D-2
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Appendix D Changing the Configuration Register Settings
About the Configuration Register
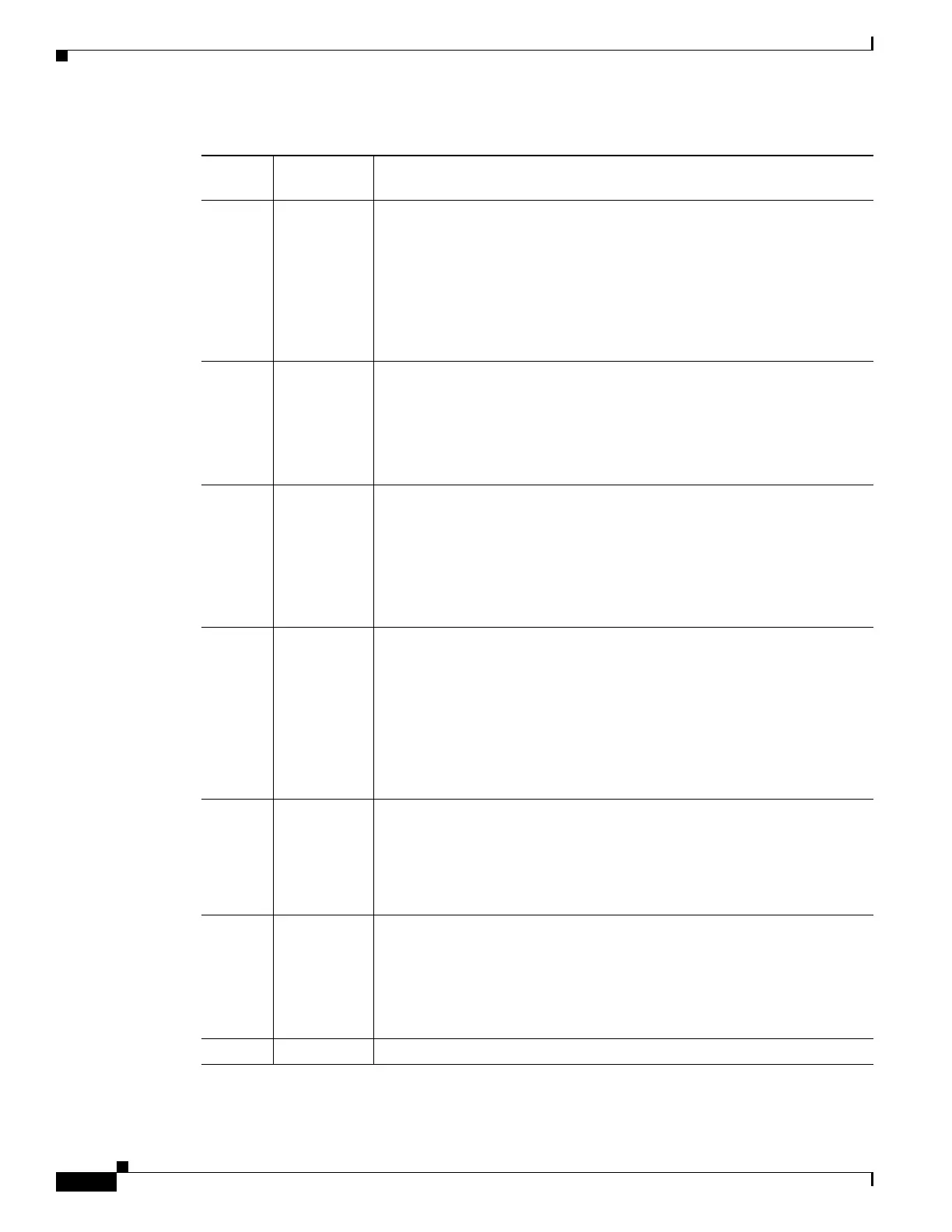
08 0x0100 Controls the console Break key:
• (Factory default) Setting bit 8 causes the processor to ignore the console
Break key.
• Clearing bit 8 causes the processor to interpret Break as a command to
force the router into the ROM monitor mode, halting normal operation.
Break can always be sent in the first 60 seconds while the router is
rebooting, regardless of the configuration register settings.
09 0x0200 This bit controls the system boot:
• Setting bit 9 causes the system to use the secondary bootstrap.
• (Factory default) Clearing bit 9 causes the system to boot from flash
memory.
• This bit is typically not modified.
10 0x0400 Controls the host portion of the IP broadcast address:
• Setting bit 10 causes the processor to use all zeros.
• (Factory default) Clearing bit 10 causes the processor to use all ones.
Bit 10 interacts with bit 14, which controls the network and subnet portions
of the IP broadcast address. See Table D-3 for the combined effects of bits
10 and 14.
05, 11,
12
0x0020,
0x0800,
0x1000
Controls the console line speed. See Table D-4 for the eight available bit
combinations and console line speeds.
Factory default is 9600 baud, where bits 5, 11, and 12 are all zero (clear).
Note You cannot change the console line speed configuration register bits
from the Cisco IOS CLI
2
. You can, however, change these bits from
the ROM monitor. Or, instead of changing the configuration register
settings, you can set the console line speed through other Cisco IOS
commands.
13 0x2000 Determines how the router responds to a network boot failure:
• Setting bit 13 causes the router to boot the default ROM software after
6 unsuccessful network boot attempts.
• (Factory default) Clearing bit 13 causes the router to indefinitely
continue network boot attempts.
14 0x4000 Controls the network and subnet portions of the IP broadcast address:
• Setting bit 10 causes the processor to use all zeros.
• (Factory default) Clearing bit 10 causes the processor to use all ones.
Bit 14 interacts with bit 10, which controls the host portion of the IP
broadcast address. See Table D-3 for the combined effect of bits 10 and 14.
15 0x8000 Enables diagnostic messages and ignores the contents of NVRAM.
1. OEM = Original Equipment Manufacturer
2. CLI = command-line interface
Table D-1 Configuration Register Bit Descriptions (continued)
Bit
Number Hexadecimal Meaning
 Loading...
Loading...











