1-8 Chapter 1
GSM Use Model
Identifying Interfering Signals
Examples of Interference Signals
Use these signal examples to help assess the bandwidth and spectral
shape of the interfering signal to determine the type of transmission
causing the interference. Best sensitivity is achieved using narrow
resolution bandwidths and minimum attenuation with the built-in
preamplifier Option 1DS. The resolution bandwidth used must be
larger than the signal bandwidth to display the amplitude accurately.
As the resolution bandwidth decreases, the amplitude of the broadband
signal decreases. Use the settings in the following examples to identify
the various signals.
Using Monitor Band/Channel to Look for Interfering Signals
Using Monitor Band and Channel feature can help you quickly identify
interfering signals within your transmission and reception bands or
channels. Simple visual inspection, peak hold, and markers can help to
determine the type of interference that may be causing network
problems.
Commercial AM/FM Broadcast Signal
Press
MEASURE, More, Monitor Band/Channel, Meas Setup,
Method Channel
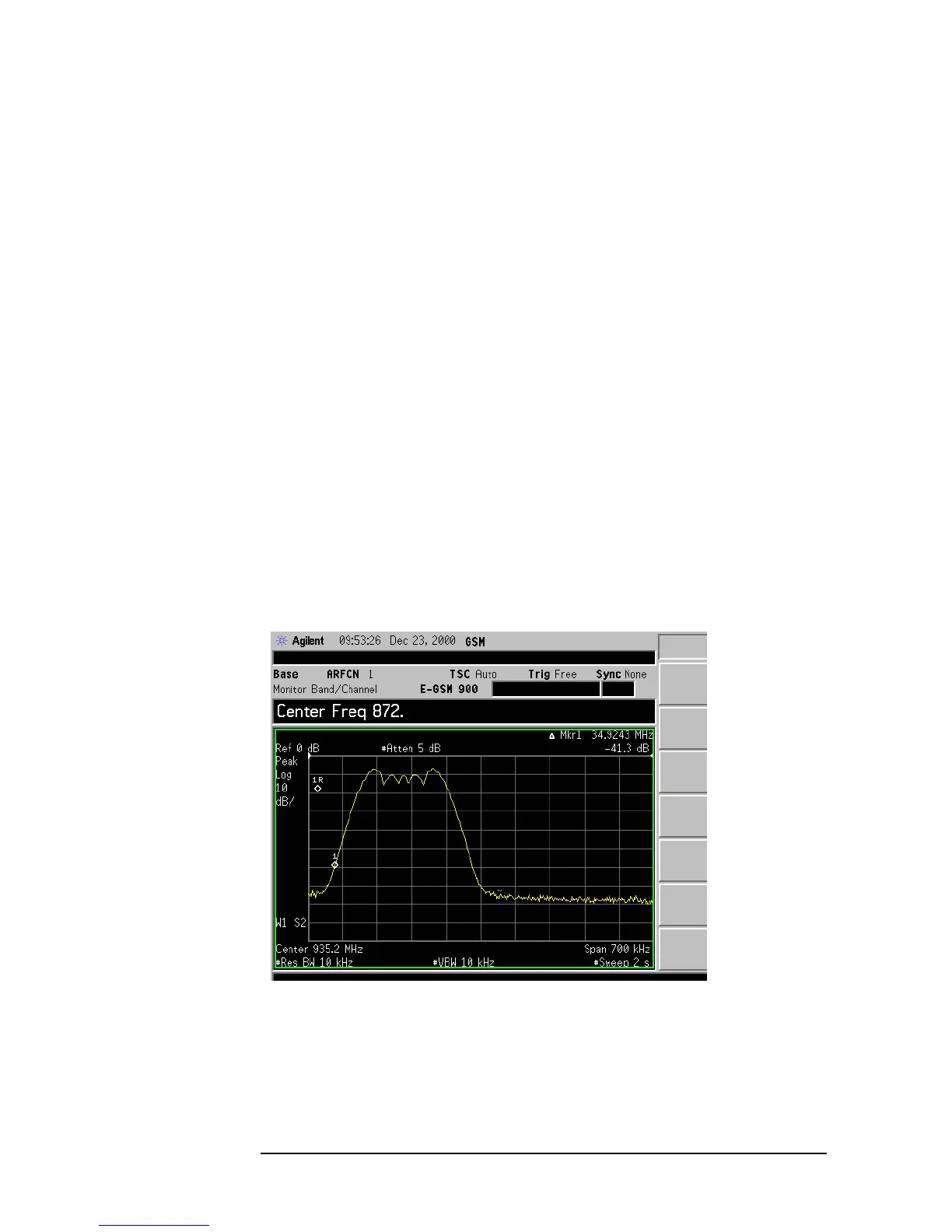
Figure 1-4 Example Showing an Interfering AM/FM Broadcast Signal
A narrow bandwidth signal within a channel, as shown above in Figure
1-4, could be caused by AM/FM channels. In SA mode use the built-in
AM or optional FM (Option BAA) demod to determine the source of the
transmission.
 Loading...
Loading...











