Multi-Axis Coordinated Motion Instructions
382 Rockwell Automation Publication MOTION-RM002H-EN-P-February 2018
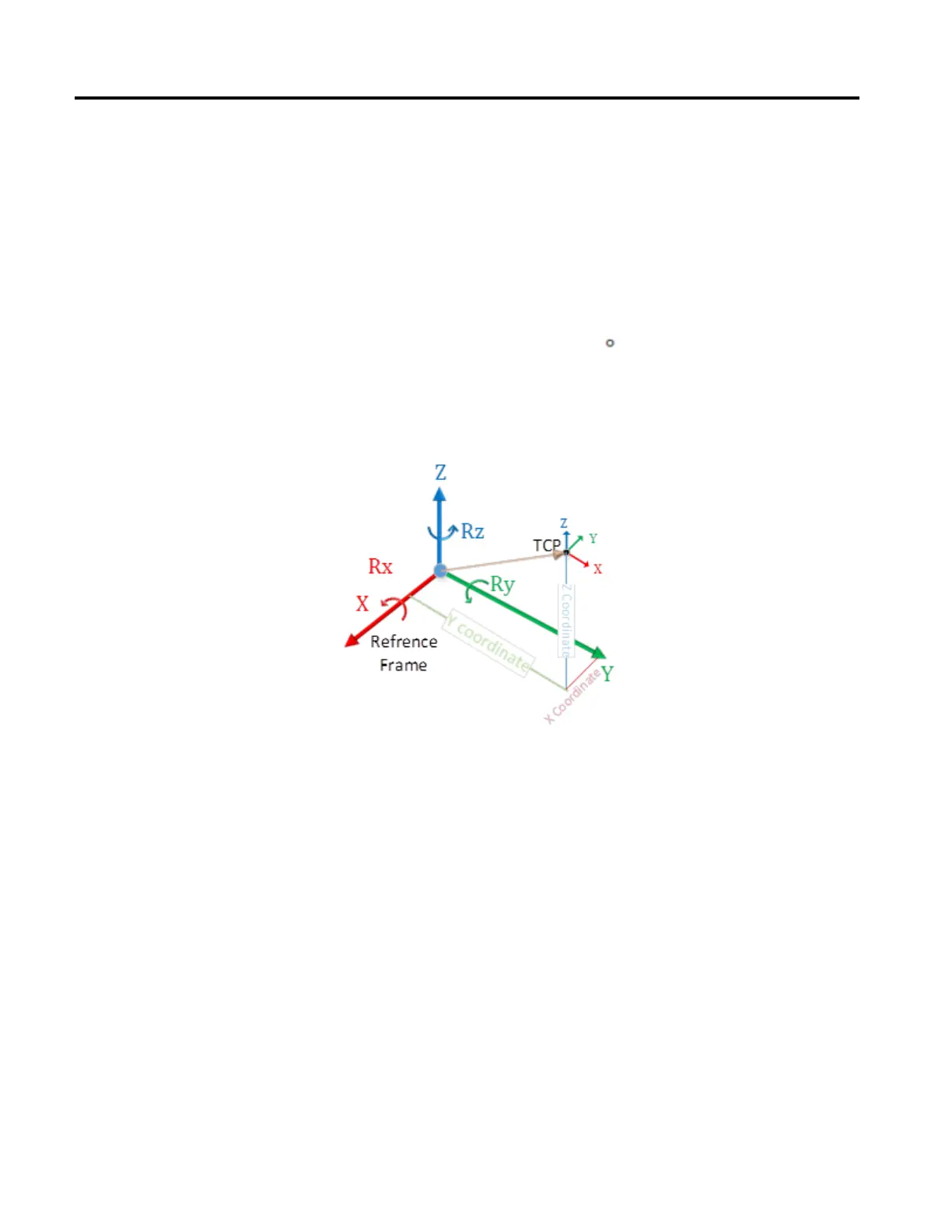
Position
This is a one dimensional array, whose dimension is defined to be at least
equivalent to the number of axes specified in the coordinate system, 6 in Cartesian
coordinate system where X, Y, Z, Rx, Ry, Rz are values of the TCP with reference
to a reference frame. The Position array defines either the new absolute or
incremental position.
Below is an example of TCP point which has translation on X, Y, and Z axis
followed with rotation on Z axis (Rz = 90
) resulting in TCP’s X axis aligning
with Y axis of reference frame.
See Configuring Cartesian XYZRxRyRz Coordinate System for more details on
Cartesian coordinate system.
Robot configuration
A robot can reach an end destination position with different joint positions and,
consequently different robot configurations. If the user wants the robot to move
to a position with a specific configuration in continuous path (CP) mode, specify
the end position along with the desired pose of the robot.
• RIGHTY versus LEFTY: For future use
• ABOVE versus BELOW: For future use
• FLIP versus NOFLIP: For future use

 Loading...
Loading...