MCS – Memory Control System
MCS, Memory Control System, is used to save data on the ClassPad. This includes
saving something as simple as a variable in Main to saving something as complex as an
eActivity file with multiple embedded applications. This section will briefly discuss the
structure of MCS and then provide information on the BIOS functions to write to MCS as
well as the C++ file classes for MCS.
MCS Overview and Structure
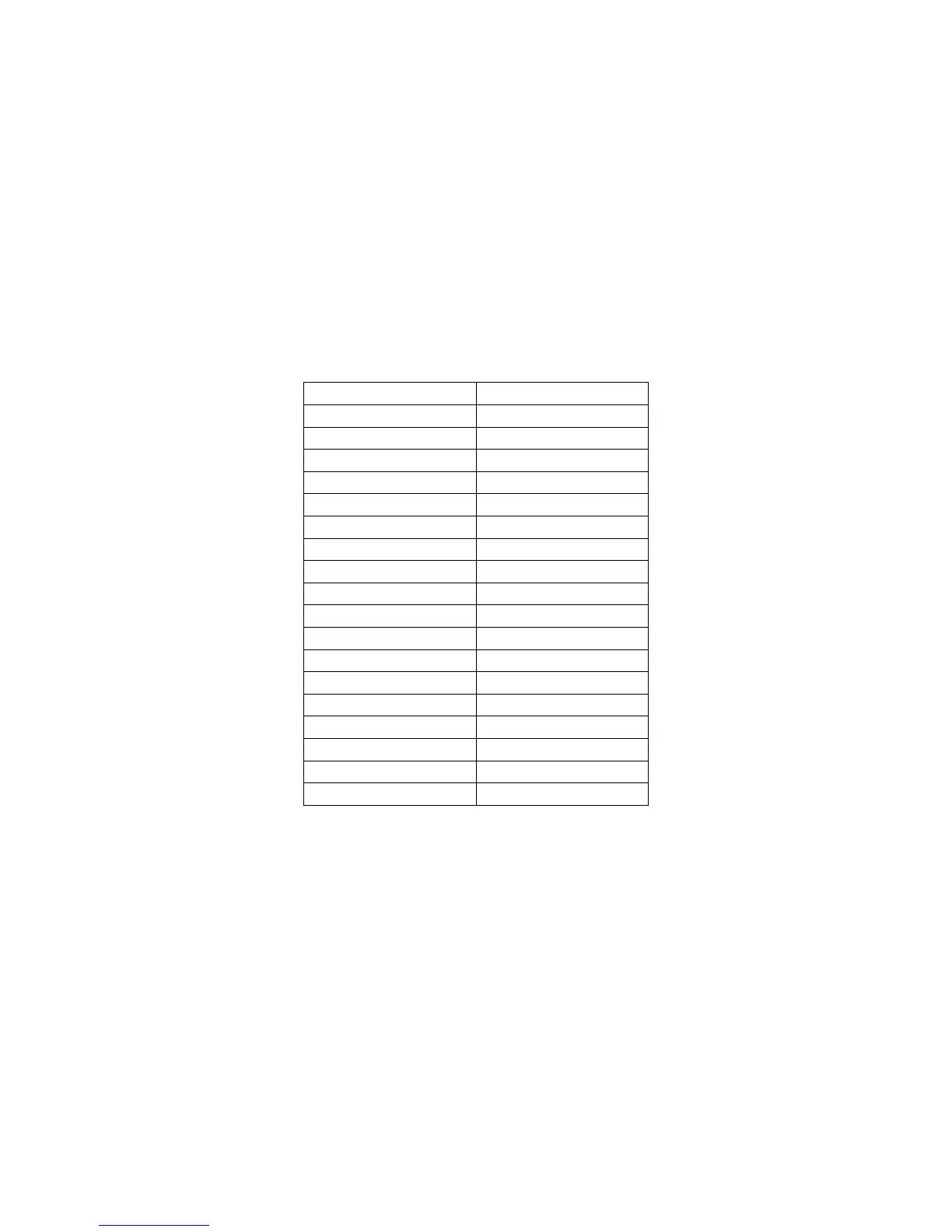
All variables on the ClassPad are saved in MCS. Each variable must have a name and a
data type. The following is a list of data types and their size in bytes:
Variable Type Size
Real number 12
Complex number 24
Integer 4
Float 8
String n
Expression n
Program n
Function n
File n
List n
Vector n
Matrix n
GraphPicture n
mem n
ProgramExe n
Gmem n
3D-Graph n
Formula process n
All variable sizes must be divisible by 4.
Variables are stored in folders. A variable’s name must be unique to its folder. Folders
can only be one level deep.
MCS has the following structure in RAM:
109

 Loading...
Loading...











