6. Fasten screws crosswise to a torque according to table.
Table 1: Tightening torques for screws
Tightening torque T
A
[Nm]Screws
Strength class 8.8Threads
25M8
51M10
87M12
214M16
431M20
4.3.2 Output drive type A
Application
●
Output drive for rising, non-rotating valve stem
●
Capable of withstanding thrust
4.3.2.1 Stem nut: finish machining
✔
This working step is only required if stem nut is supplied unbored or with pilot
bore.
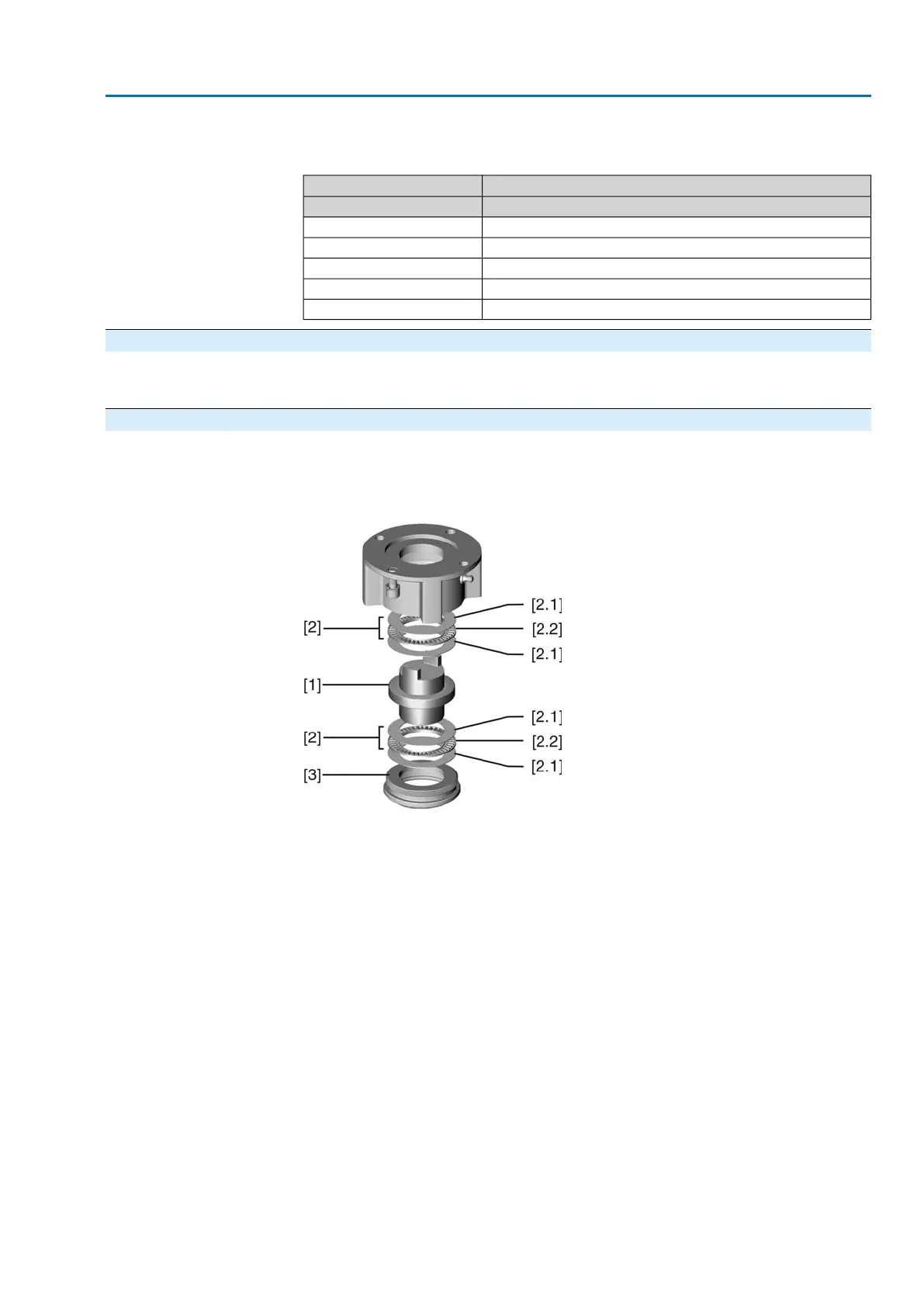
Figure 7: Design of output drive type A
[1] Stem nut
[2] Bearing
[2.1] Bearing race
[2.2] Bearing rim
[3] Spigot ring
1. Remove spigot ring [3] from output drive.
2. Remove stem nut [1] together with bearings [2].
3. Remove bearing races [2.1] and bearing rims [2.2] from stem nut [1].
4. Drill and bore stem nut [1] and cut thread.
Information: When fixing in the chuck, make sure stem nut runs true!
5. Clean the machined stem nut [1].
6. Apply sufficient Lithium soap EP multi-purpose grease to bearing rims [2.2] and
bearing races [2.1], ensuring that all hollow spaces are filled with grease.
7. Place greased bearing rims [2.2] and bearing races [2.1] onto stem nut [1].
8. Re-insert stem nut [1] with bearings [2] into output drive.
Information: Ensure that dogs or splines are placed correctly in the keyway of
the hollow shaft.
9. Screw in spigot ring [3] until it is firm against the shoulder.
13
SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Assembly

 Loading...
Loading...