4.5.2.2. Calibration settings
The calibration card is delivered with the reagent strips. Each calibration card has an in-
dividual barcode printed on it. This code contains test strip related data and the number
of measurements that can be carried out after calibration. If the number of measurement
exceeds the predefined number, the reader will stop measuring, and a new calibration has
to be carried out.
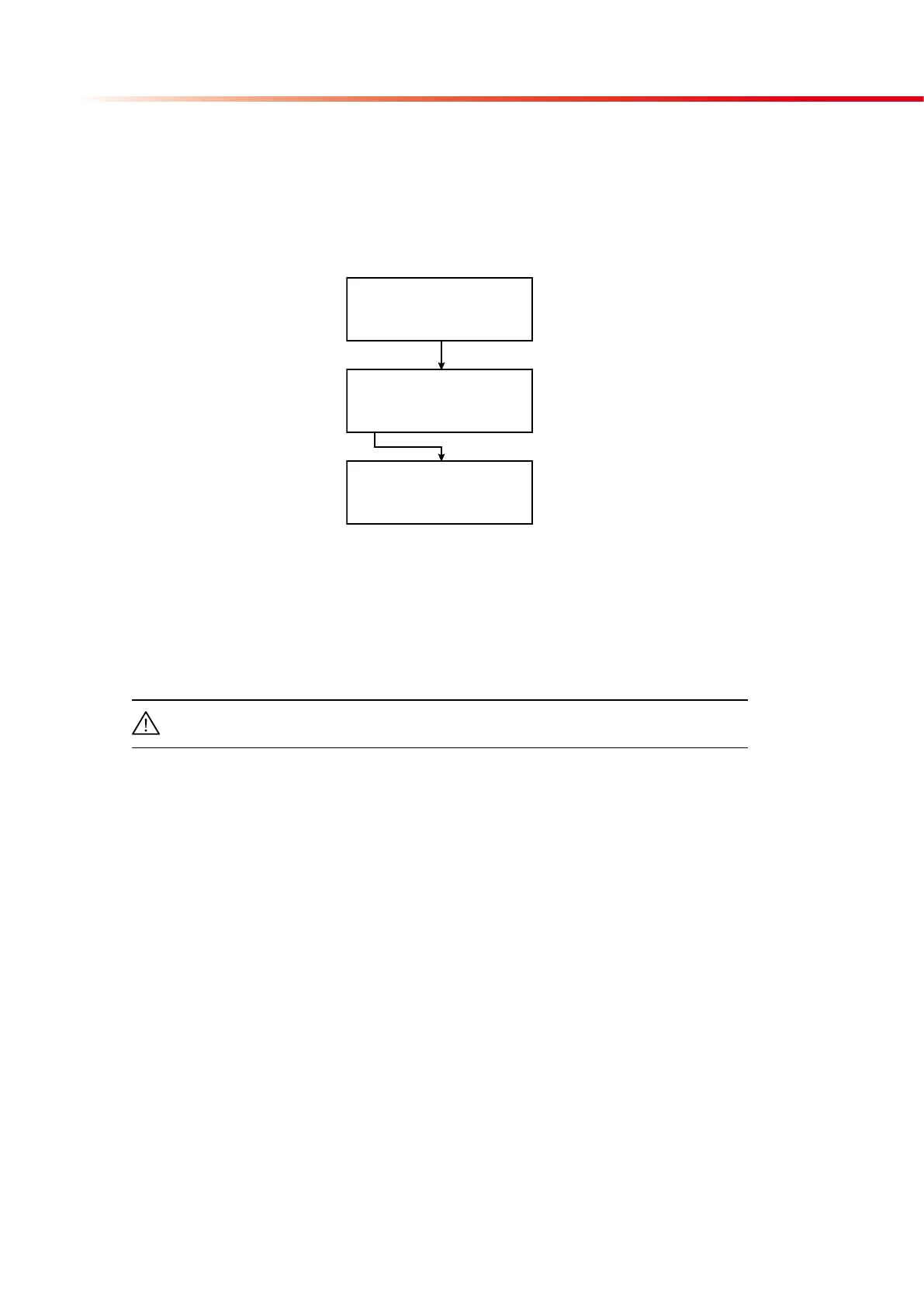
2004/08/09 19:19:26
MENU/SERVICE
CLEAN CALIBRATION
PLACE CALIBRATION CARD,
OR ENTER 1ST BARCODE!
MANUAL CANCEL
MANUAL CALIBRATION
Code:
CANCEL
If you select CALIBRATION, the conveyor will move to measurement position, but the con-
veyor will run faster than it does in the measuring modus. Place the calibration card with
the bar code upside on the conveyor. It must be placed at right angles to the conveyor in a
way, that the angle with the barcode is close to the meter. Place the card behind the strip
bumper close to the carriage. Before reaching the optical unit the conveyor will slow down
and the sensor reads the code. The conveyor starts to move in reverse direction delivering
back the calibration card. The stored calibration data will be printed out.
CAUTION! Don‘t throw the calibration card away before the package of strips is
completely consumed!
If the calibration wasn‘t successful or you want to do the calibration manually, select
MANUAL. The conveyor will move back into the housing. Now you can enter the 16 digit
number which is printed below the first barcode. As soon as all numbers are entered, the
code evaluation and calibration process takes place automatically. Details of stored cali-
bration data will be printed out.
To interrupt calibration select CANCEL or press the QUIT button.
4.5.3. Memory
The CombiScan
®
500 stores the last 999 results in memory. With the results, the se-
quence number, entered patient ID, time and date of measurement are stored as well. In
this MENU/MEMORY submenu you can clear results from memory or transfer stored data
to the built in printer or to a device connected to the serial port (i.e. host computer). To
achieve the functions mentioned above follow the flowchart below.
 Loading...
Loading...