conversion, the source
IP address of client traffic seen by the uplink gateway/switch will be the IP address of
the AP (in this case, 192.168.1.1, as shown in the diagram below).
VLAN ID: Per-SSID VLAN tagging function – when enabled, clients’ traffic which enters the AP
through this SSID will be tagged with the configured VLAN ID.
DHCP Profile: Built-in DHCP Server profile; IP settings of DHCP Server are under Home >
System > DHCP Server.
CAPWAP Tunnel Interface: Three states indicating the connectivity between AP and Controller,
when AP is managed by Controller –
Disable (No Tunnel): the AP is operating with no CAPWAP Tunnel connection to the
Controller
Split Tunnel: the AP passes only “control” traffic to the Controller via the CAPWAP
Tunnel; i.e. “data” traffic will go out locally without passing through the Tunnel
Complete Tunnel: the AP passes both “control” and “data” traffic to the Controller via
the CAPWAP Tunnel
 Loading...
Loading...