with a port that belongs to a different region, creating the possibility of receiving both internal and external
messages on a port (see the following figure).
Figure 15: MST Boundary Ports
At the boundary, the roles of MST ports do not matter; the system forces their state to be the same as the IST
port state. If the boundary flag is set for the port, the MST port-role selection process assigns a port role to
the boundary and assigns the same state as the state of the IST port. The IST port at the boundary can take up
any port role except a backup port role.
Spanning-Tree Dispute Mechanism
Currently, this feature is not present in the IEEE MST standard, but it is included in the standard-compliant
implementation. The software checks the consistency of the port role and state in the received BPDUs to
detect unidirectional link failures that could cause bridging loops.
When a designated port detects a conflict, it keeps its role but reverts to a discarding state because disrupting
connectivity in case of inconsistency is preferable to opening a bridging loop.
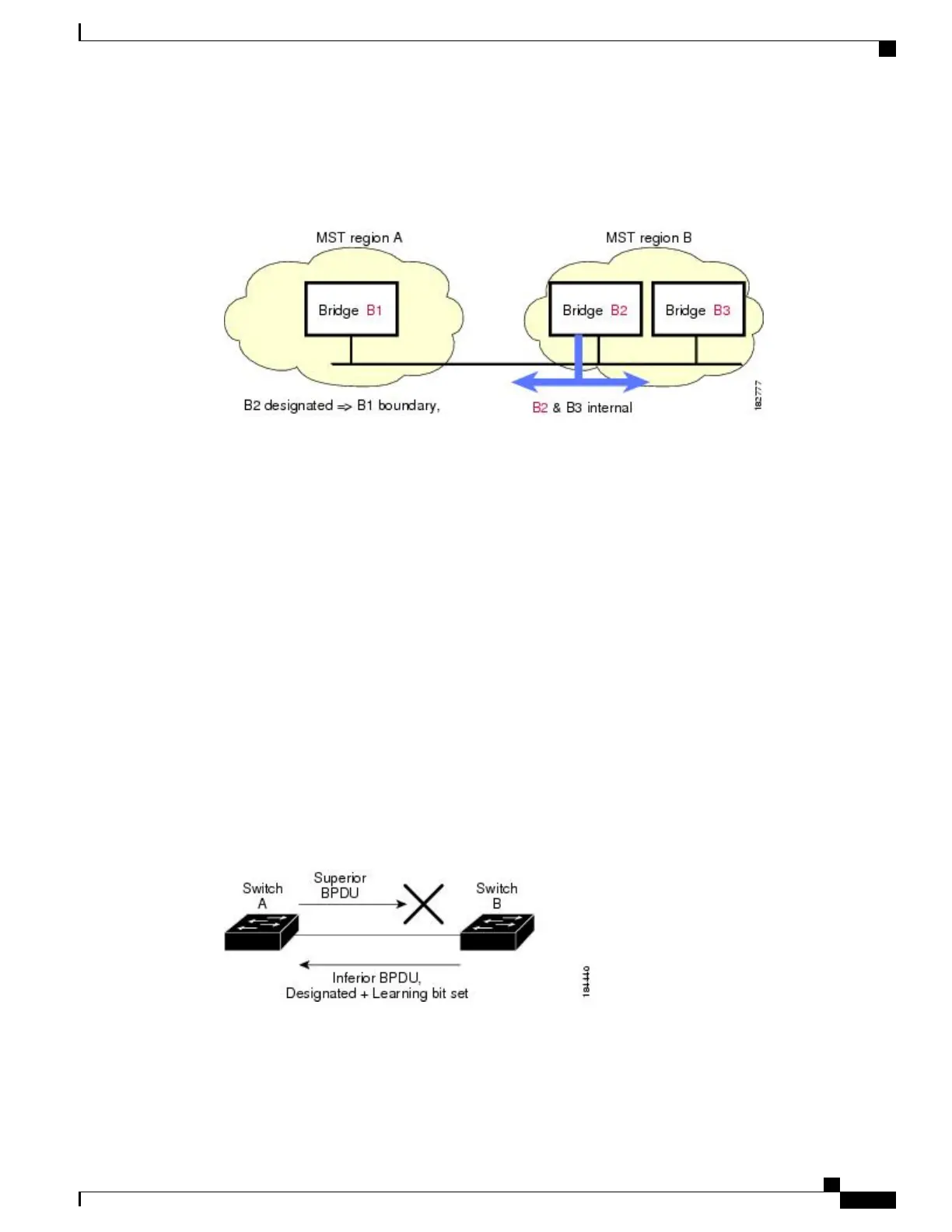
The following figure shows a unidirectional link failure that typically creates a bridging loop. Switch A is the
root bridge, and its BPDUs are lost on the link leading to Switch B. Rapid PVST+ (802.1w) and MST BPDUs
include the role and state of the sending port. With this information, Switch A can detect that Switch B does
not react to the superior BPDUs that it sends and that Switch B is the designated, not root port. As a result,
Switch A blocks (or keeps blocking) its port, which prevents the bridging loop. The block is shown as an STP
dispute.
Figure 16: Detecting a Unidirectional Link Failure
Cisco Nexus 6000 Series NX-OS Layer 2 Switching Configuration Guide, Release 7.x
75
Configuring Multiple Spanning Tree
Spanning-Tree Dispute Mechanism

 Loading...
Loading...