Specifications and Characteristics 3
U2000 Series Operating and Service Guide 55
Effects of Averaging on Average only Mode Measurement Noise
Averaging over 1 to 1024 readings is available for reducing noise. The
previous tables provide the measurement noise for a particular sensor. Use
the noise multiplier in Table 3- 4 for the appropriate speed (Normal or
x2), and the number of averages to determine the total measurement noise
value.
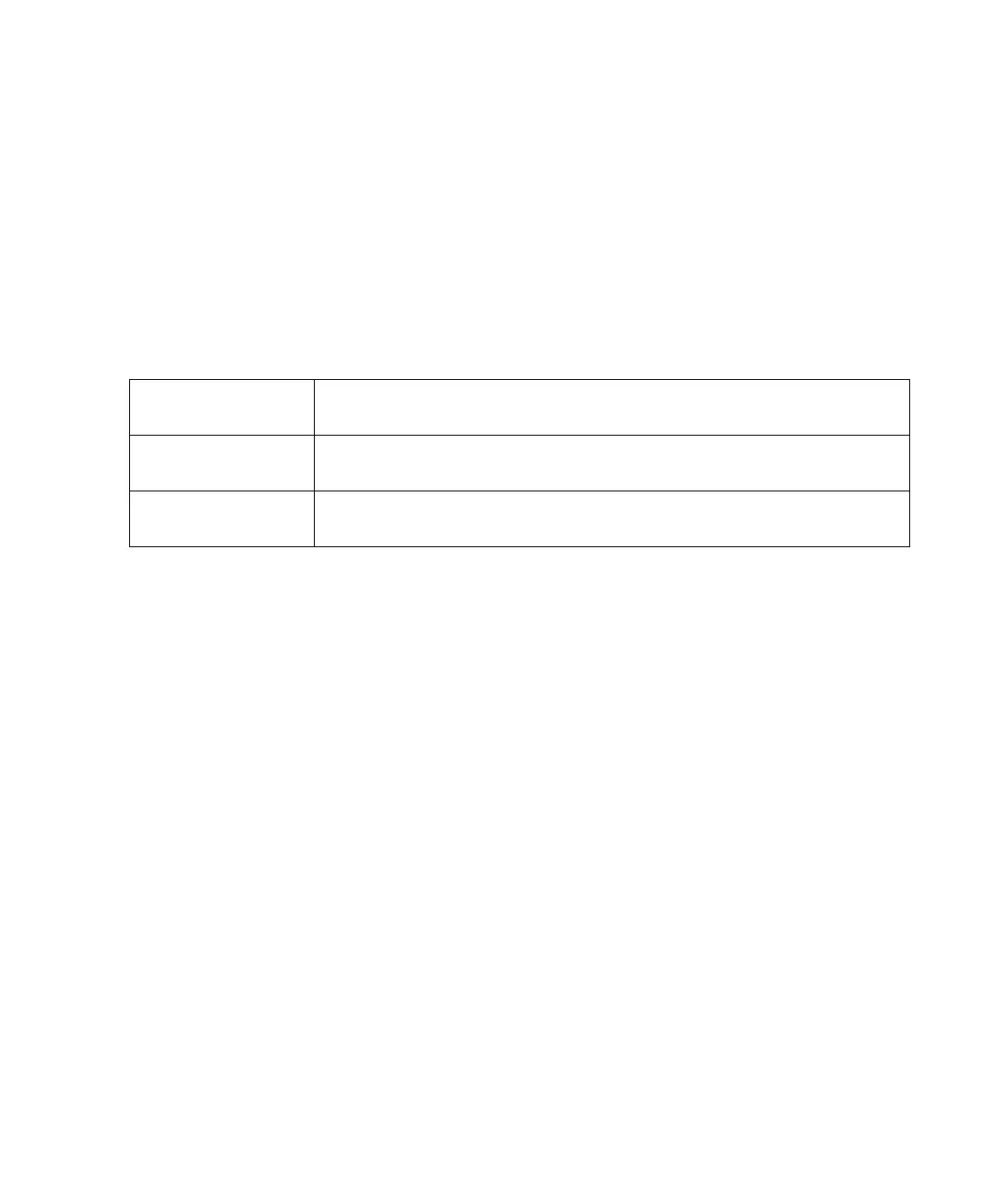
Table 3-4 Noise Multiplier for Average only Mode
Example:
U2000A power sensor, –60 dBm to –35 dBm, number of averages = 4,
normal speed.
Measurement noise calculation:
1 nW x 2.08 = 2.08 nW
Number of Averages
12481632641282565121,024
Noise Multiplier (s)
(Normal Speed)
3.65 2.75 2.08 1.45 1.00 0.75 0.54 0.42 0.33 0.24 0.17
Noise Multiplier (s)
(x2 Speed)
5.04 3.75 2.71 1.97 1.42 1.00 0.75 0.56 0.45 0.29 0.22

 Loading...
Loading...