Configuring Modular QoS Congestion Management on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Routers
Information About Configuring QoS Congestion Management on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Routers
QC-47
Cisco ASR 9000 Series Aggregation Services Router Modular Quality of Service Configuration Guide
OL-23108-02
Traffic Shaping
Traffic shaping allows you to control the traffic flow exiting an interface to match its transmission to the
speed of the remote target interface and ensure that the traffic conforms to policies contracted for it.
Traffic adhering to a particular profile can be shaped to meet downstream requirements, thereby
eliminating bottlenecks in topologies with data-rate mismatches.
To match the rate of transmission of data from the source to the target interface, you can limit the transfer
of data to one of the following:
• A specific configured rate
• A derived rate based on the level of congestion
The rate of transfer depends on these three components that constitute the token bucket: burst size, mean
rate, and time (measurement) interval. The mean rate is equal to the burst size divided by the interval.
When traffic shaping is enabled, the bit rate of the interface does not exceed the mean rate over any
integral multiple of the interval. In other words, during every interval, a maximum of burst size can be
sent. Within the interval, however, the bit rate may be faster than the mean rate at any given time.
When the peak burst size equals 0, the interface sends no more than the burst size every interval,
achieving an average rate no higher than the mean rate. However, when the peak burst size is greater than
0, the interface can send as many as the burst size plus peak burst bits in a burst, if in a previous time
period the maximum amount was not sent. Whenever less than the burst size is sent during an interval,
the remaining number of bits, up to the peak burst size, can be used to send more than the burst size in
a later interval.
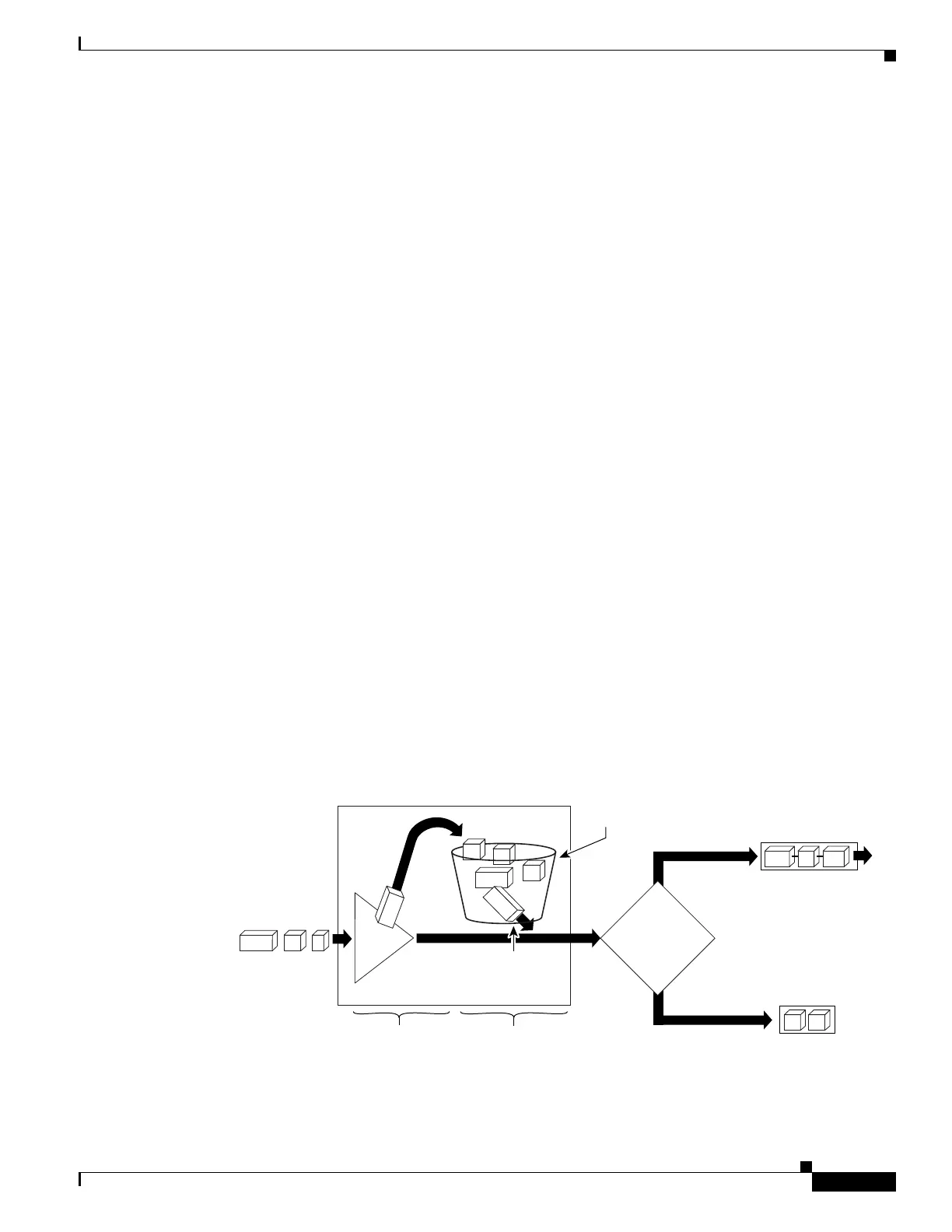
Traffic-Shaping Mechanism Regulates Traffic
When incoming packets arrive at an interface, the packets are classified using a classification technique,
such as an access control list (ACL) or the setting of the IP Precedence bits through the Modular QoS
CLI (MQC). If the packet matches the specified classification, the traffic-shaping mechanism continues.
Otherwise, no further action is taken.
Figure 1 illustrates how a traffic shaping mechanism regulates traffic flow.
Figure 1 How a Traffic Shaping Mechanism Regulates Traffic
Classify
Incoming packets
"Token bucket"
shaping
Packet classification
criteria applied
(e.g., via the MQC)
117493
Match
Token bucket
Ye s
No
Configured
traffic shaping rate
Enough
tokens in
the token
bucket?
Outgoing packets
placed in shaping queue
(transmitted later)
Outgoing packets
transmitted

 Loading...
Loading...











