Configuring Modular QoS Service Packet Classification and Marking on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Routers
Information About Configuring Modular QoS Packet Classification and Marking on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Routers
QC-15
Cisco ASR 9000 Series Aggregation Services Router Modular Quality of Service Configuration Guide
OL-23108-02
For example, weighted random early detection (WRED), a congestion avoidance technique, can be
used to determine the probability that a packet is dropped. In addition, low-latency queueing (LLQ)
can then be configured to put all packets of that mark into the priority queue.
• Use QoS unconditional packet marking to assign packets to a QoS group. To set the QoS group
identifier on MPLS packets, use the set qos-group command in policy map class configuration
mode.
Note Setting the QoS group identifier does not automatically prioritize the packets for
transmission. You must first configure an egress policy that uses the QoS group.
• Use CoS unconditional packet marking to assign packets to set the priority value of IEEE 802.1p/
Inter-Switch Link (ISL) packets. The router uses the CoS value to determine how to prioritize
packets for transmission and can use this marking to perform Layer
2-to-Layer 3 mapping. To set
the Layer 2 CoS value of an outgoing packet, use the set cos command in policy map configuration
mode.
The configuration task is described in the “Configuring Class-based Unconditional Packet Marking”
section on page 29.
Note
Specification of the CoS for a Packet with IP Precedence
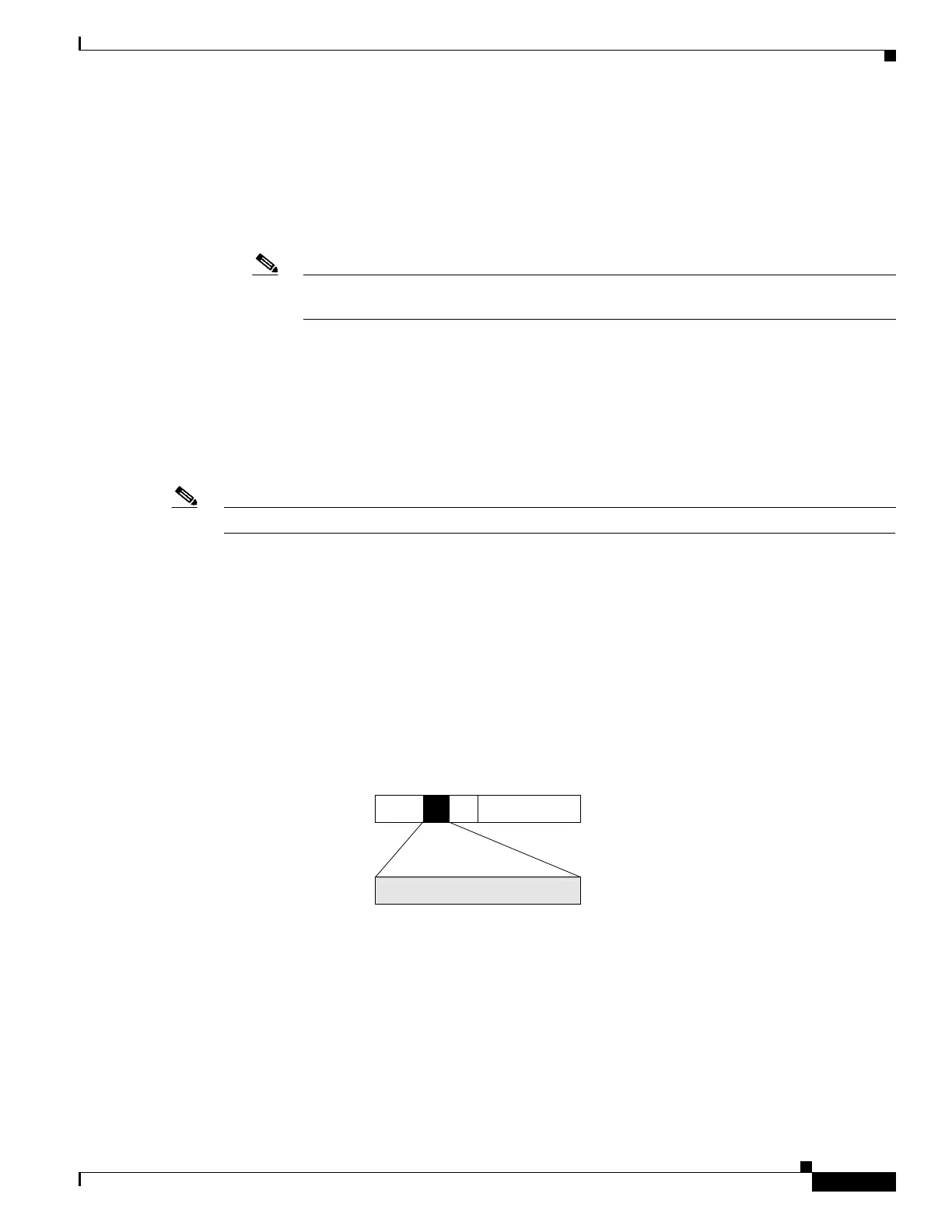
Use of IP precedence allows you to specify the CoS for a packet. You use the three precedence bits in
the ToS field of the IP version 4 (IPv4) header for this purpose.
Figure 1 shows the ToS field.
Figure 1 IPv4 Packet Type of Service Field
Using the ToS bits, you can define up to eight classes of service. Other features configured throughout
the network can then use these bits to determine how to treat the packet in regard to the ToS to grant it.
These other QoS features can assign appropriate traffic-handling policies, including congestion
management strategy and bandwidth allocation. For example, queueing features such as LLQ can use the
IP precedence setting of the packet to prioritize traffic.
By setting precedence levels on incoming traffic and using them in combination with the Cisco IOS XR
QoS queueing features, you can create differentiated service.
IPv4 packet
Data
ToS field
3-bit precedence
16757

 Loading...
Loading...











