152 Rockwell Automation Publication MOTION-RM002H-EN-P-February 2018
Actual Position When Actual is selected or entered as the MRP Position Selection, the New Position is directly applied to the actual
position of the physical axis. The command position of the axis is also adjusted along with the new actual position to
preserve any position error which exists. This ensures that there is no unexpected motion of the axis when the
positions are redefined. See the Motion Axis Object Specification for more discussion of command position, actual
position, and position error.
Command Position When Command is selected or entered as the MRP Position Selection, the New Position is directly applied to the
command position of the servo or imaginary axis. For an axis with a Position Loop type of Feedback Only, the
Command Position and the Actual Position are the same. The MRP can be used with ether the Command or Actual
Position with the same effect. The actual position of servo axes is also adjusted along with the new command position
to preserve any position error which exists. This ensures that there is no unexpected motion of the axis when the
positions are redefined.
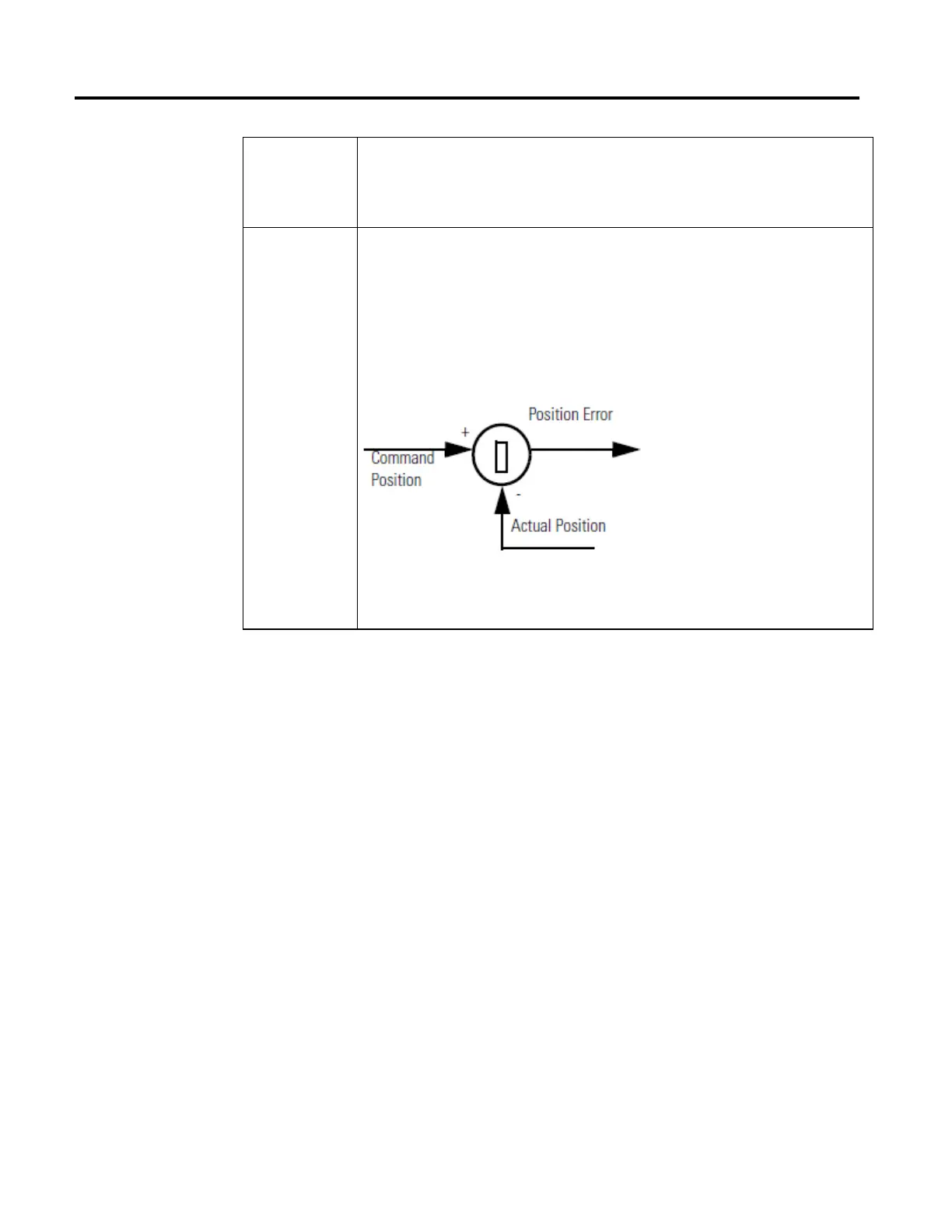
Command position is the desired or commanded position of a servo as generated by any previous motion instructions.
Actual position is the current position of a physical or virtual axis as measured by the encoder or other feedback
device. Position error is the difference between these two and is used to drive the motor to make the actual position
equal to the command position. The Figure below shows the relationship of these three positions.
To successfully execute a MRP instruction, the targeted axis must be configured as either a Servo or Feedback Only
axis. Otherwise, the instruction errs.
Important: The instruction execution may take multiple scans to execute because it requires multiple coarse updates
to complete the request. The Done (.DN) bit is not set immediately, but only after the request is completed.
In this transitional instruction, the relay ladder, toggle the Rung-condition-in
from cleared to set each time the instruction should execute.
Master Driven Speed Control (MDSC) and the MRP Instruction
You can execute an MRP on the Master or the Slave axes or coordinate system
when an MDSC is active.
The Master axis position is changed when an MRP is executed (goes IP) on the
Master while it is moving in MDSC mode; the slave is not affected.
Affects Math Status Flags
No
Major/Minor Faults
None specific to this instruction. See Common Attributes for operand-related
faults.

 Loading...
Loading...