51
ENG
MPXPRO - + 0300055EN rel. 1.1 30/08/10
Valve standby position (parameter PSb)
This indicates the position, as the absolute number of steps, that the
valve must move to after having completely closed, to restore the elastic
operating conditions of the valve spring, by releasing the compression
(for stepper valve only).
Note: the value of this parameter represents the absolute position
of the valve during the closing phase (value read using the
advanced parameter PF on the supervisor).
Par. Description Def Min Max UoM
PSb Valve standby position 0 0 400 step
Tab. 6.i.g
Enable fast update of the valve parameters to
supervisor (parameter Phr)
This is used to enable the fast update to the supervisor of the variables
relating to the electronic expansion valve, such as:
• PF: absolute position in number of steps (stepper valve only);
• SH: superheat;
• PPV: position as a percentage;
• tGS: superheated gas temperature;
• tEu: saturated evaporation temperature;
Useful in the commissioning phase or start-up:
Phr = 0: fast update disabled (update every 30 s);
Phr = 1: fast update enabled (update every 1 s).
Par. Description Def Min Max UoM
Phr Enable fast update of the valve parameters
to supervisor
0 = fast update disabled
001-
Tab. 6.i.h
Important: in the event of power failures, parameter Phr will be
reset to zero.
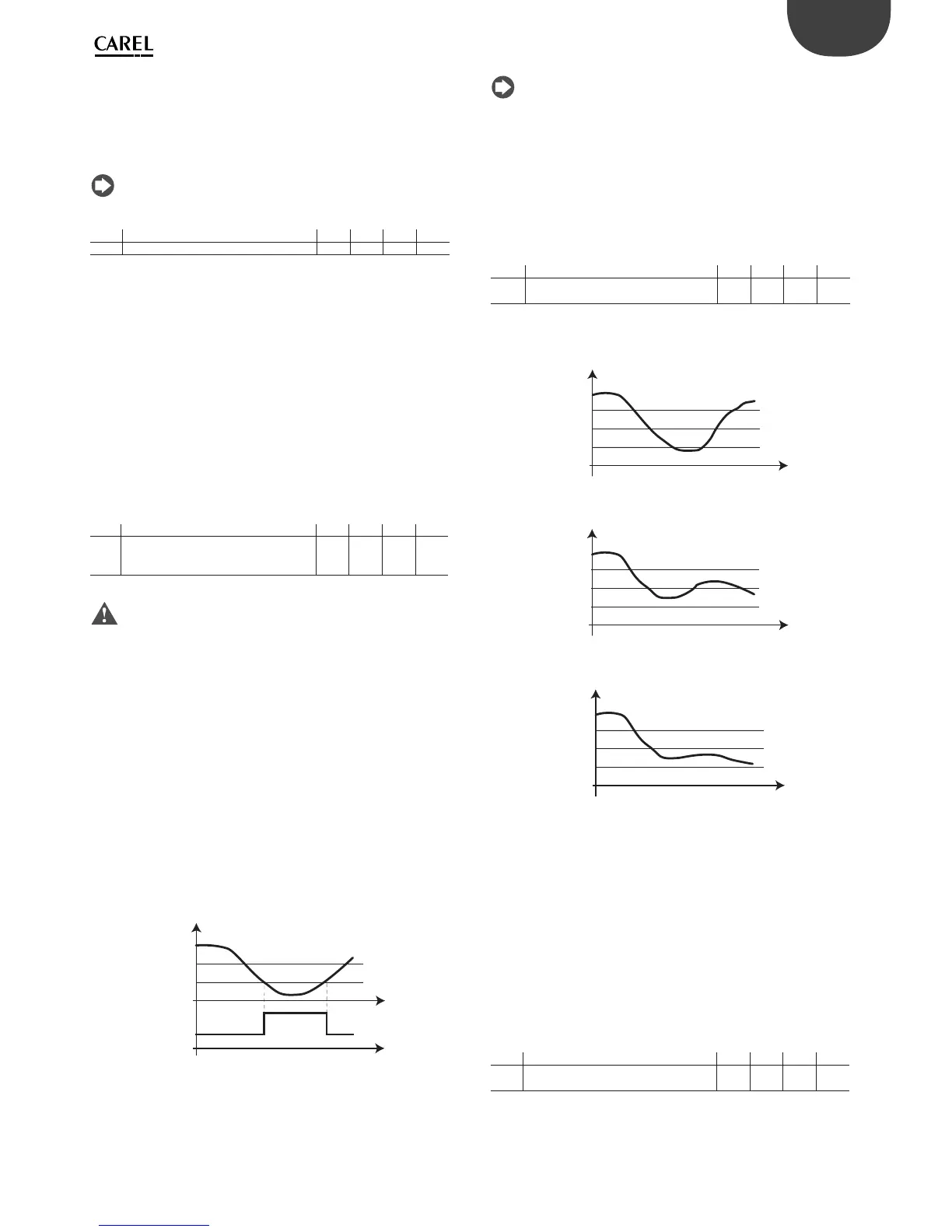
Superheat o set for modulating thermostat
(parameter OSH)
This function is used to reduce or completely eliminate the typical
temperature swings caused by sudden activation/deactivation of the
solenoid valve. The function is activated based on the refrigeration
controller control temperature and a ects the cooling capacity of
the electronic valve. In particular, the function is activated when the
control temperature falls below half of the di erential rd. In this band,
the superheat set point P3 is increased by a term proportional to the
parameter OSH. The e ect of this action is the gradual advanced closing
of the electronic valve, which makes the decrease in temperature inside
of the refrigeration controller slower and more stable. In this way, the
actual temperature of the cabinet can be kept very stable and near the
set point, without ever having to close the solenoid valve, but rather by
simply controlling the ow of refrigerant.
t
t
St+rd
Sreg
St+rd/2
ON
OFF
F
St
Fig. 6.o
Key
Sreg Control probe t time
F
Modulating thermostat
function
Note:
• The action of OSH is weighted, based on the di erence between the
temperature set point and the control temperature. The lower the
di erence, the greater the action of OSH and vice-versa.
• OSH is active in a band at maximum equal to half of the di erential rd
With double thermostat:
• the action of OSH will be determined by the thermostat with the lower
di erence between the set point and the actual temperature;
• the highest contribution is used, Tf= st + rd/2 or Tf2= St2 + rd/2, as
there are two bands.
Par. Description Def Min Max UoM
OSH Superheat o set for modulating
thermostat (0 = function disabled)
0.0 0.0 60.0 K
Tab. 6.i.i
Example
OSH too low
t
St+rd
Sreg
St+rd/2
St
Fig. 6.p
OSH too high
t
St+rd
Sreg
St+rd/2
St
Fig. 6.q
OSH ideale
t
St+rd
Sreg
St+rd/2
St
Fig. 6.r
Key:
Sreg=control probe St=set point
rd = di erential t= time
Support saturated temperature for pressure probe
error (parameter P15)
In the event of a pressure/saturated evaporation temperature probe
error, this represents the constant value used by the device to simulate
the probe reading. In centralised systems, the evaporation pressure is
determined by the compressor rack set point. Once this set point has
been set for P15, control can continue, even if not in perfect conditions,
in emergency situations.
Par. Description Def Min Max UoM
P15 Support saturated temperature for
pressure probe error
-15.0 -50.0 50.0 °C/°F
Tab. 6.i.j
 Loading...
Loading...